Effective financial supervision ensures the stability and integrity of financial institutions by enforcing regulations and monitoring compliance. It mitigates risks such as fraud and market failures, protecting both investors and the broader economy. Discover how robust financial supervision can safeguard Your assets and contribute to economic resilience by exploring the full article.
Table of Comparison
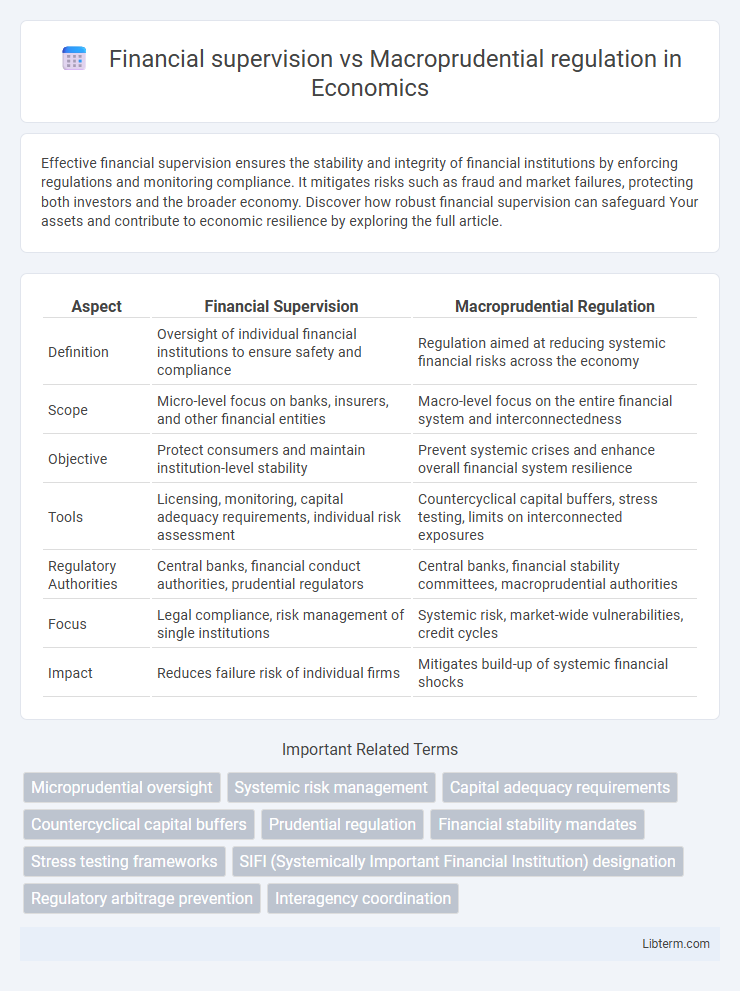
| Aspect | Financial Supervision | Macroprudential Regulation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Oversight of individual financial institutions to ensure safety and compliance | Regulation aimed at reducing systemic financial risks across the economy |
| Scope | Micro-level focus on banks, insurers, and other financial entities | Macro-level focus on the entire financial system and interconnectedness |
| Objective | Protect consumers and maintain institution-level stability | Prevent systemic crises and enhance overall financial system resilience |
| Tools | Licensing, monitoring, capital adequacy requirements, individual risk assessment | Countercyclical capital buffers, stress testing, limits on interconnected exposures |
| Regulatory Authorities | Central banks, financial conduct authorities, prudential regulators | Central banks, financial stability committees, macroprudential authorities |
| Focus | Legal compliance, risk management of single institutions | Systemic risk, market-wide vulnerabilities, credit cycles |
| Impact | Reduces failure risk of individual firms | Mitigates build-up of systemic financial shocks |
Introduction to Financial Supervision and Macroprudential Regulation
Financial supervision involves the oversight of individual financial institutions to ensure their safety, soundness, and compliance with regulatory requirements, focusing on the stability of banks, insurance companies, and other financial entities. Macroprudential regulation targets systemic risks by monitoring and mitigating vulnerabilities within the entire financial system, aiming to prevent widespread crises and enhance overall economic resilience. Both frameworks are essential for maintaining financial stability, with financial supervision concentrating on micro-level risks and macroprudential regulation addressing broader, interconnected risks.
Definitions: Financial Supervision vs Macroprudential Regulation
Financial supervision refers to the ongoing oversight of individual financial institutions to ensure their safety, soundness, and compliance with regulatory standards. Macroprudential regulation, by contrast, focuses on monitoring and mitigating systemic risks that threaten the stability of the entire financial system. While financial supervision targets micro-level risks within firms, macroprudential regulation addresses broader vulnerabilities affecting market-wide resilience.
Objectives and Scopes: Comparing the Two Approaches
Financial supervision primarily aims to ensure the safety and soundness of individual financial institutions by monitoring their compliance with regulatory standards and risk management practices. Macroprudential regulation focuses on maintaining the stability of the entire financial system by addressing systemic risks and preventing widespread financial crises through tools targeting interconnectedness and procyclicality. While financial supervision concentrates on micro-level risks within firms, macroprudential regulation adopts a broader scope, emphasizing the resilience of the financial sector as a whole across economic cycles.
Key Institutions Involved in Both Frameworks
The key institutions involved in financial supervision typically include central banks, financial regulatory authorities, and securities commissions that oversee individual financial entities' safety and soundness. In macroprudential regulation, the focus shifts to systemic risk oversight, involving coordination among central banks, financial stability boards, and treasury departments to monitor and mitigate risks across the entire financial system. Both frameworks often require collaboration between institutions like the International Monetary Fund (IMF) and the Bank for International Settlements (BIS) to ensure comprehensive regulatory coverage.
Tools and Instruments: Microprudential vs Macroprudential
Microprudential tools focus on the soundness of individual financial institutions through capital requirements, stress testing, and supervisory reviews to prevent insolvency and protect depositors. Macroprudential instruments target systemic risks by addressing interconnectedness and procyclicality via countercyclical capital buffers, sectoral capital requirements, and loan-to-value ratio limits to safeguard overall financial stability. While microprudential regulation aims at institution-specific resilience, macroprudential frameworks employ broad-based measures to mitigate risks spanning the entire financial system.
Role in Preventing Systemic Risks
Financial supervision plays a critical role in monitoring individual financial institutions to ensure their safety, soundness, and compliance with regulations, thereby reducing the risk of failures that could trigger systemic crises. Macroprudential regulation focuses on the stability of the entire financial system by identifying and mitigating systemic risks arising from interconnectedness, market imbalances, and pro-cyclicality. Together, these frameworks work to prevent financial contagion and maintain economic stability by addressing risks at both microprudential and macroprudential levels.
Case Studies: Effectiveness in Past Financial Crises
Financial supervision primarily targets individual financial institutions to ensure their soundness and compliance, while macroprudential regulation addresses systemic risks affecting the entire financial system. Case studies from the 2008 global financial crisis reveal that countries with strong macroprudential frameworks, such as the UK and South Korea, experienced faster recovery and reduced systemic vulnerabilities compared to those relying solely on microprudential supervision. Data from the European debt crisis further highlight that integrated macroprudential tools, including countercyclical capital buffers, effectively mitigated credit booms and asset bubbles, reducing the severity of financial disruptions.
Challenges and Limitations of Each Approach
Financial supervision faces challenges in detecting systemic risks due to its micro-level focus on individual institutions, often leading to regulatory blind spots in interconnected markets. Macroprudential regulation struggles with the timely identification of emerging threats because of data limitations and the complexity of modeling entire financial systems, which can delay intervention measures. Both approaches encounter limitations in balancing market stability with financial innovation, risking either excessive restrictions or insufficient oversight.
Complementarity and Coordination between Frameworks
Financial supervision focuses on monitoring individual financial institutions to ensure their safety and soundness, while macroprudential regulation targets systemic risks affecting the entire financial system. Effective complementarity and coordination between these frameworks enhance financial stability by addressing both micro-level vulnerabilities and broader economic shocks simultaneously. Integrated information sharing and regulatory collaboration are essential to prevent regulatory gaps and promote a resilient financial environment.
Future Trends in Financial Supervision and Macroprudential Regulation
Future trends in financial supervision and macroprudential regulation emphasize the integration of advanced technologies such as artificial intelligence and machine learning to enhance real-time risk monitoring and predictive analytics. Regulatory frameworks are evolving to address emerging risks from digital assets, climate-related financial risks, and interconnected global markets, promoting resilience and systemic stability. Enhanced cooperation among international regulatory bodies and the adoption of dynamic, forward-looking policies are set to improve coordination and efficacy in managing systemic financial vulnerabilities.
Financial supervision Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com