Pecuniary externalities occur when a market participant's actions indirectly affect others through changes in prices rather than physical external effects. These externalities influence resource allocation and market outcomes by altering demand or supply conditions, impacting Your costs or revenues. Explore the rest of the article to understand how pecuniary externalities shape economic efficiency and policy decisions.
Table of Comparison
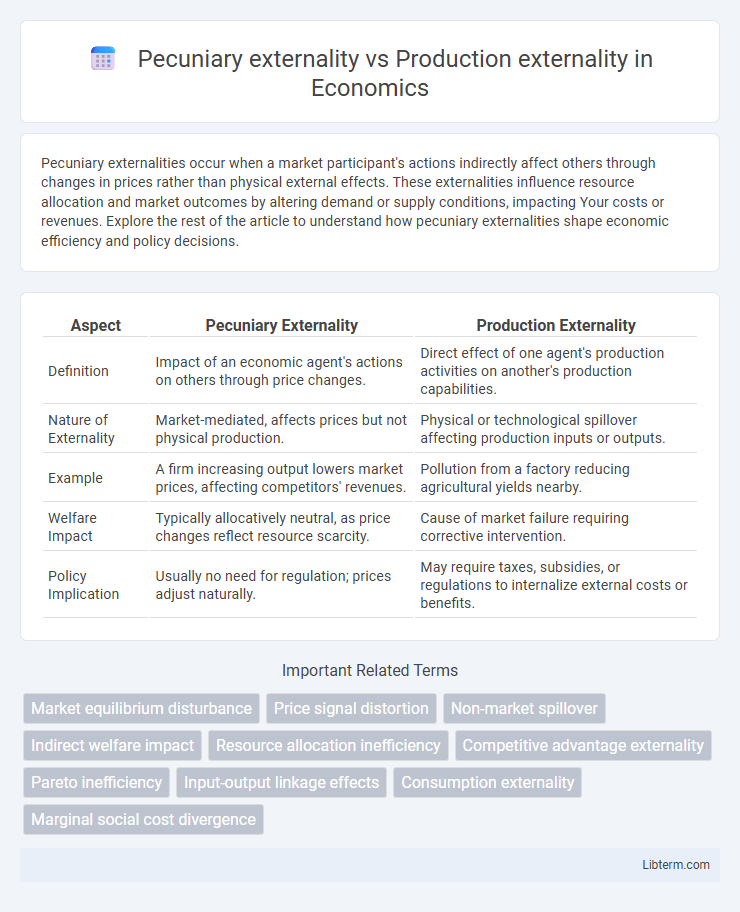
| Aspect | Pecuniary Externality | Production Externality |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Impact of an economic agent's actions on others through price changes. | Direct effect of one agent's production activities on another's production capabilities. |
| Nature of Externality | Market-mediated, affects prices but not physical production. | Physical or technological spillover affecting production inputs or outputs. |
| Example | A firm increasing output lowers market prices, affecting competitors' revenues. | Pollution from a factory reducing agricultural yields nearby. |
| Welfare Impact | Typically allocatively neutral, as price changes reflect resource scarcity. | Cause of market failure requiring corrective intervention. |
| Policy Implication | Usually no need for regulation; prices adjust naturally. | May require taxes, subsidies, or regulations to internalize external costs or benefits. |
Introduction to Externalities
Pecuniary externalities arise when a market participant's actions influence others through changes in prices rather than physical effects, affecting welfare indirectly. Production externalities occur when one firm's production directly impacts another's output or costs without involving price mechanisms. Understanding these distinctions is crucial in externalities analysis, as pecuniary effects often do not justify intervention, while production externalities can cause market failures requiring regulation.
Defining Pecuniary Externality
Pecuniary externality occurs when an economic activity affects others through changes in market prices rather than direct resource use or pollution, distinguishing it from production externalities that involve physical effects on production inputs or outputs. This type of externality manifests in price fluctuations influencing the welfare of third parties without altering overall resource efficiency. Understanding pecuniary externalities is essential for analyzing market dynamics where external impacts arise indirectly through price mechanisms.
Understanding Production Externality
Production externality occurs when a firm's production activities impose costs or benefits on other firms or individuals without compensation, affecting resource allocation and market efficiency. Unlike pecuniary externalities that arise through price changes in markets, production externalities directly impact physical production processes and environmental resources. Understanding production externalities is essential for designing effective policies such as taxes, subsidies, or regulations to internalize these external costs or benefits and improve social welfare.
Key Differences: Pecuniary vs Production Externality
Pecuniary externalities affect market prices without changing overall resource allocation, occurring when one agent's actions influence others solely through price shifts, such as a new business raising local rent costs. Production externalities directly impact the production process or resource use, causing changes in output or efficiency, like pollution reducing neighboring farms' crop yields. The key difference lies in pecuniary externalities being price-mediated and not leading to allocative inefficiency, whereas production externalities create real spillover effects that distort optimal resource distribution.
Economic Impact of Pecuniary Externalities
Pecuniary externalities occur when a market participant's actions influence prices, indirectly affecting others' economic well-being without changing resource allocation efficiency, unlike production externalities that directly impact production costs or outputs. The economic impact of pecuniary externalities is significant in altering wealth distribution and market welfare, often leading to income redistribution effects without causing deadweight loss. Understanding these externalities is crucial for policy design, as interventions targeting pecuniary effects may have limited efficiency gains compared to those addressing production externalities.
Real-World Examples of Production Externalities
Production externalities occur when a firm's production activities impose costs or benefits on others that are not reflected in market prices, such as a factory emitting pollution that harms nearby residents' health. Real-world examples include industrial facilities releasing toxic waste into rivers, negatively impacting communities and ecosystems, or beekeepers inadvertently boosting nearby crop yields through pollination, providing positive externalities. These externalities require government intervention through regulations or taxes to internalize the social costs or benefits and promote efficient resource allocation.
Market Outcomes and Efficiency
Pecuniary externalities affect market outcomes through price changes that influence supply and demand without causing direct welfare loss, thus maintaining overall market efficiency. Production externalities arise when a firm's output or production process generates spillover effects--either positive or negative--that impact third parties and lead to market failures by distorting resource allocation. Unlike pecuniary externalities, production externalities cause inefficiency because the market price does not reflect the true social cost or benefit of production, necessitating corrective interventions for optimal outcomes.
Policy Responses to Externalities
Pecuniary externalities occur when market prices reflect the costs or benefits imposed on others, often requiring limited direct government intervention since they are internalized through market adjustments. Production externalities involve costs or benefits not reflected in market prices, necessitating policy responses like Pigouvian taxes, subsidies, or regulations to correct market failures and achieve social efficiency. Effective policy design targets production externalities to address negative impacts such as pollution or positive spillovers like innovation, ensuring optimal resource allocation.
Measuring and Quantifying Externality Effects
Measuring pecuniary externalities involves assessing changes in market prices and their impact on economic agents, relying heavily on observed price fluctuations and demand-supply shifts in competitive markets. In contrast, quantifying production externalities requires estimating the direct non-market impacts of production activities on third parties, often using tools like cost-benefit analysis, shadow pricing, or environmental valuation techniques to capture external costs or benefits. Accurate quantification of both externality types depends on robust econometric models and empirical data to isolate market distortions and welfare changes effectively.
Conclusion: Implications for Economic Policy
Pecuniary externalities influence market prices without creating allocative inefficiency, thus generally requiring limited direct intervention from economic policy. Production externalities generate genuine welfare losses or gains by affecting third parties outside market transactions, necessitating corrective measures such as taxes, subsidies, or regulation to achieve optimal resource allocation. Policymakers should therefore prioritize targeting production externalities to enhance social welfare while recognizing that pecuniary externalities often reflect market adjustments rather than market failures.
Pecuniary externality Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com