Horizontal trade involves the exchange of goods and services between businesses operating at the same level in the supply chain, often within the same industry. This type of trade fosters collaboration, increases market reach, and can lead to enhanced efficiencies and competitive advantages. Discover how horizontal trade can impact your business strategy and open new opportunities in the detailed analysis below.
Table of Comparison
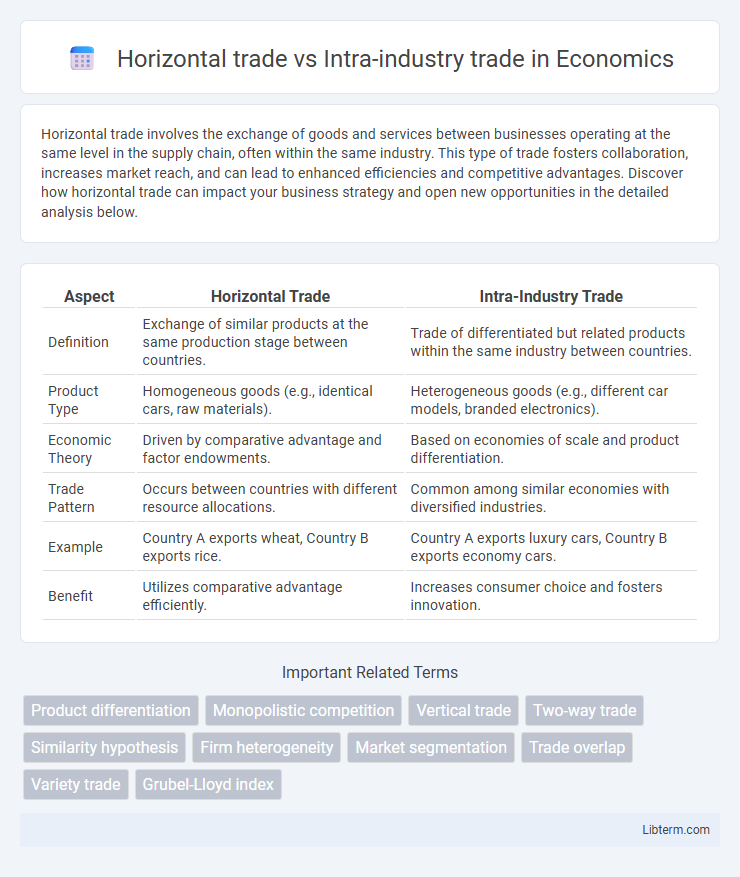
| Aspect | Horizontal Trade | Intra-Industry Trade |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Exchange of similar products at the same production stage between countries. | Trade of differentiated but related products within the same industry between countries. |
| Product Type | Homogeneous goods (e.g., identical cars, raw materials). | Heterogeneous goods (e.g., different car models, branded electronics). |
| Economic Theory | Driven by comparative advantage and factor endowments. | Based on economies of scale and product differentiation. |
| Trade Pattern | Occurs between countries with different resource allocations. | Common among similar economies with diversified industries. |
| Example | Country A exports wheat, Country B exports rice. | Country A exports luxury cars, Country B exports economy cars. |
| Benefit | Utilizes comparative advantage efficiently. | Increases consumer choice and fosters innovation. |
Understanding Horizontal Trade: A Brief Overview
Horizontal trade involves the exchange of similar goods and services between countries at the same stage of production, reflecting comparable consumer preferences and incomes. It allows countries to specialize in differentiated products within the same industry, such as cars or electronics, enhancing variety and competition in global markets. This form of trade contrasts with intra-industry trade, which encompasses both horizontal and vertical exchanges, but specifically emphasizes the trade of similar-level goods contributing to economic specialization and efficiency.
Defining Intra-Industry Trade: Key Concepts
Intra-industry trade involves the exchange of similar products within the same industry, allowing countries to specialize in different varieties or qualities of goods, unlike horizontal trade which focuses solely on goods of the same quality level. Key concepts of intra-industry trade include product differentiation, economies of scale, and consumer preference diversity, which drive specialized production and exchange between countries. Measuring intra-industry trade typically uses the Grubel-Lloyd index, highlighting the balance between imports and exports of related goods within an industry.
Main Differences Between Horizontal and Intra-Industry Trade
Horizontal trade involves the exchange of similar goods produced at the same stage of production but by different countries, typically differentiated by brand or quality, while intra-industry trade encompasses both horizontal and vertical trade within the same industry, including goods of varying quality and production levels. The main difference lies in the nature of goods traded: horizontal trade features similar products for similar consumer needs, whereas intra-industry trade covers a broader spectrum, including both similar and vertically differentiated products. Economies engaged in horizontal trade benefit from product variety and consumer preferences, while intra-industry trade also promotes specialization and efficiency gains across different production stages.
Economic Theories Underpinning Trade Types
Horizontal trade involves the exchange of similar goods produced at the same stage of production but differing in features or brands, grounded in Product Differentiation Theory and Monopolistic Competition models that explain consumer preference for variety. Intra-industry trade extends to the simultaneous import and export of products within the same industry but may encompass both horizontal and vertical dimensions, supported by theories such as New Trade Theory emphasizing economies of scale and imperfect competition. Both trade types challenge the traditional comparative advantage framework by highlighting the role of market structure, product differentiation, and scale economies in shaping international trade patterns.
Factors Driving Horizontal Trade
Factors driving horizontal trade predominantly include similarities in factor endowments such as capital intensity, technology levels, and consumer preferences across countries, encouraging the exchange of similar goods. Market size and product differentiation also play crucial roles, enabling firms to exploit economies of scale while catering to varied tastes within the same industry. Transportation costs and trade policies further influence the extent of horizontal trade by affecting the feasibility and profitability of exporting similar products between countries.
Determinants of Intra-Industry Trade Patterns
Intra-industry trade patterns are primarily determined by product differentiation, economies of scale, and similarities in factor endowments between trading countries. Horizontal trade involves exchanging similar products targeting diverse consumer preferences, influenced by factors such as income distribution and market size. In contrast, vertical intra-industry trade is driven by differences in production costs and quality across countries, reflecting variations in technological advancement and labor skill levels.
Advantages and Challenges of Horizontal Trade
Horizontal trade involves the exchange of similar products produced by different countries, enabling firms to exploit economies of scale and increase market variety for consumers. Advantages of horizontal trade include enhanced product differentiation, increased competition leading to innovation, and access to diverse consumer preferences without major differences in production technology. Challenges faced in horizontal trade encompass difficulties in maintaining product differentiation, high transportation and marketing costs, and vulnerability to demand fluctuations in similar goods across markets.
Benefits and Limitations of Intra-Industry Trade
Intra-industry trade offers significant benefits such as increased product variety for consumers, economies of scale for producers, and reduced adjustment costs due to trade in similar goods within the same industry. However, it faces limitations including dependence on market size for sustaining trade volumes, vulnerability to demand fluctuations across countries, and challenges in accurately measuring trade flows due to overlapping product categories. Horizontal trade contrasts by involving exchange of similar products at the same production stage, but tends to generate less specialization and fewer scale economies compared to intra-industry trade.
Real-World Examples: Horizontal vs. Intra-Industry Trade
Horizontal trade occurs when countries exchange similar goods at the same stage of production, such as the trade of passenger cars between Germany and Japan, reflecting consumer preferences and variety. Intra-industry trade, exemplified by the U.S. exporting and importing different types of electronic equipment, involves the exchange of related but differentiated products within the same industry, driven by economies of scale and product differentiation. Real-world examples demonstrate that horizontal trade often involves standardized goods, while intra-industry trade thrives in industries with diverse product lines and specialization.
Policy Implications and Future Trends in International Trade
Horizontal trade involves exchanges of similar products at the same stage of production between countries with comparable factor endowments, leading to policies that emphasize competitive regulation and market access. Intra-industry trade, characterized by the simultaneous import and export of differentiated goods within the same industry, often prompts policies fostering innovation, standards harmonization, and investment in technology to enhance comparative advantage. Future trends in international trade suggest increasing intra-industry trade due to globalization and product differentiation, requiring adaptive trade agreements and dynamic policy frameworks to manage complex supply chains and intellectual property rights.
Horizontal trade Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com