Economic growth drives improvements in living standards by increasing the production of goods and services, creating job opportunities, and boosting income levels. Sustainable growth hinges on factors such as technological innovation, investment in education, and sound economic policies. Explore the rest of the article to learn how economic growth impacts your daily life and what strategies can foster long-term prosperity.
Table of Comparison
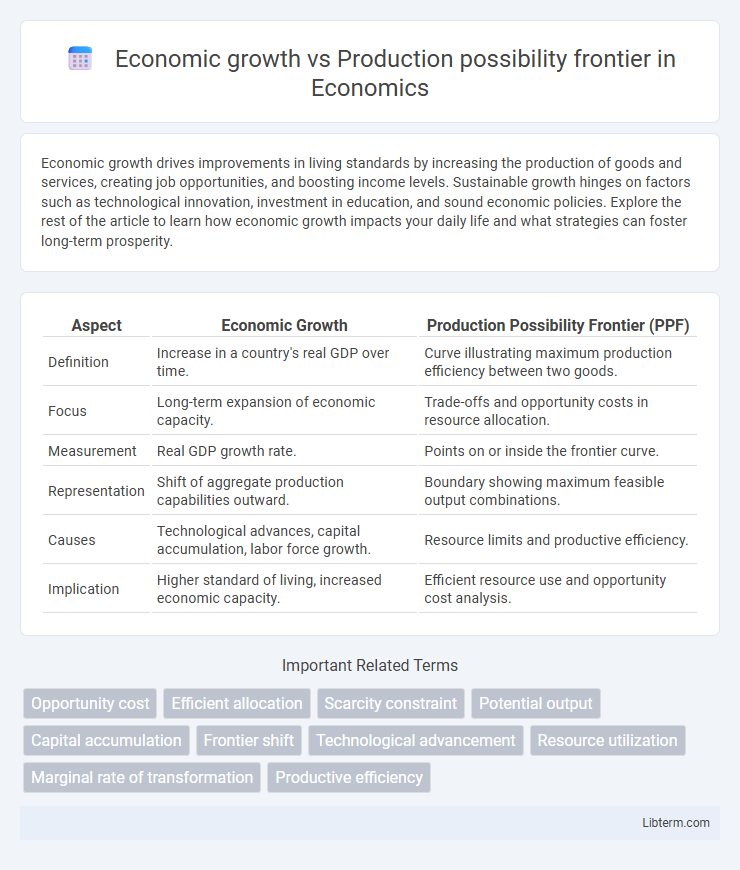
| Aspect | Economic Growth | Production Possibility Frontier (PPF) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Increase in a country's real GDP over time. | Curve illustrating maximum production efficiency between two goods. |
| Focus | Long-term expansion of economic capacity. | Trade-offs and opportunity costs in resource allocation. |
| Measurement | Real GDP growth rate. | Points on or inside the frontier curve. |
| Representation | Shift of aggregate production capabilities outward. | Boundary showing maximum feasible output combinations. |
| Causes | Technological advances, capital accumulation, labor force growth. | Resource limits and productive efficiency. |
| Implication | Higher standard of living, increased economic capacity. | Efficient resource use and opportunity cost analysis. |
Understanding Economic Growth: Key Concepts
Economic growth is illustrated by an outward shift of the Production Possibility Frontier (PPF), which represents the maximum output combinations an economy can achieve using available resources and technology. Factors such as capital accumulation, technological advancements, and labor force expansion contribute to this shift, indicating increased productive capacity. Understanding these key drivers helps analyze how economies can sustainably enhance output and improve overall living standards.
The Production Possibility Frontier (PPF) Explained
The Production Possibility Frontier (PPF) illustrates the maximum output combinations of two goods or services an economy can achieve when resources are fully and efficiently utilized. Economic growth shifts the PPF outward, indicating an increase in an economy's capacity to produce more goods and services due to improvements in factors like technology, labor, and capital. This expansion allows for higher production levels beyond the previous frontier, highlighting growth potential and resource optimization.
Relationship Between Economic Growth and the PPF
Economic growth causes the Production Possibility Frontier (PPF) to shift outward, representing an increase in an economy's maximum production capacity for goods and services. This outward shift results from improvements in factors such as technology, labor force, and capital resources. As the PPF expands, the economy can produce more, enabling higher standards of living and increased potential output.
Factors Influencing Economic Growth
Economic growth represents an increase in a country's output and is illustrated by the outward shift of the Production Possibility Frontier (PPF), reflecting enhanced capacity for goods and services. Key factors influencing economic growth include technological advancements, capital accumulation, labor force expansion, and improvements in human capital. Investment in infrastructure, education, and innovation drives the PPF outward, enabling higher production efficiency and sustained economic development.
Shifts in the Production Possibility Frontier
Economic growth is demonstrated by an outward shift of the Production Possibility Frontier (PPF), indicating an increase in an economy's capacity to produce goods and services. Factors causing shifts include technological advancements, accumulation of capital, improvements in labor quality, and discovery of new resources. These shifts signify enhanced productive efficiency and potential output, enabling higher standards of living.
Opportunity Cost and the PPF
Economic growth expands the Production Possibility Frontier (PPF) outward, indicating increased capacity to produce goods and services without raising opportunity costs. The opportunity cost on the PPF reflects the trade-offs between producing different goods, where producing more of one good requires sacrificing some quantity of another. As economic growth shifts the PPF outward, opportunity costs may change if resources become more or less efficient in producing certain goods.
Investment, Technology, and Economic Expansion
Investment boosts capital accumulation, shifting the production possibility frontier (PPF) outward by enabling higher output levels. Technological advancements enhance productive efficiency, allowing the economy to produce more goods with the same resources, thus expanding the PPF. These factors drive sustained economic growth and long-term economic expansion beyond existing production constraints.
Trade-offs Illustrated Through the PPF
The Production Possibility Frontier (PPF) illustrates economic growth by showing the maximum output combinations of two goods an economy can produce given its resources and technology. Trade-offs are demonstrated on the PPF as producing more of one good requires sacrificing some quantity of the other, highlighting opportunity costs. Economic growth expands the PPF outward, enabling higher production levels and shifting trade-off curves, reflecting increased resource efficiency or technological advancements.
Policy Implications: Promoting Sustainable Growth
Economic growth expands the production possibility frontier (PPF), enabling an economy to produce more goods and services over time. Policy implications include investing in technology, education, and infrastructure to shift the PPF outward sustainably while considering environmental constraints. Sustainable growth policies balance resource utilization with long-term capacity, ensuring economic development does not deplete natural capital or degrade ecosystems.
Comparing Economic Growth and Efficiency with the PPF
Economic growth is represented by an outward shift of the Production Possibility Frontier (PPF), indicating an increase in an economy's capacity to produce goods and services through factors like technological advancements or capital accumulation. Efficiency, depicted by points on the PPF curve, reflects optimal resource allocation where maximum output is achieved without waste. Comparing the two, economic growth expands the PPF frontier itself, while efficiency optimizes production within the existing PPF boundaries.
Economic growth Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com