Angel investing offers a unique opportunity to fund early-stage startups with high growth potential, often providing both capital and valuable mentorship. By carefully selecting promising entrepreneurs and innovative business models, angel investors can achieve significant financial returns while supporting innovation. Discover how you can navigate the risks and rewards of angel investing by reading the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
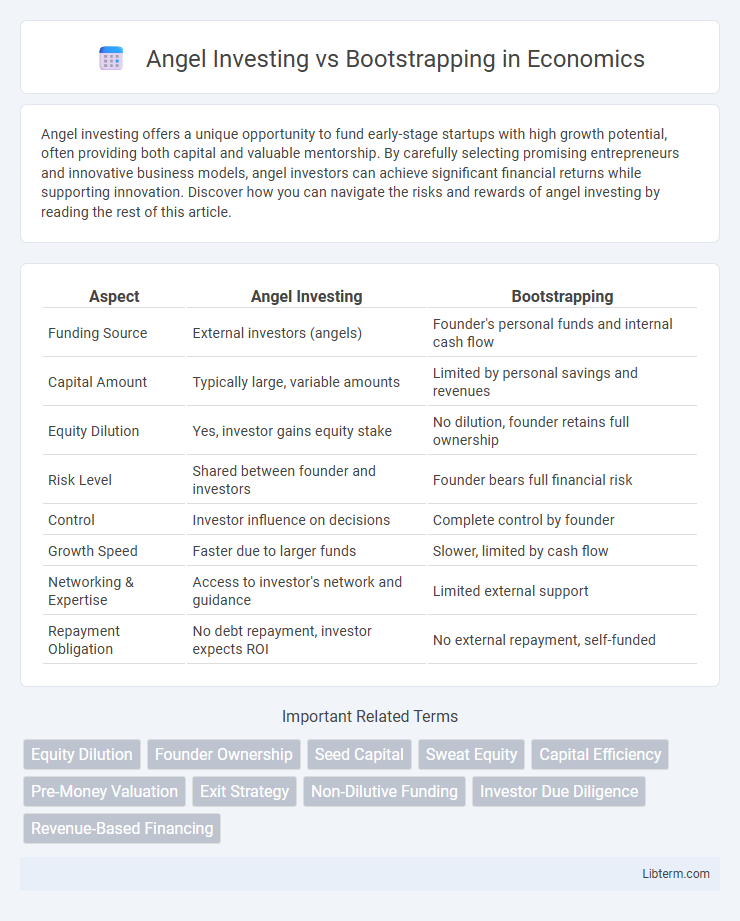
| Aspect | Angel Investing | Bootstrapping |
|---|---|---|
| Funding Source | External investors (angels) | Founder's personal funds and internal cash flow |
| Capital Amount | Typically large, variable amounts | Limited by personal savings and revenues |
| Equity Dilution | Yes, investor gains equity stake | No dilution, founder retains full ownership |
| Risk Level | Shared between founder and investors | Founder bears full financial risk |
| Control | Investor influence on decisions | Complete control by founder |
| Growth Speed | Faster due to larger funds | Slower, limited by cash flow |
| Networking & Expertise | Access to investor's network and guidance | Limited external support |
| Repayment Obligation | No debt repayment, investor expects ROI | No external repayment, self-funded |
Introduction to Angel Investing and Bootstrapping
Angel investing involves external investors providing capital to startups in exchange for equity, enabling faster growth and access to valuable mentorship networks. Bootstrapping relies on personal savings and operating revenues, fostering financial discipline and full ownership control but often limiting rapid expansion. Choosing between angel investing and bootstrapping depends on a startup's growth goals, risk tolerance, and funding needs.
Key Differences Between Angel Investing and Bootstrapping
Angel investing involves securing external funding from wealthy individuals who provide capital in exchange for equity, enabling faster growth and access to mentorship. Bootstrapping relies on personal savings and internal cash flow, maintaining full ownership but potentially limiting scalability and speed. Key differences include funding source, ownership dilution, growth pace, and risk distribution.
Pros and Cons of Angel Investing
Angel investing provides startups with significant capital infusion, valuable mentorship, and access to investor networks, accelerating growth and market entry. However, it often involves equity dilution, loss of some control, and pressure for rapid scaling to meet investor expectations. While angel investors bring strategic guidance, founders must balance their influence with maintaining the company's vision and autonomy.
Advantages and Challenges of Bootstrapping
Bootstrapping offers entrepreneurs full control over their business decisions and equity, allowing for organic growth without external pressure from investors. The primary challenge lies in limited financial resources, which can slow expansion and strain cash flow management. However, this approach encourages lean operations, innovation, and strong fiscal discipline essential for sustainable success.
Funding Timeline: Speed vs Control
Angel investing provides rapid access to capital, accelerating the funding timeline and enabling startups to scale quickly. Bootstrapping prioritizes full ownership and control but often results in slower growth due to limited financial resources. Entrepreneurs must balance the urgency of growth against the desire for independence when choosing between angel funding and self-financing.
Impact on Equity and Ownership
Angel investing provides entrepreneurs with capital in exchange for equity, resulting in ownership dilution but often accelerating growth and market entry. Bootstrapping maintains full ownership and control, preserving equity but potentially limiting resources and scaling speed. Founders must weigh the trade-off between retaining equity and accessing external funding to optimize long-term business value.
Influence on Business Growth Trajectory
Angel investing accelerates business growth by providing essential capital, strategic mentorship, and access to extensive networks, enabling startups to scale rapidly and seize market opportunities. Bootstrapping fosters organic growth through reinvested profits and operational discipline, often resulting in slower but more sustainable expansion with full founder control. Choosing between angel investing and bootstrapping significantly impacts a company's growth trajectory, risk tolerance, and long-term scalability.
Risk Management and Decision-Making
Angel investing offers access to significant capital and mentorship but involves higher risk due to investor expectations and equity dilution, requiring founders to carefully evaluate investor alignment and control preservation. Bootstrapping minimizes external risk by relying on personal resources, fostering disciplined cash flow management and gradual growth, which can enhance decision-making autonomy and responsiveness. Effective risk management hinges on balancing financial exposure with strategic flexibility, where angel investing accelerates scaling potential while bootstrapping ensures sustainable decision-making under constrained resources.
Suitability for Different Startup Types
Angel investing suits startups with high growth potential and scalable business models requiring significant early capital, such as tech or biotech ventures. Bootstrapping fits entrepreneurs aiming for steady growth with limited funding needs, often seen in service-based or niche market startups. Choosing depends on the startup's risk tolerance, capital requirements, and growth objectives.
Choosing the Right Path: Angel Investing or Bootstrapping?
Choosing between angel investing and bootstrapping hinges on the founder's growth goals and risk tolerance; angel investing provides access to critical capital and mentorship but may dilute ownership, whereas bootstrapping offers full control and organic growth at the cost of slower expansion and limited resources. Angel investors often bring industry expertise and networks, accelerating product development and market entry, while bootstrapping relies heavily on lean operations and customer-funded growth to maintain autonomy. Evaluating business scalability, funding needs, and long-term vision ensures an informed decision aligning with the startup's strategic objectives.
Angel Investing Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com