Opportunity cost represents the value of the next best alternative that you forego when making a decision. Understanding this concept is crucial for optimizing resource allocation and maximizing potential benefits in both personal and business contexts. Explore the rest of the article to learn how opportunity cost impacts your daily choices and financial planning.
Table of Comparison
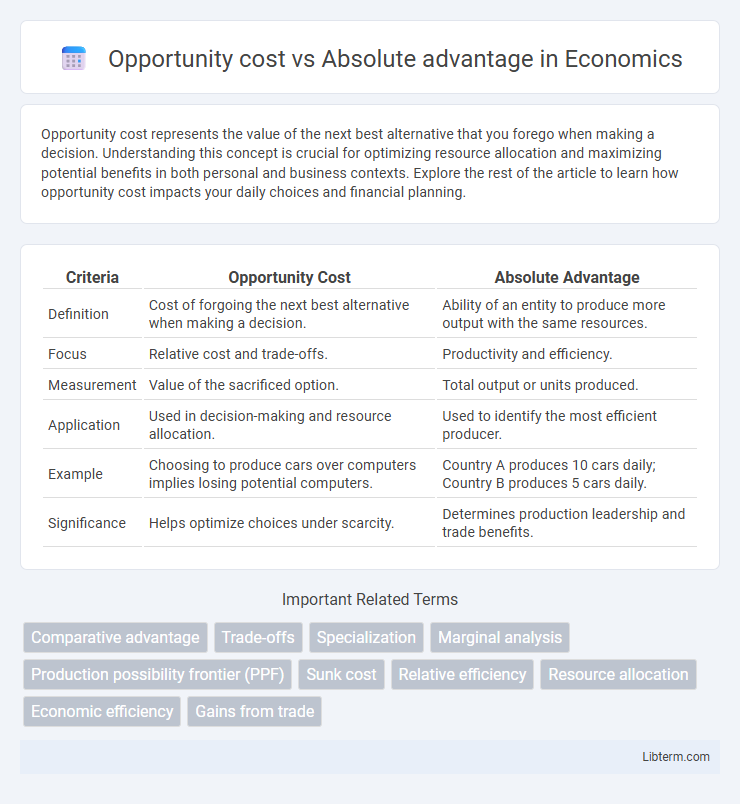
| Criteria | Opportunity Cost | Absolute Advantage |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Cost of forgoing the next best alternative when making a decision. | Ability of an entity to produce more output with the same resources. |
| Focus | Relative cost and trade-offs. | Productivity and efficiency. |
| Measurement | Value of the sacrificed option. | Total output or units produced. |
| Application | Used in decision-making and resource allocation. | Used to identify the most efficient producer. |
| Example | Choosing to produce cars over computers implies losing potential computers. | Country A produces 10 cars daily; Country B produces 5 cars daily. |
| Significance | Helps optimize choices under scarcity. | Determines production leadership and trade benefits. |
Understanding Opportunity Cost
Opportunity cost represents the value of the next best alternative foregone when choosing a specific action, crucial for decision-making in economics. Absolute advantage measures the ability of an individual, firm, or country to produce more of a good or service using the same amount of resources. Understanding opportunity cost highlights the true trade-offs involved, guiding efficient resource allocation beyond merely comparing absolute production capabilities.
Defining Absolute Advantage
Absolute advantage refers to the ability of an entity, such as a country or individual, to produce a good or service more efficiently than others using the same amount of resources. It highlights the productivity differences by measuring who can produce the maximum output with given inputs. Unlike opportunity cost, which considers what is sacrificed to produce one good over another, absolute advantage strictly focuses on overall efficiency in production.
Key Differences Between Opportunity Cost and Absolute Advantage
Opportunity cost measures the value of the next best alternative foregone when making a decision, highlighting trade-offs in resource allocation. Absolute advantage refers to the ability of a party to produce more of a good or service with the same amount of resources compared to another. The key difference lies in opportunity cost emphasizing efficiency and choice, while absolute advantage focuses on overall productivity levels.
The Role of Scarcity in Decision Making
Scarcity forces individuals and nations to evaluate opportunity costs when choosing between alternatives, as resources are limited and must be allocated efficiently. Absolute advantage focuses on the ability to produce more output with the same resources, but opportunity cost emphasizes what is sacrificed in producing one good over another. The interplay between scarcity and these economic concepts drives decision-making processes to maximize overall benefits and minimize wasted resources.
How Opportunity Cost Influences Choices
Opportunity cost influences choices by requiring individuals and businesses to evaluate the potential benefits of alternative options before making decisions. Unlike absolute advantage, which focuses on producing more output with the same resources, opportunity cost emphasizes the value of the next best alternative foregone. Understanding opportunity cost helps in resource allocation by highlighting trade-offs and ensuring that decision-makers prioritize options with the highest returns or lowest sacrifices.
Measuring Absolute Advantage in Production
Measuring absolute advantage in production involves comparing the total output of goods or services that one producer can create using the same amount of resources as another. This metric highlights the efficiency of a producer by quantifying who can produce more units with identical inputs. Unlike opportunity cost, absolute advantage focuses solely on total productivity rather than trade-offs or alternative uses of resources.
Practical Examples: Opportunity Cost vs Absolute Advantage
Farmers deciding between growing wheat or corn face opportunity cost by sacrificing the yield of one crop to produce another, while absolute advantage is seen when a farmer produces more wheat per acre than neighbors using the same resources. A factory with machinery that assembles 100 cars daily has an absolute advantage over a smaller plant assembling 50 cars but evaluating opportunity cost involves assessing what is forgone, such as producing trucks instead of cars. Understanding both concepts helps businesses and individuals optimize resource allocation by measuring productivity (absolute advantage) and trade-offs (opportunity cost) in practical scenarios.
Importance in International Trade
Opportunity cost measures the potential benefits lost when choosing one option over another, guiding countries to specialize in goods with the lowest opportunity costs. Absolute advantage refers to a country's ability to produce goods more efficiently than others, but international trade benefits more from comparative advantage based on opportunity costs. Understanding these concepts is crucial for maximizing global resource allocation, increasing overall trade efficiency, and boosting economic growth.
Limitations of Both Concepts
Opportunity cost oversimplifies decision-making by assuming constant trade-offs and ignoring external factors like market dynamics or resource scarcity, limiting its application in complex economic environments. Absolute advantage fails to address the benefits of specialization and trade when one party is more efficient in producing all goods, overlooking potential gains from comparative advantage. Both concepts provide foundational insights but lack comprehensive scope for real-world economic complexity and strategic decision-making.
Maximizing Benefits Through Strategic Decision Making
Maximizing benefits through strategic decision making involves assessing opportunity cost to determine the most efficient allocation of resources, ensuring choices yield the highest possible returns. Absolute advantage highlights the ability to produce goods or services using fewer inputs than competitors, but incorporating opportunity cost provides a deeper understanding of trade-offs and potential gains. Firms and individuals optimize outcomes by balancing absolute advantage with opportunity cost analysis, enabling informed decisions that enhance productivity and economic efficiency.
Opportunity cost Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com