A tailored approach customizes strategies to fit the unique needs and goals of your project or business, maximizing effectiveness and results. By focusing on specific challenges and opportunities, it delivers more precise solutions than one-size-fits-all methods. Discover how a tailored approach can transform your outcomes by exploring the full article.
Table of Comparison
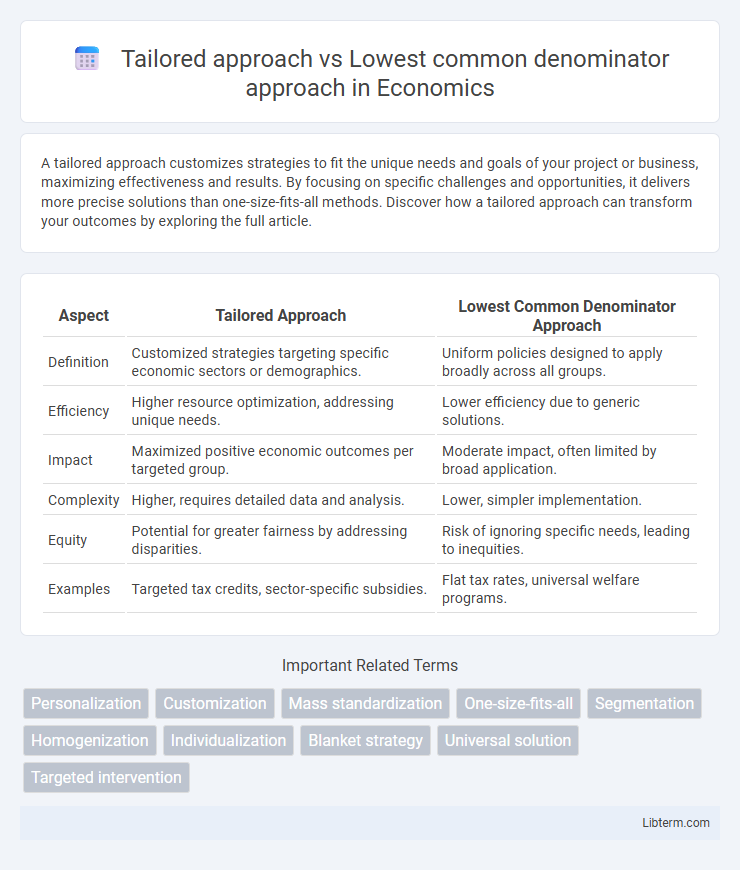
| Aspect | Tailored Approach | Lowest Common Denominator Approach |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Customized strategies targeting specific economic sectors or demographics. | Uniform policies designed to apply broadly across all groups. |
| Efficiency | Higher resource optimization, addressing unique needs. | Lower efficiency due to generic solutions. |
| Impact | Maximized positive economic outcomes per targeted group. | Moderate impact, often limited by broad application. |
| Complexity | Higher, requires detailed data and analysis. | Lower, simpler implementation. |
| Equity | Potential for greater fairness by addressing disparities. | Risk of ignoring specific needs, leading to inequities. |
| Examples | Targeted tax credits, sector-specific subsidies. | Flat tax rates, universal welfare programs. |
Understanding Tailored and Lowest Common Denominator Approaches
The tailored approach customizes strategies and solutions to meet the specific needs and preferences of distinct target audiences, enhancing relevance and effectiveness. In contrast, the lowest common denominator approach aims to create broad, generic content that appeals to the widest possible audience by minimizing complexity and specificity. Understanding these approaches helps businesses balance personalization with scalability, optimizing customer engagement and resource allocation.
Key Differences Between Tailored and Lowest Common Denominator Methods
The tailored approach customizes solutions based on specific needs, preferences, and contexts, enabling higher engagement and relevance, whereas the lowest common denominator approach aims for broad compatibility by simplifying features to accommodate the largest possible audience. Tailored methods leverage detailed data and segmentation to enhance user experience, while the lowest common denominator approach prioritizes universal accessibility at the expense of personalization. This key difference impacts outcomes significantly, with tailored solutions driving targeted effectiveness and lowest common denominator approaches focusing on widespread usability.
Pros and Cons of a Tailored Approach
A tailored approach offers the advantage of customized solutions that directly address specific needs, leading to higher efficiency and better user satisfaction compared to the lowest common denominator approach. It allows for flexibility and innovation, adapting to diverse requirements, but it can be resource-intensive and harder to scale. The complexity and cost of implementation may outweigh benefits in environments where broad applicability and simplicity are prioritized.
Advantages and Drawbacks of the Lowest Common Denominator Strategy
The lowest common denominator approach simplifies content to appeal broadly, increasing accessibility but often sacrificing depth and nuance essential for engaged audiences. This strategy reduces complexity, making messages more digestible but risks alienating specialized or sophisticated users by ignoring their specific needs and preferences. While cost-effective and easy to implement, it can lead to generic outcomes lacking differentiation, ultimately diminishing brand loyalty and user satisfaction.
Impact on Customer Experience
A tailored approach enhances customer experience by addressing individual needs, preferences, and behaviors, leading to higher satisfaction and loyalty. In contrast, the lowest common denominator approach often results in generic solutions that may fail to engage or satisfy diverse customer segments, reducing overall engagement and retention rates. Personalized interactions driven by data analytics and customer insights create meaningful experiences that foster long-term relationships and brand advocacy.
Efficiency and Scalability: A Comparative Analysis
The tailored approach enhances efficiency by customizing solutions to specific requirements, reducing waste and boosting performance in targeted areas. In contrast, the lowest common denominator approach prioritizes broad applicability, often sacrificing optimal performance to maintain scalability across varied contexts. While tailored strategies excel in optimizing resource use for defined environments, the lowest common denominator method supports rapid expansion but may lead to inefficiencies due to generic implementations.
Industry Applications and Case Studies
The tailored approach in industry applications customizes solutions to specific client needs, enhancing performance and customer satisfaction in sectors like healthcare, finance, and manufacturing. Case studies reveal companies using tailored strategies achieve higher ROI and operational efficiency compared to those adopting lowest common denominator approaches, which prioritize broad usability but often sacrifice user engagement and effectiveness. For example, customized software in banking enabled precise risk management, while generalized platforms resulted in suboptimal decision-making and increased error rates.
Cost Implications of Each Approach
A tailored approach typically incurs higher upfront costs due to customization, specialized resources, and thorough analysis, but it enhances efficiency and long-term savings through targeted solutions. The lowest common denominator approach reduces initial expenses by applying generic, broad strategies that require minimal adaptation, yet it often leads to increased operational costs and inefficiencies over time due to lack of specificity. Evaluating total cost of ownership reveals that investing in tailored solutions can provide superior cost-effectiveness compared to the short-term savings of the lowest common denominator method.
When to Choose Tailored Over Lowest Common Denominator
Choose a tailored approach when targeting diverse customer segments with specific needs, as it enhances user experience and drives higher engagement through personalization. This method is ideal for markets with varied preferences, complex products, or when brand differentiation is crucial. In contrast, the lowest common denominator approach suits homogeneous audiences or budget constraints but often sacrifices relevance and effectiveness.
Future Trends in Customization vs. Standardization
Future trends in customization emphasize AI-driven tailored approaches that deliver personalized experiences based on real-time data and consumer behavior. Standardization continues to support scalability and cost-efficiency through lowest common denominator strategies, particularly in mass markets and global supply chains. Hybrid models integrating both customization and standardization offer optimized balance between personalization and operational efficiency.
Tailored approach Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com