Internationalization involves adapting products, services, and content to meet the linguistic, cultural, and regulatory requirements of different global markets, ensuring seamless user experiences across diverse regions. It reduces development time and costs by enabling scalable localization processes while maintaining brand consistency worldwide. Explore the rest of this article to understand how internationalization can elevate your business on the global stage.
Table of Comparison
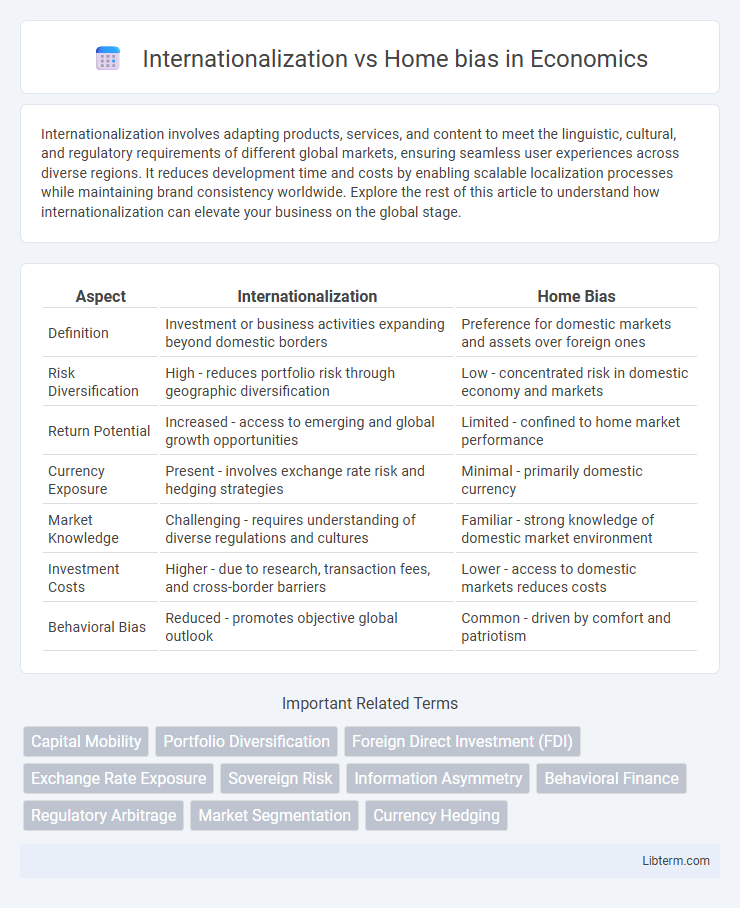
| Aspect | Internationalization | Home Bias |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Investment or business activities expanding beyond domestic borders | Preference for domestic markets and assets over foreign ones |
| Risk Diversification | High - reduces portfolio risk through geographic diversification | Low - concentrated risk in domestic economy and markets |
| Return Potential | Increased - access to emerging and global growth opportunities | Limited - confined to home market performance |
| Currency Exposure | Present - involves exchange rate risk and hedging strategies | Minimal - primarily domestic currency |
| Market Knowledge | Challenging - requires understanding of diverse regulations and cultures | Familiar - strong knowledge of domestic market environment |
| Investment Costs | Higher - due to research, transaction fees, and cross-border barriers | Lower - access to domestic markets reduces costs |
| Behavioral Bias | Reduced - promotes objective global outlook | Common - driven by comfort and patriotism |
Understanding Internationalization and Home Bias
Internationalization refers to the expansion of business operations or investment portfolios beyond domestic borders, aiming to diversify risk and tap into global markets. Home bias is an investor's tendency to favor domestic assets over foreign ones, often due to familiarity, perceived lower risk, or information advantage. Understanding these concepts helps explain why many portfolios remain concentrated in local markets despite the potential benefits of international diversification.
Key Drivers of Investment Home Bias
Key drivers of investment home bias include familiarity with domestic markets, information asymmetry favoring local assets, and perceived currency risk associated with foreign investments. Investors tend to prefer domestic securities due to better access to reliable data, stronger legal protections, and lower transaction costs compared to international options. Behavioral factors such as patriotism and risk aversion further consolidate the preference for home-country assets over foreign diversification.
Advantages of Internationalization in Portfolios
Internationalization in portfolios enhances diversification by spreading investments across varied economic environments, reducing country-specific risks. It offers access to emerging markets with higher growth potential, improving the portfolio's overall return profile. Investors benefit from currency diversification, which can further stabilize returns and offset domestic market downturns.
Risks Associated with Home Bias
Home bias exposes investors to concentrated risks by limiting diversification across global markets, increasing vulnerability to domestic economic downturns, political instability, and sector-specific shocks. Internationalization mitigates these risks by spreading investments across different countries, currencies, and regulatory environments, thereby enhancing portfolio resilience. Empirical studies highlight that portfolios with strong home bias often underperform due to higher exposure to idiosyncratic risks and missed opportunities in emerging and developed markets abroad.
Barriers to International Investment
Barriers to international investment include regulatory constraints, currency risks, and lack of information about foreign markets, which contribute significantly to home bias in portfolios. Investors often face unfamiliar legal systems, geopolitical risks, and transaction costs that deter diversification beyond domestic assets. Language differences, cultural misunderstandings, and limited access to reliable data further restrict effective international investment strategies.
Impact of Globalization on Investment Patterns
Globalization has dramatically altered investment patterns by reducing home bias and encouraging investors to diversify across international markets. Increased access to global information, technological advancements, and lower transaction costs have facilitated cross-border investments, enhancing portfolio efficiency and risk management. Multinational corporations and emerging markets now attract substantial foreign capital, reflecting the growing integration of global financial systems.
Behavioral Economics Behind Home Bias
Home bias in investment reflects behavioral economics principles such as familiarity bias and loss aversion, where investors prefer domestic assets due to greater knowledge and perceived lower risk. Internationalization challenges this bias by exposing investors to diversified portfolios, yet psychological comfort with local markets often outweighs rational diversification benefits. Cognitive limitations and information asymmetry further reinforce the tendency to underinvest internationally despite global market integration.
Performance Comparison: International vs Domestic Portfolios
International portfolios often exhibit higher diversification benefits compared to domestic portfolios, leading to potentially enhanced risk-adjusted returns. Studies show that while home bias persists among investors, international investments tend to outperform domestic-only portfolios by capturing growth opportunities in emerging and developed markets worldwide. Performance differences depend on factors like currency risk, market integration, and economic cycles, emphasizing the importance of global asset allocation for optimizing portfolio returns.
Strategies to Overcome Home Bias
Diversifying investment portfolios through global asset allocation is a key strategy to overcome home bias, reducing reliance on domestic markets and capturing international growth opportunities. Employing exchange-traded funds (ETFs) and mutual funds focused on foreign markets facilitates efficient access to global equities and bonds, enhancing portfolio diversification. Investors benefit from incorporating currency-hedged products and conducting thorough geopolitical and economic analysis to manage risks associated with international investments.
Future Trends in International Investing
Future trends in international investing reveal a gradual reduction in home bias as investors increasingly seek diversification across global markets to mitigate risks and capture growth opportunities. Advances in technology and data analytics enhance access to foreign assets, making cross-border investments more efficient and attractive. Regulatory harmonization and rising investor awareness further drive the shift towards greater internationalization in portfolio construction.
Internationalization Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com