Forward guidance is a monetary policy tool used by central banks to communicate the expected path of interest rates and economic conditions. This strategy aims to influence financial decisions by providing clarity on future policy moves, helping to stabilize markets and guide investor expectations. Discover how forward guidance impacts your financial planning and economic outlook in the detailed article ahead.
Table of Comparison
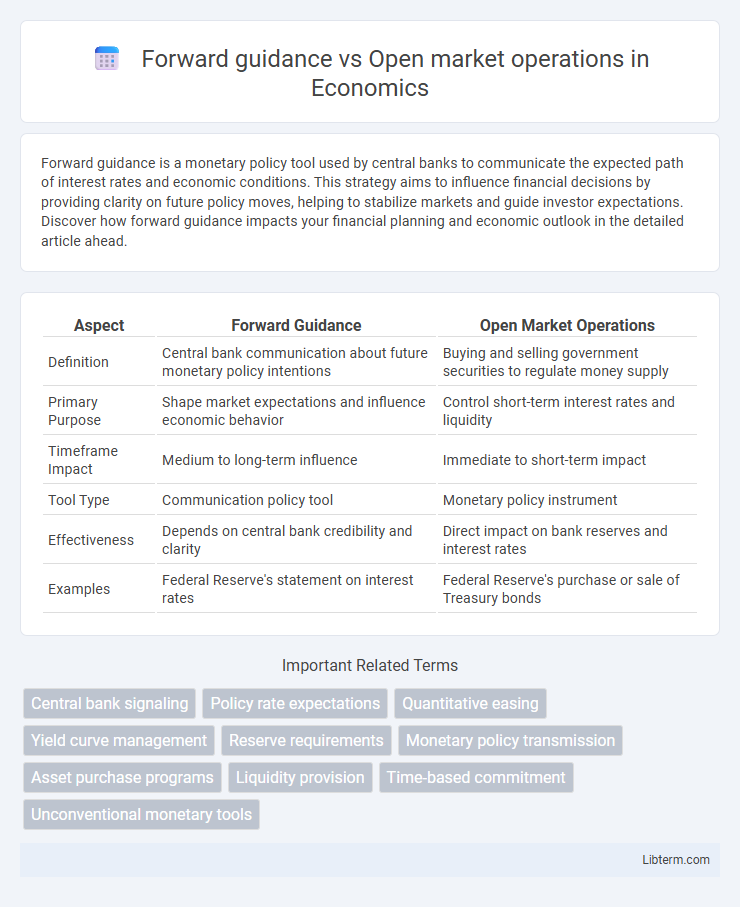
| Aspect | Forward Guidance | Open Market Operations |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Central bank communication about future monetary policy intentions | Buying and selling government securities to regulate money supply |
| Primary Purpose | Shape market expectations and influence economic behavior | Control short-term interest rates and liquidity |
| Timeframe Impact | Medium to long-term influence | Immediate to short-term impact |
| Tool Type | Communication policy tool | Monetary policy instrument |
| Effectiveness | Depends on central bank credibility and clarity | Direct impact on bank reserves and interest rates |
| Examples | Federal Reserve's statement on interest rates | Federal Reserve's purchase or sale of Treasury bonds |
Understanding Forward Guidance
Forward guidance involves central banks communicating future monetary policy intentions to influence market expectations and economic decisions, enhancing transparency and predictability. Unlike open market operations, which directly buy or sell government securities to regulate liquidity and short-term interest rates, forward guidance shapes economic behavior through informed anticipation of policy moves. Clear, credible forward guidance can effectively lower long-term interest rates and stimulate investment by reducing uncertainty about future monetary conditions.
Defining Open Market Operations
Open Market Operations (OMOs) refer to the buying and selling of government securities by a central bank to regulate the money supply and influence short-term interest rates. OMOs directly impact liquidity in the banking system, allowing the central bank to steer economic activity by controlling inflation and stabilizing currency. Unlike forward guidance, which communicates future policy intentions, OMOs enact immediate changes in monetary conditions through market transactions.
Key Objectives of Forward Guidance
Forward guidance primarily aims to influence market expectations about the future path of interest rates to steer economic behavior, enhance transparency, and improve monetary policy effectiveness. It helps manage inflation expectations and stabilize financial markets by signaling central bank intentions over an extended horizon. Unlike open market operations, which directly affect short-term liquidity and interest rates through asset purchases or sales, forward guidance shapes long-term economic outlook and investor confidence.
Main Goals of Open Market Operations
Open market operations primarily aim to regulate liquidity in the banking system by buying or selling government securities, influencing short-term interest rates and controlling inflation. These operations directly affect money supply and credit availability, stabilizing economic growth and promoting price stability. Forward guidance, in contrast, aims to shape market expectations about future monetary policy to influence long-term interest rates and economic behavior indirectly.
Transmission Mechanisms Compared
Forward guidance influences expectations about future interest rates, affecting long-term borrowing costs through anticipated policy paths, which in turn impact consumer spending and investment decisions. Open market operations directly alter short-term interest rates by buying or selling government securities, changing the liquidity in the banking system and influencing lending activity immediately. While forward guidance shapes economic behavior via communicated expectations and delayed effects, open market operations have more immediate impacts through changes in money supply and interbank rates.
Impact on Interest Rates and Expectations
Forward guidance influences interest rates primarily by shaping market expectations about the future path of central bank policy, which can lower long-term rates even before any policy action occurs. Open market operations directly affect short-term interest rates by adjusting the supply of reserves in the banking system, thereby influencing the federal funds rate and overall liquidity. The combination of these tools enables central banks to manage both immediate interest rates and market expectations to achieve monetary policy goals.
Flexibility and Limitations
Forward guidance offers central banks flexibility by influencing market expectations about future interest rates without immediate balance sheet changes, allowing communication-driven policy shaping. Open market operations directly adjust the money supply through buying or selling government securities, providing precise control but limited by market liquidity and operational constraints. Both tools have limitations: forward guidance depends on credible communication to be effective, while open market operations may be constrained during periods of low liquidity or when interest rates approach the zero lower bound.
Historical Examples and Case Studies
Forward guidance, exemplified by the Federal Reserve's clear communication during the 2008 financial crisis, influenced market expectations by signaling prolonged low interest rates to stabilize the economy. Open market operations, as demonstrated by the Bank of England's quantitative easing programs post-2009, directly injected liquidity into financial systems through asset purchases to support credit flow. Historical case studies reveal forward guidance shapes investor behavior via expectations, while open market operations provide immediate monetary stimulus through balance sheet adjustments.
Market Reactions to Policy Announcements
Market reactions to forward guidance typically involve changes in investor expectations and long-term interest rates, as clear communication shapes future monetary policy outlooks without immediate liquidity shifts. Open market operations prompt immediate adjustments in short-term interest rates and liquidity conditions by directly buying or selling government securities. While forward guidance influences market sentiment gradually, open market operations produce swift, tangible impacts on financial markets and bank reserves.
Choosing the Right Tool: Policy Considerations
Forward guidance shapes market expectations about future interest rates to influence economic behavior, while open market operations directly adjust the money supply through buying or selling government securities. Policymakers prioritize forward guidance when aiming to signal long-term monetary policy intentions amid low interest rates, whereas open market operations are preferred for immediate liquidity adjustments and controlling short-term interest rates. The choice depends on the economic context, monetary policy goals, and the effectiveness of influencing inflation and employment targets.
Forward guidance Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com