Diversification spreads your investments across various asset classes to minimize risk and enhance potential returns. By balancing stocks, bonds, and other securities, it protects your portfolio from market volatility. Explore the rest of this article to learn how diversification can strengthen your financial strategy.
Table of Comparison
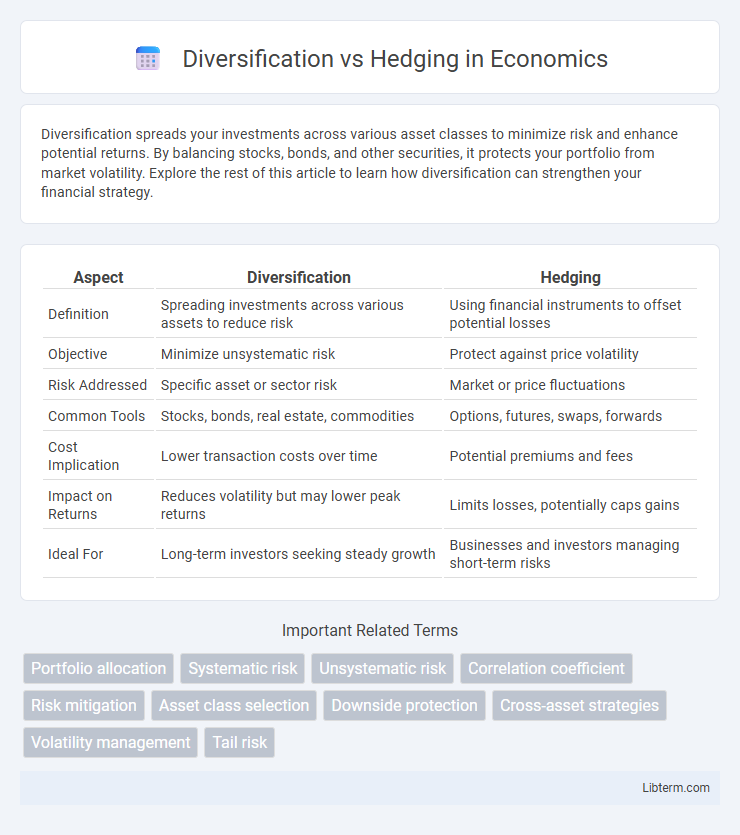
| Aspect | Diversification | Hedging |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Spreading investments across various assets to reduce risk | Using financial instruments to offset potential losses |
| Objective | Minimize unsystematic risk | Protect against price volatility |
| Risk Addressed | Specific asset or sector risk | Market or price fluctuations |
| Common Tools | Stocks, bonds, real estate, commodities | Options, futures, swaps, forwards |
| Cost Implication | Lower transaction costs over time | Potential premiums and fees |
| Impact on Returns | Reduces volatility but may lower peak returns | Limits losses, potentially caps gains |
| Ideal For | Long-term investors seeking steady growth | Businesses and investors managing short-term risks |
Understanding Diversification: Definition and Principles
Diversification involves spreading investments across various asset classes, sectors, or geographic regions to reduce risk and enhance portfolio stability. Its core principle is that by combining assets with low or negative correlations, overall volatility decreases, protecting against significant losses from any single investment. Effective diversification aims to balance risk and return, leveraging the inverse relationships between assets to achieve more consistent performance.
Hedging Explained: Purpose and Techniques
Hedging involves using financial instruments or strategies to reduce exposure to price fluctuations and manage risk in investments or business operations. Common hedging techniques include options, futures contracts, swaps, and forward contracts, which help offset potential losses by taking an opposing position in related assets. The primary purpose of hedging is to provide stability and protect against adverse price movements in commodities, currencies, interest rates, and securities.
Key Differences Between Diversification and Hedging
Diversification reduces investment risk by spreading assets across various sectors, industries, or asset classes to minimize the impact of any single asset's poor performance. Hedging involves using financial instruments such as options, futures, or swaps to offset potential losses in a specific investment or portfolio. The key difference lies in diversification's broad risk reduction approach versus hedging's targeted risk management strategy designed to protect against specific market movements.
Pros and Cons of Diversification Strategies
Diversification strategies spread investments across various asset classes, industries, or geographic regions to reduce risk and enhance portfolio stability, benefiting investors by minimizing exposure to any single market downturn. However, diversification can dilute potential high returns from individual assets and increase management complexity and costs. While it provides risk mitigation and smoother performance, over-diversification may lead to diminishing returns and challenges in effectively monitoring all investments.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Hedging
Hedging provides significant advantages such as risk reduction by protecting investments against price volatility and market uncertainties, allowing businesses to stabilize cash flows and safeguard profit margins. However, disadvantages include potential costs like premiums for options or margin requirements for futures, which can reduce overall returns, and the complexity of implementing effective hedging strategies that require expertise and constant monitoring. Inefficient hedging may also lead to opportunity costs when favorable market movements are offset by hedge positions.
Real-World Examples: Diversification in Action
Diversification in investment portfolios is exemplified by multinational corporations like Apple, which spreads risk by entering varied sectors such as technology, wearables, and services, reducing dependence on any single market. In financial markets, mutual funds that invest across different asset classes--stocks, bonds, and real estate--illustrate diversification's role in risk mitigation by balancing growth potential and volatility. This contrasts with hedging strategies often used by commodity producers like airlines, which use futures contracts to lock in fuel prices and protect against market fluctuations rather than broadening asset exposure.
Case Studies: Effective Hedging Practices
Case studies in effective hedging practices reveal how multinational corporations use currency options and futures contracts to mitigate foreign exchange risk, preserving profit margins during volatile market conditions. For example, Coca-Cola's strategic use of natural hedges, balancing revenue and costs in multiple currencies, minimizes exposure without extensive derivative use. These cases demonstrate that targeted hedging, unlike general diversification, directly addresses specific financial risks with measurable impact on company stability.
Diversification vs. Hedging: Impact on Portfolio Risk
Diversification reduces portfolio risk by spreading investments across various asset classes, industries, and geographies to minimize unsystematic risk and enhance overall stability. Hedging involves using financial instruments such as options, futures, or derivatives to offset potential losses from specific investments, primarily targeting market or systemic risk. Combining diversification with hedging strategies can optimize risk management by addressing different dimensions of portfolio volatility and protecting against adverse market movements.
Choosing the Right Strategy: Factors to Consider
Choosing the right strategy between diversification and hedging depends on factors such as risk tolerance, investment goals, and market conditions. Diversification reduces portfolio risk by spreading investments across various asset classes, while hedging involves taking positions to offset potential losses in specific assets. Analyzing asset correlations, cost implications, and time horizons helps investors determine the optimal approach for managing financial risks effectively.
Integrating Diversification and Hedging for Optimal Risk Management
Integrating diversification and hedging strategies enhances optimal risk management by balancing risk reduction and cost efficiency. Diversification spreads investment exposure across varied assets to minimize unsystematic risk, while hedging uses derivatives like options and futures to protect against market volatility and adverse price movements. Combining these approaches allows investors to achieve stable returns and safeguard portfolios against both market fluctuations and sector-specific downturns.
Diversification Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com