Home bias refers to investors' tendency to favor domestic assets over foreign investments, often leading to a less diversified portfolio and increased risk exposure. This phenomenon can limit your potential gains by restricting access to global growth opportunities and reducing the benefits of international diversification. Explore the rest of this article to understand how overcoming home bias can enhance your investment strategy and improve returns.
Table of Comparison
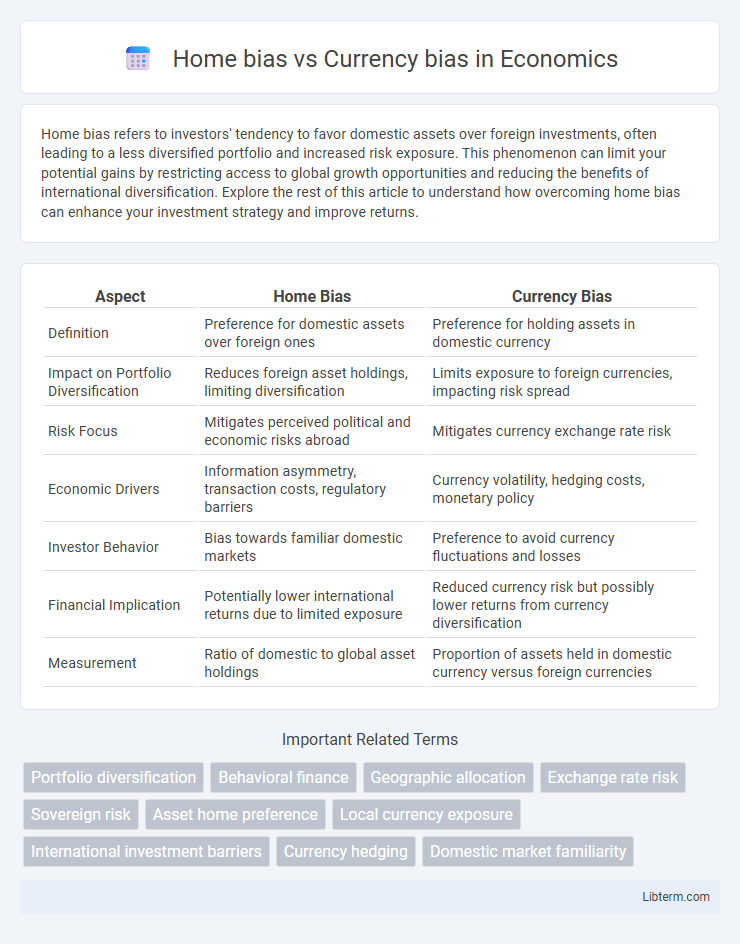
| Aspect | Home Bias | Currency Bias |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Preference for domestic assets over foreign ones | Preference for holding assets in domestic currency |
| Impact on Portfolio Diversification | Reduces foreign asset holdings, limiting diversification | Limits exposure to foreign currencies, impacting risk spread |
| Risk Focus | Mitigates perceived political and economic risks abroad | Mitigates currency exchange rate risk |
| Economic Drivers | Information asymmetry, transaction costs, regulatory barriers | Currency volatility, hedging costs, monetary policy |
| Investor Behavior | Bias towards familiar domestic markets | Preference to avoid currency fluctuations and losses |
| Financial Implication | Potentially lower international returns due to limited exposure | Reduced currency risk but possibly lower returns from currency diversification |
| Measurement | Ratio of domestic to global asset holdings | Proportion of assets held in domestic currency versus foreign currencies |
Understanding Home Bias: Definition and Causes
Home bias refers to investors' tendency to favor domestic assets over foreign ones, driven by familiarity, information asymmetry, and perceived lower risk. Causes include cultural affinity, regulatory environments, and currency risk concerns, which lead to portfolio concentration in local markets. This bias can limit diversification benefits and increase exposure to country-specific economic downturns.
Decoding Currency Bias: Key Concepts
Currency bias refers to the tendency of investors to prefer holding assets denominated in their domestic currency, often leading to undervaluation of foreign currency risks. This bias can distort portfolio diversification and affect international investment returns, as currency fluctuations introduce non-traditional risk elements. Understanding currency bias involves analyzing exchange rate volatility, hedging costs, and investor sentiment towards currency stability.
Home Bias vs Currency Bias: Core Differences
Home bias refers to investors' tendency to favor domestic assets over foreign ones, leading to under-diversification across international markets. Currency bias, on the other hand, involves preference or aversion to certain currencies, impacting exposure to exchange rate risk regardless of geographic investment location. The core difference lies in home bias's focus on geographic asset allocation, while currency bias centers on the selection and impact of currency exposure within a portfolio.
Psychological Factors Behind Home and Currency Bias
Psychological factors driving home bias include familiarity and perceived safety of domestic investments, where investors feel more confident with known companies and regulatory environments. Currency bias stems from a comfort with the native currency, leading to underestimation of currency risk and a preference for assets denominated in familiar money. Both biases reflect cognitive limitations and emotional attachments influencing portfolio decisions beyond rational risk-return assessments.
Impact of Home Bias on Investment Portfolios
Home bias causes investors to heavily favor domestic assets, reducing diversification and increasing exposure to country-specific risks. This concentration in local equities and bonds can lead to suboptimal risk-adjusted returns compared to globally diversified portfolios. Currency risk is less emphasized in home bias, potentially limiting gains achievable through foreign currency exposure and hedging strategies.
Currency Bias and Its Effect on Global Asset Allocation
Currency bias significantly impacts global asset allocation by causing investors to favor domestic currency holdings, leading to under-diversification in international portfolios. This bias often results in concentrated exposure to currency risk and missed opportunities for risk-adjusted returns in foreign assets. Studies reveal that overcoming currency bias enhances portfolio diversification and improves global investment outcomes by mitigating home currency depreciation effects.
Measuring the Extent of Home and Currency Bias
Measuring the extent of home bias involves analyzing the proportion of domestic versus foreign assets in an investor's portfolio, often using the Home Bias Index which compares actual holdings with global market capitalizations. Currency bias is assessed by examining the preference for holding assets denominated in the investor's domestic currency relative to foreign currencies, focusing on currency exposure and hedging behaviors. Both biases can be quantified through portfolio allocation data, exchange rate risk metrics, and analysis of investment flows to reveal preferences that deviate from optimal diversification.
Risks Associated with Home and Currency Biases
Home bias risk involves overinvestment in domestic markets, exposing investors to localized economic downturns, political instability, and sector-specific shocks, which reduces diversification benefits. Currency bias risk arises from excessive holdings in a single currency, leading to potential losses due to exchange rate volatility and unpredictable currency depreciation. Both biases can magnify portfolio risk by limiting global diversification and increasing susceptibility to country-specific and currency-specific shocks.
Strategies to Overcome Home and Currency Biases
Effective strategies to overcome home bias and currency bias include diversifying investments across multiple countries and currencies, utilizing international exchange-traded funds (ETFs), and employing currency-hedged investment vehicles to minimize foreign exchange risk. Investors should implement systematic portfolio rebalancing and leverage global asset allocation models that optimize risk-adjusted returns while reducing geographic and currency concentration. Incorporating behavioral finance education and analytic tools, such as currency overlay management and scenario analysis, further enhances decision-making to mitigate these biases.
Future Trends: Reducing Biases in Global Investing
Future trends in global investing show increased emphasis on reducing home bias and currency bias through advanced portfolio diversification techniques and the integration of sophisticated risk management tools. The rise of AI-driven analytics and blockchain-based platforms enables investors to access real-time data, enhancing cross-border investment decisions and currency exposure strategies. Regulatory enhancements promoting transparency and international cooperation further facilitate bias reduction, fostering more efficient and balanced global investment portfolios.
Home bias Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com