The Impossible Trinity, also known as the Trilemma, highlights the challenge in international economics where a country cannot simultaneously maintain a fixed foreign exchange rate, free capital movement, and an independent monetary policy. Policymakers must choose two out of these three options, often impacting economic stability and growth strategies. Explore the full article to understand how this economic principle shapes your country's financial decisions and global market interactions.
Table of Comparison
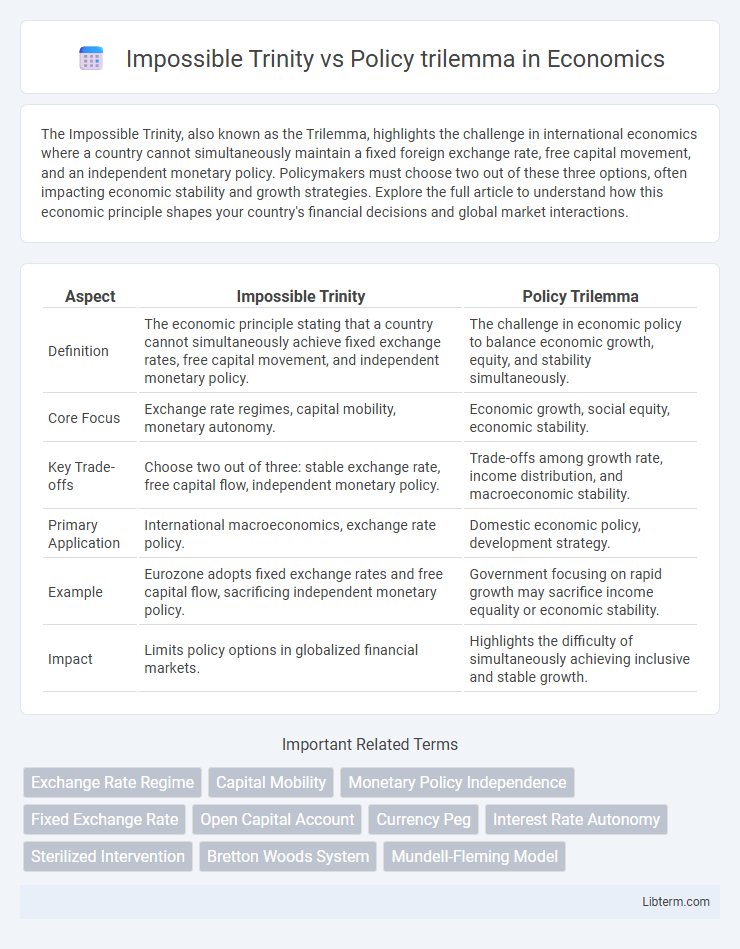
| Aspect | Impossible Trinity | Policy Trilemma |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | The economic principle stating that a country cannot simultaneously achieve fixed exchange rates, free capital movement, and independent monetary policy. | The challenge in economic policy to balance economic growth, equity, and stability simultaneously. |
| Core Focus | Exchange rate regimes, capital mobility, monetary autonomy. | Economic growth, social equity, economic stability. |
| Key Trade-offs | Choose two out of three: stable exchange rate, free capital flow, independent monetary policy. | Trade-offs among growth rate, income distribution, and macroeconomic stability. |
| Primary Application | International macroeconomics, exchange rate policy. | Domestic economic policy, development strategy. |
| Example | Eurozone adopts fixed exchange rates and free capital flow, sacrificing independent monetary policy. | Government focusing on rapid growth may sacrifice income equality or economic stability. |
| Impact | Limits policy options in globalized financial markets. | Highlights the difficulty of simultaneously achieving inclusive and stable growth. |
Understanding the Impossible Trinity
The Impossible Trinity, also known as the Policy Trilemma, states that a country cannot simultaneously maintain a fixed foreign exchange rate, free capital movement, and an independent monetary policy. Policymakers must choose two out of these three options, as achieving all three is impossible due to inherent economic constraints. This trade-off shapes monetary and fiscal strategies in open economies, influencing currency stability and financial market integration.
Defining the Policy Trilemma
The Policy Trilemma, also known as the Impossible Trinity, states that a country cannot simultaneously achieve a fixed foreign exchange rate, free capital movement, and an independent monetary policy. Policymakers must prioritize two of these three goals, sacrificing the third to maintain economic stability. This framework highlights the trade-offs inherent in international macroeconomic policy decisions.
Historical Origins of Both Concepts
The Impossible Trinity, or Trilemma, originated from the 1960s monetary policy debates, emphasizing the challenge countries face in simultaneously achieving fixed exchange rates, free capital movement, and independent monetary policy. The Policy Trilemma, rooted in the Mundell-Fleming model of the 1960s, builds on this by illustrating the trade-offs policymakers confront in an open economy. Both concepts derive from the early work of economists Robert Mundell and Marcus Fleming, reflecting fundamental constraints in international macroeconomics.
Core Principles Compared
The Impossible Trinity, or policy trilemma, posits that a country cannot simultaneously maintain a fixed foreign exchange rate, free capital movement, and an independent monetary policy, forcing policymakers to choose only two. Core principles compare how the trinity limits economic sovereignty by highlighting trade-offs between exchange rate stability, monetary autonomy, and capital mobility. Understanding these constraints enables governments to design monetary and fiscal policies that align with their preferred balance of economic control and global financial integration.
Examples in International Economics
The Impossible Trinity, also known as the Policy Trilemma, asserts that a country cannot simultaneously achieve a fixed exchange rate, free capital movement, and independent monetary policy. For example, China maintains a fixed exchange rate and controls capital flows, sacrificing full monetary autonomy, while the United States allows free capital movement and monetary autonomy, accepting flexible exchange rates. The European Monetary Union fixed exchange rates and capital mobility but abandoned independent monetary policies, demonstrating the policy trade-offs highlighted by the trilemma.
Trade-offs in Macroeconomic Policy
The Impossible Trinity, also known as the Policy Trilemma, highlights the trade-offs policymakers face between exchange rate stability, monetary policy independence, and capital mobility. Maintaining two out of these three goals simultaneously forces a compromise on the third, such as sacrificing monetary autonomy to preserve a fixed exchange rate under open capital accounts. This trade-off shapes macroeconomic policy decisions, influencing inflation control, interest rate settings, and economic openness in global financial systems.
Case Studies of Currency Crises
Currency crises often exemplify the Impossible Trinity, where countries cannot simultaneously maintain fixed exchange rates, free capital flows, and independent monetary policy. The 1997 Asian Financial Crisis highlighted this policy trilemma, as countries like Thailand abandoned fixed pegs to regain monetary control amid capital flight. Similarly, the 1994 Mexican Peso Crisis underscored the vulnerability of fixed exchange rate regimes combined with open capital accounts, forcing policymakers to choose between currency stability and monetary sovereignty.
Policy Responses and Limitations
The Impossible Trinity, or Policy Trilemma, forces governments to choose between exchange rate stability, monetary policy autonomy, and free capital movement, but policy responses often prioritize two objectives at the expense of the third. Central banks may impose capital controls to maintain fixed exchange rates while preserving monetary policy, or they may allow exchange rate flexibility to retain independent monetary policies alongside open capital accounts. Limitations arise as no policy configuration fully satisfies all three goals simultaneously, leading to trade-offs that impact economic stability and investor confidence.
Contemporary Relevance and Debates
The Impossible Trinity, also known as the Policy Trilemma, remains critically relevant in contemporary economic debates, especially amid globalization and digital currency expansion. Policymakers face persistent challenges balancing monetary policy autonomy, exchange rate stability, and capital mobility, with recent crises highlighting trade-offs in emerging markets and advanced economies. Discussions intensify around optimal policy mixes to manage these constraints in the context of evolving financial technologies and international cooperation frameworks.
Future Implications for Global Finance
The Impossible Trinity, or trilemma, dictates that countries cannot simultaneously maintain fixed exchange rates, free capital movement, and an independent monetary policy, forcing policymakers to prioritize two of the three. This trade-off shapes future global financial stability as increasing globalization and financial integration pressure governments to reconsider their exchange rate regimes and capital control policies. Emerging trends in digital currencies and cross-border financial technologies will further challenge the existing policy trilemma, potentially reshaping international monetary coordination and financial market volatility.
Impossible Trinity Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com