Gross National Income (GNI) measures a country's total economic output, including the value of goods and services produced domestically and the net income earned from abroad. It reflects the overall economic strength and average income of residents, providing insight into living standards and economic wellbeing. Discover how GNI impacts economic policies and influences Your financial planning by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
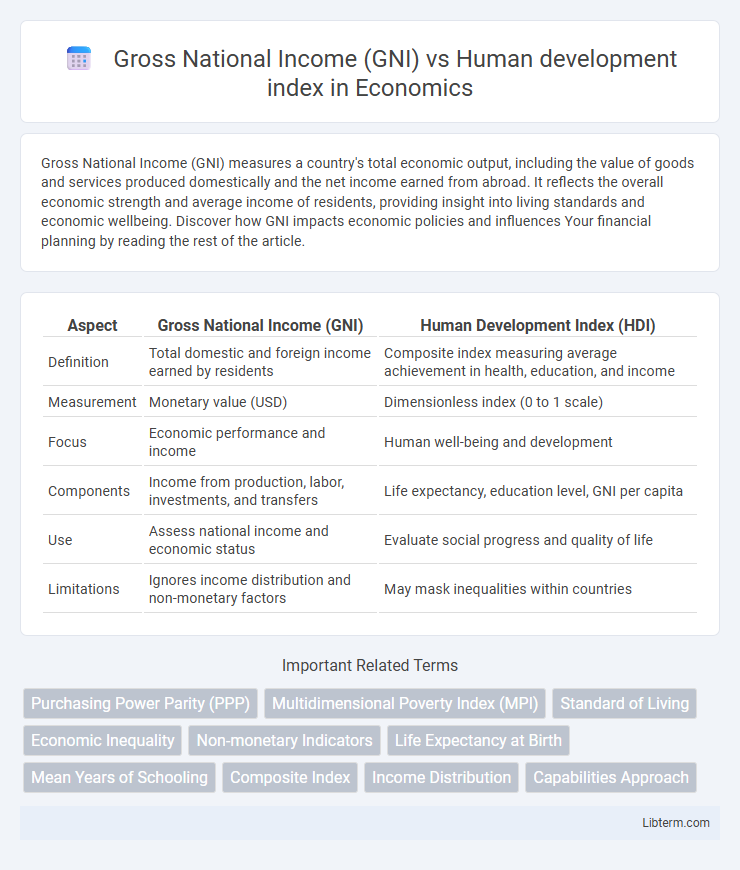
| Aspect | Gross National Income (GNI) | Human Development Index (HDI) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Total domestic and foreign income earned by residents | Composite index measuring average achievement in health, education, and income |
| Measurement | Monetary value (USD) | Dimensionless index (0 to 1 scale) |
| Focus | Economic performance and income | Human well-being and development |
| Components | Income from production, labor, investments, and transfers | Life expectancy, education level, GNI per capita |
| Use | Assess national income and economic status | Evaluate social progress and quality of life |
| Limitations | Ignores income distribution and non-monetary factors | May mask inequalities within countries |
Understanding Gross National Income (GNI)
Gross National Income (GNI) measures the total income earned by a country's residents and businesses, including any income earned abroad, providing a comprehensive indicator of economic activity. It differs from the Human Development Index (HDI), which incorporates GNI per capita but also factors in health and education metrics to assess overall well-being. Understanding GNI helps evaluate economic strength, but it must be combined with HDI for a fuller picture of human development.
Defining the Human Development Index (HDI)
The Human Development Index (HDI) is a composite statistic measuring average achievement in key dimensions of human development: health, education, and standard of living. Unlike Gross National Income (GNI), which focuses solely on economic output, HDI incorporates life expectancy, mean years of schooling, and gross national income per capita to assess overall societal well-being. This multidimensional approach provides a broader understanding of development beyond economic metrics alone.
Key Components of GNI and HDI
Gross National Income (GNI) measures the total domestic and foreign income earned by a country's residents, emphasizing the sum of Gross Domestic Product (GDP) plus net income from abroad, which includes wages, rents, and profits. The Human Development Index (HDI) evaluates a nation's overall well-being based on three core components: life expectancy at birth (health), mean years of schooling and expected years of schooling (education), and Gross National Income per capita adjusted for purchasing power parity (standard of living). While GNI focuses primarily on economic output and income generation, HDI provides a broader perspective by integrating health and education indicators alongside income to assess human development comprehensively.
Calculation Methods: GNI vs HDI
Gross National Income (GNI) is calculated by summing the total domestic and foreign income earned by residents, including GDP plus net income from abroad, measured in monetary terms. The Human Development Index (HDI) employs a composite approach, combining normalized indicators of life expectancy, education (mean years of schooling and expected years of schooling), and GNI per capita adjusted for purchasing power parity (PPP). GNI focuses strictly on economic output and income, whereas HDI integrates health, education, and income dimensions to provide a broader assessment of human development.
Indicators Covered by GNI and HDI
Gross National Income (GNI) measures the total domestic and foreign income claimed by residents of a country, primarily focusing on economic indicators such as GDP plus net income from abroad, reflecting income levels and economic performance. The Human Development Index (HDI) incorporates a broader range of indicators, including GNI per capita, life expectancy at birth, and educational attainment (mean years of schooling and expected years of schooling), providing a composite measure of health, education, and income dimensions to assess overall human development. While GNI emphasizes income statistics, HDI integrates social indicators to present a more comprehensive view of a country's developmental status.
Comparative Importance in Economic Analysis
Gross National Income (GNI) quantifies the total domestic and foreign income earned by a country's residents, serving as a fundamental metric for economic performance and wealth assessment. The Human Development Index (HDI) integrates GNI with education and life expectancy data to provide a broader measure of social and economic well-being. Comparing GNI and HDI reveals that while GNI emphasizes economic output, HDI offers a more comprehensive view of human development by including health and educational dimensions critical for policy evaluation.
Limitations of GNI as a Development Metric
Gross National Income (GNI) measures a country's total income but fails to capture the distribution of wealth, quality of life, and access to essential services, which limits its effectiveness as a development metric. The Human Development Index (HDI) incorporates income along with life expectancy and education, providing a more comprehensive assessment of social progress. Reliance solely on GNI can mask inequalities and overlook crucial factors like health and education that significantly impact human development.
Strengths of HDI in Measuring Well-being
Human Development Index (HDI) excels in measuring well-being by incorporating multidimensional aspects such as life expectancy, education levels, and per capita income, providing a broader perspective than Gross National Income (GNI) alone. While GNI captures total economic output, HDI reflects quality of life and social progress, highlighting disparities in health and education that pure economic metrics overlook. This comprehensive approach offers a more accurate evaluation of human development and societal welfare across countries.
Country Rankings: GNI vs HDI Insights
Country rankings based on Gross National Income (GNI) per capita often highlight economic strength but may not fully capture overall well-being, while the Human Development Index (HDI) incorporates health, education, and income to provide a broader measure of quality of life. Countries with high GNI sometimes rank lower on the HDI due to disparities in healthcare or education, illustrating how income alone does not guarantee human development. Comparative analysis of GNI and HDI rankings reveals socioeconomic imbalances and guides policy priorities for sustainable development.
Policy Implications and Real-World Applications
Gross National Income (GNI) measures a country's total economic output, guiding fiscal policies aimed at income growth and resource allocation, while the Human Development Index (HDI) integrates health, education, and income metrics to inform social policies targeting quality of life improvements. Policymakers utilize GNI data to design economic strategies that enhance national wealth, whereas HDI drives comprehensive development programs that address poverty, literacy, and healthcare access. Real-world applications include using GNI for macroeconomic planning and investment decisions, and leveraging HDI to prioritize human-centered interventions within sustainable development frameworks.
Gross National Income (GNI) Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com