Delta represents change in mathematics, science, and technology, often symbolizing differences in quantities or variables. It plays a crucial role in fields like calculus, physics, and finance for calculating rates and variations. Explore the rest of this article to uncover how Delta impacts your daily decisions and innovations.
Table of Comparison
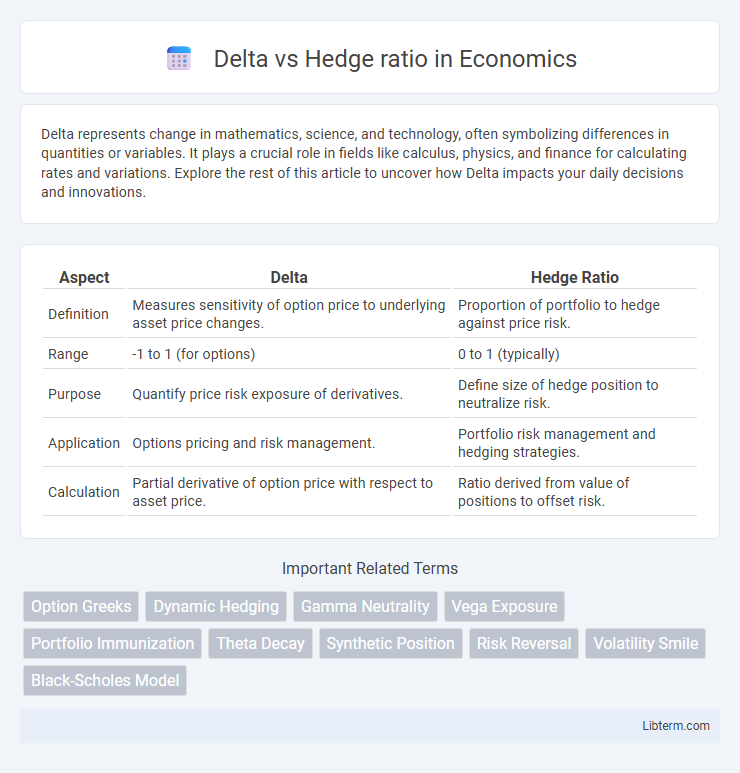
| Aspect | Delta | Hedge Ratio |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Measures sensitivity of option price to underlying asset price changes. | Proportion of portfolio to hedge against price risk. |
| Range | -1 to 1 (for options) | 0 to 1 (typically) |
| Purpose | Quantify price risk exposure of derivatives. | Define size of hedge position to neutralize risk. |
| Application | Options pricing and risk management. | Portfolio risk management and hedging strategies. |
| Calculation | Partial derivative of option price with respect to asset price. | Ratio derived from value of positions to offset risk. |
Understanding Delta in Options Trading
Delta measures the sensitivity of an option's price to changes in the underlying asset's price, ranging from 0 to 1 for calls and 0 to -1 for puts. It represents the expected change in the option's premium for a $1 move in the stock, providing traders a way to estimate directional risk and potential profit. Unlike the hedge ratio, which quantifies the number of units needed to offset risk, delta directly reflects the probability of an option expiring in-the-money.
What is the Hedge Ratio?
The hedge ratio measures the proportion of a position that should be hedged to minimize risk exposure, often expressed as the ratio between the value of the hedge position and the value of the underlying asset. It is commonly used in options trading to determine the number of options contracts needed to offset the risk of price movements in the underlying security. Unlike delta, which represents the sensitivity of an option's price to the underlying asset, the hedge ratio directly guides the construction of a hedging strategy to achieve effective risk management.
Key Differences Between Delta and Hedge Ratio
Delta measures the sensitivity of an option's price to changes in the underlying asset's price, representing the expected change in option value for a one-unit move in the asset. The hedge ratio quantifies the number of units of the underlying asset needed to offset the risk of holding an option position, typically calculated as the absolute value of delta. While delta reflects directional exposure, the hedge ratio focuses on practical position adjustment to maintain a risk-neutral stance.
Calculation Methods for Delta and Hedge Ratio
Delta is calculated by measuring the rate of change in an option's price relative to a one-unit change in the underlying asset's price, typically derived through the Black-Scholes model or numerical methods like finite differences. The hedge ratio, often synonymous with delta in options trading, determines the quantity of the underlying asset needed to offset the risk of an option position, computed by multiplying delta by the number of contracts and contract size. Accurate calculation of both delta and hedge ratio ensures effective risk management and portfolio hedging strategies in dynamic market conditions.
The Role of Delta in Risk Management
Delta plays a crucial role in risk management by quantifying the sensitivity of an option's price to changes in the underlying asset's price, allowing traders to estimate potential gains or losses. The delta value, ranging between 0 and 1 for calls and -1 to 0 for puts, helps in constructing hedging strategies that offset directional risks in portfolios. By continuously adjusting the hedge ratio based on delta, risk managers can maintain a balanced exposure to price movements, minimizing the impact of market volatility on option positions.
Utilizing Hedge Ratio for Portfolio Protection
The hedge ratio quantifies the proportion of an asset position that should be offset using derivatives to minimize risk, contrasting with delta which measures the sensitivity of an option's price to its underlying asset. Utilizing the hedge ratio effectively enables portfolio managers to balance exposure and reduce potential losses by dynamically adjusting positions based on market movements. Implementing a precise hedge ratio is critical for maintaining optimal portfolio protection against adverse price fluctuations and managing systematic risk.
How Delta and Hedge Ratio Influence hedging Strategies
Delta measures the sensitivity of an option's price to changes in the underlying asset's price, serving as the foundation for calculating the hedge ratio, which represents the proportion of the underlying asset needed to offset risk. A precise hedge ratio ensures that portfolios are dynamically adjusted to maintain a neutral position against price fluctuations, minimizing potential losses. Effective hedging strategies rely on continuously monitoring delta and adjusting the hedge ratio to accommodate market volatility and changes in option Greeks.
Practical Examples: Delta vs Hedge Ratio
Delta measures the sensitivity of an option's price relative to the underlying asset's price changes, often expressed as a value between 0 and 1 for calls and 0 and -1 for puts. The hedge ratio uses delta to quantify the number of shares of the underlying asset needed to hedge an option position, ensuring minimal risk from price fluctuations. For example, if an option has a delta of 0.6, an investor would buy or sell 0.6 shares of the underlying per option contract to maintain a delta-neutral position.
Common Misconceptions About Delta and Hedge Ratio
Delta measures the sensitivity of an option's price to changes in the underlying asset's price, while the hedge ratio quantifies the number of shares needed to offset the risk of holding an option. A common misconception is that delta always equals the hedge ratio, but delta only approximates the hedge ratio under certain conditions and ignores factors like gamma and theta. Traders often overlook that the hedge ratio adjusts dynamically with market changes, whereas delta is a snapshot metric that can mislead risk management decisions if used in isolation.
Choosing Between Delta and Hedge Ratio for Effective Hedging
Choosing between delta and hedge ratio depends on the specific hedging objective and asset characteristics. Delta measures the sensitivity of an option's price to changes in the underlying asset, ideal for simple strategies involving small price movements. Hedge ratio accounts for the proportion of the underlying asset needed to offset risk, offering more precise protection in complex portfolios or larger price fluctuations.
Delta Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com