The strike price is the predetermined price at which an option holder can buy or sell the underlying asset. Understanding how the strike price affects your options strategy is crucial for maximizing profits and managing risks. Explore the full article to learn how to choose the best strike price for your investments.
Table of Comparison
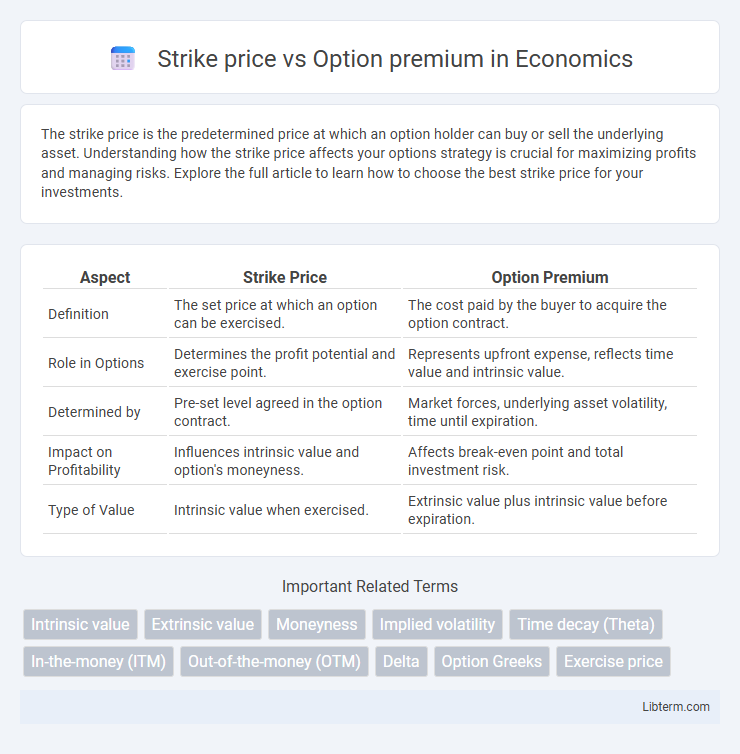
| Aspect | Strike Price | Option Premium |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | The set price at which an option can be exercised. | The cost paid by the buyer to acquire the option contract. |
| Role in Options | Determines the profit potential and exercise point. | Represents upfront expense, reflects time value and intrinsic value. |
| Determined by | Pre-set level agreed in the option contract. | Market forces, underlying asset volatility, time until expiration. |
| Impact on Profitability | Influences intrinsic value and option's moneyness. | Affects break-even point and total investment risk. |
| Type of Value | Intrinsic value when exercised. | Extrinsic value plus intrinsic value before expiration. |
Understanding Strike Price in Options
The strike price in options represents the predetermined price at which the underlying asset can be bought or sold when exercising the option. It directly influences the option's intrinsic value and ultimately impacts the option premium, which is the price paid by the buyer to acquire the option contract. Understanding the relationship between the strike price and the option premium is essential for effective options trading and risk management.
What Is an Option Premium?
An option premium is the price paid by the buyer to the seller for acquiring the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell an underlying asset at a specified strike price within a predetermined time frame. The premium reflects intrinsic value, which depends on the difference between the underlying asset's current price and the strike price, as well as time value influenced by volatility and time until expiration. Factors like interest rates, dividends, and market demand also affect the option premium, making it a critical component in options trading strategies.
Core Differences: Strike Price vs. Option Premium
The strike price is the predetermined price at which the underlying asset can be bought or sold when exercising an option, directly influencing the option's intrinsic value. The option premium is the total cost paid by the buyer to acquire the option contract, encompassing intrinsic value, time value, and market volatility. While the strike price determines the potential profitability threshold, the option premium reflects the upfront investment and market sentiment.
How Strike Price Influences Option Premium
The strike price directly impacts the option premium by determining the intrinsic value of the option, where options with strike prices closer to the current underlying asset price generally have higher premiums due to increased likelihood of profitability. In-the-money options command higher premiums because their strike price already favors exercise, while out-of-the-money options carry lower premiums reflecting lower immediate value and higher risk. The relationship between strike price and option premium is also influenced by factors like volatility and time to expiration, but strike price remains a primary determinant of the option's cost.
The Role of Intrinsic Value in Option Pricing
The strike price directly influences the intrinsic value of an option, which is the difference between the underlying asset's current price and the option's strike price when favorable to the holder. The option premium comprises both intrinsic value and time value, making intrinsic value a core component in determining the option's market price. Understanding how intrinsic value fluctuates with the strike price helps traders evaluate the true worth of an option and make informed pricing decisions.
Impact of Volatility on Strike Price and Premium
Volatility directly impacts the option premium, causing it to rise with increased market fluctuations due to greater uncertainty in the underlying asset's future price. The strike price remains fixed and does not change with volatility, but its relative attractiveness to buyers fluctuates as implied volatility affects the premium values of in-the-money, at-the-money, and out-of-the-money options differently. High volatility generally increases the time value component of the premium, reflecting the higher probability of the option finishing in-the-money despite an unchanged strike price.
Time Value and Its Effect on Premium
The strike price directly impacts the intrinsic value of an option, while the option premium consists of both intrinsic value and time value, which reflects the potential for the option to gain value before expiration. Time value decreases as the expiration date approaches, causing the option premium to erode, a phenomenon known as time decay or theta. Higher volatility and longer time to expiration increase the time value, thus raising the option premium despite the strike price remaining constant.
Choosing the Right Strike Price for Your Strategy
Selecting the right strike price is crucial for optimizing option trading strategies, as it directly influences the option premium and potential profitability. In-the-money strike prices carry higher premiums but offer greater intrinsic value, while out-of-the-money strikes have lower premiums with higher leverage and risk. Balancing strike price selection with market outlook, volatility, and risk tolerance ensures alignment with investment goals and maximizes returns.
Real-World Examples: Strike Price vs. Option Premium
In an Apple call option with a strike price of $150, if the option premium is $5, the buyer pays $500 per contract (100 shares) for the right to purchase Apple shares at $150 each. Real-world trading shows that if Apple's stock price rises to $160, the intrinsic value becomes $10 per share, making the option premium typically higher than the original $5, reflecting both intrinsic value and time value. Conversely, if the stock stays below $150, the premium may decrease as the option risks expiring worthless, illustrating how strike price and option premium interact dynamically in actual markets.
Key Takeaways for Options Traders
Strike price determines the fixed price at which an option can be exercised, directly influencing an option's intrinsic value and profitability. Option premium reflects the total cost to purchase the option, encompassing intrinsic value and time value driven by volatility, time until expiration, and underlying asset price movements. Understanding the interplay between strike price and option premium is crucial for options traders to optimize entry points, manage risk, and maximize potential returns.
Strike price Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com