Fiscal policy involves government decisions on taxation and spending to influence the economy's growth, inflation, and employment levels. Effective implementation of fiscal policy can stabilize business cycles, promote sustainable development, and address economic inequalities. Explore this article to understand how your government's fiscal strategies impact your financial well-being and the broader economy.
Table of Comparison
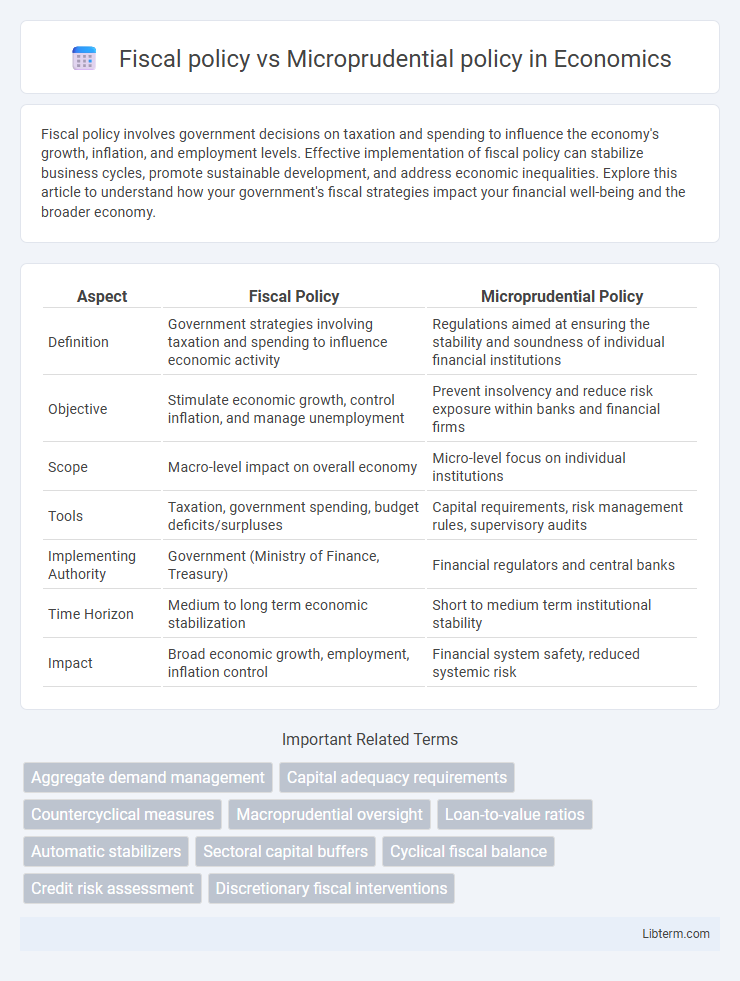
| Aspect | Fiscal Policy | Microprudential Policy |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Government strategies involving taxation and spending to influence economic activity | Regulations aimed at ensuring the stability and soundness of individual financial institutions |
| Objective | Stimulate economic growth, control inflation, and manage unemployment | Prevent insolvency and reduce risk exposure within banks and financial firms |
| Scope | Macro-level impact on overall economy | Micro-level focus on individual institutions |
| Tools | Taxation, government spending, budget deficits/surpluses | Capital requirements, risk management rules, supervisory audits |
| Implementing Authority | Government (Ministry of Finance, Treasury) | Financial regulators and central banks |
| Time Horizon | Medium to long term economic stabilization | Short to medium term institutional stability |
| Impact | Broad economic growth, employment, inflation control | Financial system safety, reduced systemic risk |
Introduction to Fiscal and Microprudential Policies
Fiscal policy involves government decisions on taxation and public spending to influence economic activity, aiming to stabilize growth and control inflation. Microprudential policy targets the stability of individual financial institutions through regulation and supervision, reducing the risk of bank failures and protecting depositors. Both policies serve distinct roles: fiscal policy drives overall economic demand, while microprudential policy ensures the resilience of the financial sector.
Defining Fiscal Policy: Scope and Objectives
Fiscal policy involves government decisions on taxation and public spending aimed at influencing economic activity, stabilizing the economy, and promoting growth. Its scope includes adjusting budget deficits or surpluses to control inflation, stimulate demand, and reduce unemployment, typically through targeted investments and social welfare programs. The primary objectives of fiscal policy are to achieve sustainable economic growth, equitable income distribution, and macroeconomic stability.
Microprudential Policy: Purpose and Mechanisms
Microprudential policy aims to ensure the stability and soundness of individual financial institutions through regulatory oversight and risk management frameworks. It employs mechanisms such as capital adequacy requirements, stress testing, and supervisory inspections to mitigate the risk of bank failures and protect depositors. This policy complements broader fiscal policy by targeting micro-level financial health rather than macroeconomic stabilization.
Key Instruments of Fiscal Policy
Fiscal policy primarily uses government spending, taxation, and borrowing as key instruments to influence economic activity, control inflation, and promote employment. These tools directly affect aggregate demand by adjusting public expenditure levels, modifying tax rates, and managing budget deficits or surpluses. Unlike microprudential policy, which targets financial institution stability through capital requirements and risk management, fiscal policy operates at the macroeconomic level to steer overall economic growth and stability.
Tools and Implementation of Microprudential Policy
Microprudential policy employs regulatory tools such as capital adequacy requirements, liquidity coverage ratios, and stress testing to ensure the soundness of individual financial institutions. Implementation involves continuous supervision, risk-based capital standards, and early intervention mechanisms to prevent insolvency and maintain financial stability. These tools function at the micro-level, contrasting with fiscal policy's broader use of government spending and taxation to influence overall economic conditions.
Impact on Economic Stability: A Comparative Overview
Fiscal policy influences economic stability by adjusting government spending and taxation to manage demand, control inflation, and promote growth, directly affecting employment and GDP levels. Microprudential policy targets the health of individual financial institutions by enforcing regulations that minimize risks and prevent failures, thereby enhancing the resilience of the banking sector and protecting depositors. Together, fiscal policy shapes macroeconomic conditions while microprudential policy ensures the soundness of financial intermediaries, both crucial for sustaining overall economic stability.
Fiscal Policy vs Microprudential Policy: Policy Interactions
Fiscal policy influences aggregate demand and economic stability through government spending and taxation, while microprudential policy targets the resilience and soundness of individual financial institutions to prevent systemic risk. Interactions occur as fiscal measures affect credit conditions, asset prices, and bank balance sheets, which microprudential tools monitor and regulate to manage financial vulnerabilities. Coordinated implementation enhances overall economic stability by aligning macroeconomic objectives with the financial sector's health.
Case Studies: Global Applications and Outcomes
Fiscal policy influences economic stability through government spending and taxation, as evidenced by Brazil's stimulus measures during the 2015 recession, which boosted consumption but increased public debt. Microprudential policy, targeting individual financial institutions' health, proved effective in the 2008 UK banking crisis, where enhanced capital requirements contained systemic risks. Comparative studies reveal fiscal interventions drive macroeconomic growth, while microprudential strategies ensure sectoral resilience, highlighting their complementary roles in global financial stability.
Challenges and Limitations of Each Policy
Fiscal policy faces challenges in timing and political constraints, often leading to delayed or insufficient responses to economic fluctuations, while its broad scope can dilute targeted effects on specific sectors. Microprudential policy struggles with limitations in identifying and mitigating risks at the institutional level due to complexity in financial products and interconnections. Both policies encounter difficulties in adapting to rapidly changing economic environments and global financial integration, which can undermine their effectiveness and coordination.
Future Directions: Integrating Fiscal and Microprudential Policies
Future directions in economic governance emphasize the integration of fiscal policy and microprudential policy to enhance financial stability and macroeconomic resilience. Coordinated frameworks can optimize resource allocation, manage systemic risks, and support sustainable economic growth by aligning government spending with regulatory oversight of financial institutions. Emerging approaches include leveraging data analytics and real-time monitoring to dynamically adjust fiscal measures and microprudential regulations in response to evolving economic conditions.
Fiscal policy Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com