Job sharing allows two employees to split the responsibilities and hours of a full-time position, enhancing work-life balance and increasing productivity. This flexible work arrangement can reduce burnout and improve job satisfaction by matching individual schedules and strengths. Explore the rest of the article to discover how job sharing can benefit your career and workplace.
Table of Comparison
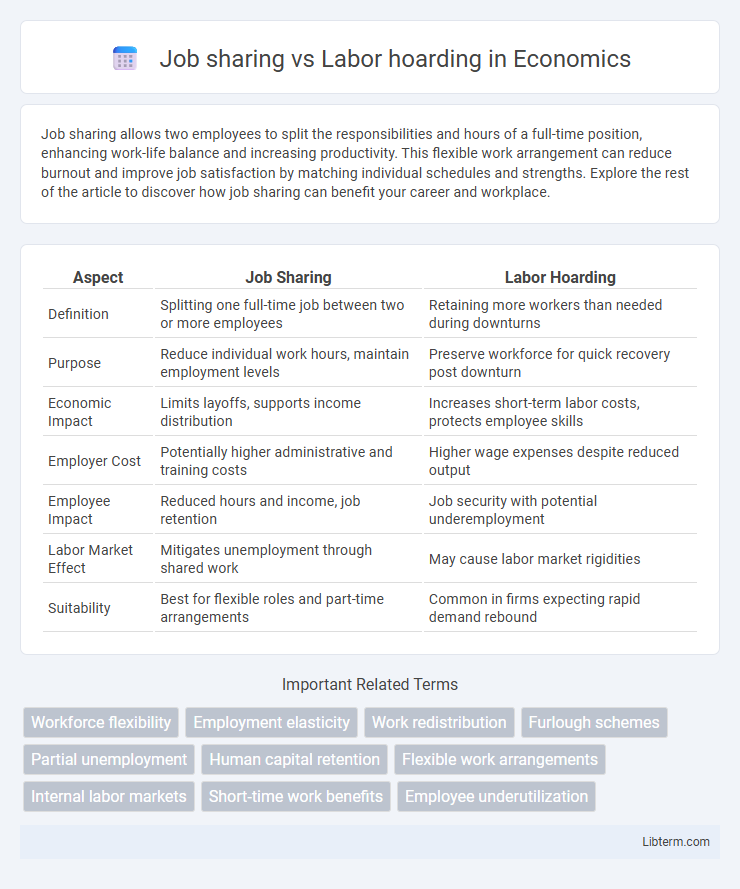
| Aspect | Job Sharing | Labor Hoarding |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Splitting one full-time job between two or more employees | Retaining more workers than needed during downturns |
| Purpose | Reduce individual work hours, maintain employment levels | Preserve workforce for quick recovery post downturn |
| Economic Impact | Limits layoffs, supports income distribution | Increases short-term labor costs, protects employee skills |
| Employer Cost | Potentially higher administrative and training costs | Higher wage expenses despite reduced output |
| Employee Impact | Reduced hours and income, job retention | Job security with potential underemployment |
| Labor Market Effect | Mitigates unemployment through shared work | May cause labor market rigidities |
| Suitability | Best for flexible roles and part-time arrangements | Common in firms expecting rapid demand rebound |
Introduction to Job Sharing and Labor Hoarding
Job sharing involves splitting a full-time position between two or more employees, allowing flexible work hours and reducing individual workloads while maintaining overall productivity. Labor hoarding refers to the strategy where companies retain more employees than necessary during economic slowdowns to preserve skills and avoid future hiring costs. Both practices aim to manage labor resources efficiently but differ in approach, with job sharing emphasizing workload distribution and labor hoarding focusing on workforce retention.
Defining Job Sharing: Concepts and Benefits
Job sharing involves splitting a full-time position between two or more employees who share responsibilities, hours, and pay, promoting work-life balance and reducing unemployment risks. This flexible employment arrangement enhances productivity by leveraging diverse skills while maintaining continuity in job functions. Employers benefit from job sharing through cost savings on overtime and improved employee morale, making it a strategic alternative to labor hoarding during economic fluctuations.
Understanding Labor Hoarding: Meaning and Motivations
Labor hoarding refers to a business strategy where companies retain more employees than necessary during economic downturns to avoid future rehiring costs and skill shortages. This approach preserves organizational knowledge and workforce stability, reducing disruptions when demand recovers. In contrast to job sharing, which redistributes work hours among employees, labor hoarding prioritizes long-term resource retention despite short-term inefficiencies.
Key Differences Between Job Sharing and Labor Hoarding
Job sharing involves dividing one full-time job between two employees to reduce working hours while maintaining productivity, often improving work-life balance. Labor hoarding occurs when companies retain more employees than needed during downturns to preserve skills and avoid rehiring costs, despite reduced workloads. Key differences include job sharing's proactive workforce management for flexibility versus labor hoarding's strategic retention to mitigate future labor shortages.
Economic Impacts of Job Sharing vs. Labor Hoarding
Job sharing reduces unemployment rates by distributing available work hours among multiple employees, lowering wage costs and increasing labor market flexibility, which can enhance overall economic productivity. Labor hoarding, characterized by firms retaining surplus workers during downturns, preserves firm-specific skills and reduces future hiring costs but may lead to increased short-term labor expenses and lower immediate efficiency. The economic impact of job sharing tends to favor broader labor market stability, while labor hoarding supports long-term firm adaptability and workforce retention during economic fluctuations.
Employee Engagement and Workplace Culture Comparison
Job sharing enhances employee engagement by promoting work-life balance and fostering collaboration, which cultivates a positive workplace culture characterized by mutual support and shared responsibility. Labor hoarding, while preserving jobs during economic downturns, can lead to reduced motivation and decreased productivity if employees feel underutilized or uncertain about their roles. Comparing both, job sharing actively boosts engagement and positively shapes organizational culture, whereas labor hoarding may protect employment but risks stifling enthusiasm and innovation.
Pros and Cons of Job Sharing for Employers and Employees
Job sharing allows employers to reduce labor costs and increase workforce flexibility while maintaining employee satisfaction and productivity, though it may lead to coordination challenges and potential communication gaps. Employees benefit from better work-life balance and reduced stress, but face potential drawbacks like lower income and limited career advancement opportunities. Balancing these pros and cons is crucial for organizations aiming to optimize talent utilization and employee engagement.
Risks and Rewards of Labor Hoarding in Business
Labor hoarding entails retaining more employees than needed during downturns, which can safeguard institutional knowledge and enhance workforce morale but increases wage and overhead costs. The risk involves diminished operational efficiency and financial strain due to underutilized labor, potentially leading to reduced competitiveness. However, labor hoarding can accelerate recovery post-recession by preserving skilled workers, minimizing recruitment costs, and maintaining production capacity.
Industry Trends: Which Sectors Favor Job Sharing or Labor Hoarding?
Manufacturing and retail sectors often favor labor hoarding to maintain skilled workforces during demand fluctuations, ensuring operational continuity and reducing rehiring costs. In contrast, professional services and technology industries lean towards job sharing to enhance work-life balance and retain talent by offering flexible employment arrangements. Emerging sectors like healthcare blend both approaches, balancing critical workforce retention with adaptable staffing solutions amid changing care demands.
Choosing the Right Strategy: Factors to Consider
Choosing the right strategy between job sharing and labor hoarding depends on factors such as workforce flexibility, cost management, and long-term business objectives. Job sharing optimizes talent utilization by splitting responsibilities among employees, which can enhance job satisfaction and reduce layoffs during downturns. Labor hoarding, while maintaining full employment during slow periods, often involves higher payroll costs and may impact operational efficiency depending on business volatility and market conditions.
Job sharing Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com