A volatility spike indicates a sudden and significant increase in market price fluctuations, often triggered by unexpected news or economic events. This surge can lead to heightened risk and trading opportunities as asset prices experience rapid changes. Explore the rest of the article to understand how volatility spikes impact your investment strategy and risk management.
Table of Comparison
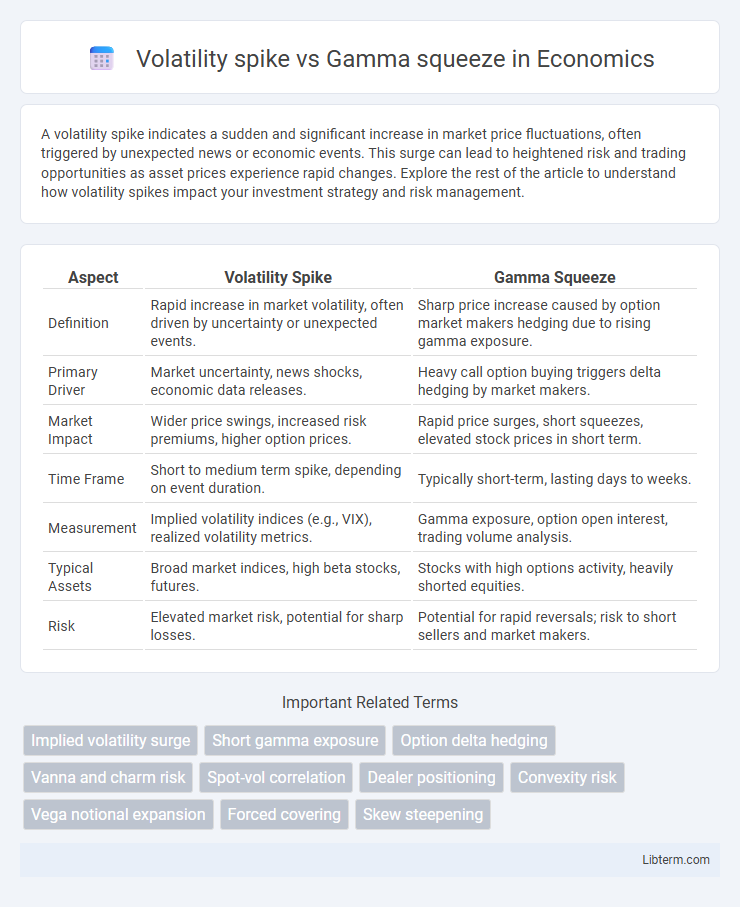
| Aspect | Volatility Spike | Gamma Squeeze |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Rapid increase in market volatility, often driven by uncertainty or unexpected events. | Sharp price increase caused by option market makers hedging due to rising gamma exposure. |
| Primary Driver | Market uncertainty, news shocks, economic data releases. | Heavy call option buying triggers delta hedging by market makers. |
| Market Impact | Wider price swings, increased risk premiums, higher option prices. | Rapid price surges, short squeezes, elevated stock prices in short term. |
| Time Frame | Short to medium term spike, depending on event duration. | Typically short-term, lasting days to weeks. |
| Measurement | Implied volatility indices (e.g., VIX), realized volatility metrics. | Gamma exposure, option open interest, trading volume analysis. |
| Typical Assets | Broad market indices, high beta stocks, futures. | Stocks with high options activity, heavily shorted equities. |
| Risk | Elevated market risk, potential for sharp losses. | Potential for rapid reversals; risk to short sellers and market makers. |
Understanding Volatility Spikes: Key Drivers
Volatility spikes occur due to sudden market uncertainty driven by unexpected news, economic data releases, or geopolitical events, causing rapid price fluctuations in underlying assets. These spikes often coincide with increased option trading activity, especially in high gamma options that amplify price sensitivity to underlying asset movements. Unlike gamma squeezes, which stem from option market makers hedging large directional bets, volatility spikes reflect broader systemic risk and heightened market fear.
Introduction to Gamma Squeeze in Options Markets
A gamma squeeze occurs in options markets when heavy buying of short-dated call options forces market makers to purchase the underlying asset to hedge their positions, driving up the stock price rapidly. This phenomenon contrasts with a typical volatility spike, which reflects broader market uncertainty without the direct influence of options hedging dynamics. Understanding gamma squeezes is crucial for traders as it reveals how concentrated options activity can create sharp, short-term price movements beyond normal volatility patterns.
Comparing Volatility Spikes and Gamma Squeezes
Volatility spikes represent sudden increases in market price fluctuations, often triggered by unexpected news or events causing rapid shifts in implied volatility. Gamma squeezes occur when options market makers hedge their short gamma exposure by buying underlying shares aggressively, driving prices sharply higher in a feedback loop. While volatility spikes affect overall market uncertainty, gamma squeezes specifically amplify price movements due to reactive liquidity dynamics tied to options hedging strategies.
Underlying Market Mechanics Explained
A volatility spike occurs when there is a sudden increase in the underlying asset's price fluctuations, driven by heightened market uncertainty or impactful news events, causing option premiums to rise sharply. A gamma squeeze happens when market makers, hedging their delta exposure from heavy call option buying, buy more of the underlying asset as its price rises, accelerating upward momentum and causing rapid price spikes. The underlying market mechanics differ as volatility spikes reflect increased uncertainty affecting option pricing broadly, whereas gamma squeezes result from dynamic hedging activity that directly influences the asset's price through feedback loops.
Role of Options Traders in Gamma Squeeze Events
Options traders play a critical role in gamma squeeze events by dynamically hedging their positions to maintain a delta-neutral stance. When the underlying asset's price rises rapidly, market makers must buy more shares to offset their increasing delta, amplifying the price movement and triggering a feedback loop known as a gamma squeeze. This activity contrasts with a volatility spike, where rapid changes in implied volatility drive option prices independently of the underlying's directional moves.
How Volatility Spikes Affect Asset Prices
Volatility spikes cause rapid, significant price fluctuations in asset markets, increasing uncertainty and risk for traders. These surges in implied volatility often lead to wider bid-ask spreads and reduced liquidity, impacting asset pricing and investor behavior. High volatility can trigger protective hedging by market makers, further intensifying price movements during a gamma squeeze scenario.
Gamma Squeeze: Triggers and Market Impact
Gamma squeeze occurs when rapid buying of options forces market makers to hedge by purchasing the underlying asset, leading to accelerated price increases. Key triggers include heavy call option buying, low liquidity, and significant short interest in the underlying stock. This dynamic often results in sharp, short-term price surges that exacerbate volatility and put pressure on short sellers.
Risk Management During High Volatility and Gamma Squeezes
Volatility spikes and gamma squeezes create extreme market conditions that demand robust risk management strategies to mitigate potential losses and capitalize on price swings. Implementing dynamic hedging techniques, such as adjusting delta positions in response to rapidly changing gamma exposure, helps control portfolio risk during these volatile events. Monitoring implied volatility levels and liquidity constraints alongside position sizing ensures enhanced protection against sudden market reversals typical in gamma squeezes.
Case Studies: Recent Volatility Spikes vs. Gamma Squeeze Events
Recent volatility spikes, such as those during the 2020 COVID-19 market crash, showcased rapid price fluctuations driven by macroeconomic uncertainty and elevated VIX levels. In contrast, gamma squeeze events, exemplified by the January 2021 GameStop surge, were fueled by intense options market activity causing market makers to buy underlying shares aggressively to hedge, pushing prices higher. Case studies reveal that volatility spikes arise from broad market stress, while gamma squeezes stem from specific options market dynamics influencing stock price momentum.
Strategies for Investors Facing Volatility or Gamma Squeeze
Investors facing a volatility spike can deploy options strategies such as straddles or strangles to capitalize on rapid price swings without directional bias. During a gamma squeeze, purchasing options with high gamma exposure enables traders to benefit from accelerated price moves as market makers adjust their hedges. Risk management techniques like setting stop-loss orders and adjusting position sizes are crucial to navigating the intense price movements in both scenarios.
Volatility spike Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com