Accurate forecasting helps businesses anticipate market trends and make informed decisions to minimize risks and maximize profits. By leveraging data analysis and predictive models, companies can align their strategies with future demands and opportunities. Discover how you can enhance your forecasting techniques by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
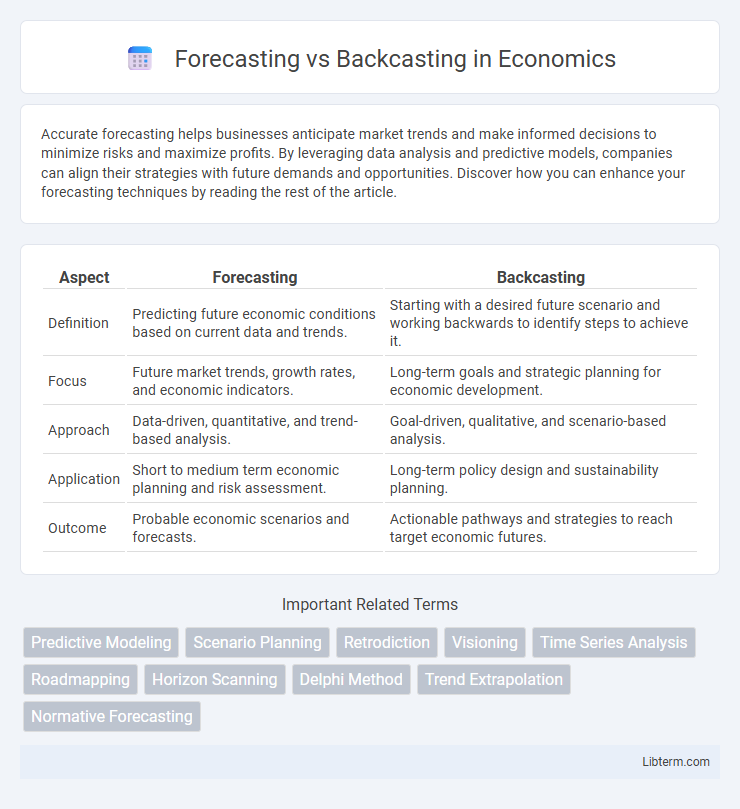
| Aspect | Forecasting | Backcasting |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Predicting future economic conditions based on current data and trends. | Starting with a desired future scenario and working backwards to identify steps to achieve it. |
| Focus | Future market trends, growth rates, and economic indicators. | Long-term goals and strategic planning for economic development. |
| Approach | Data-driven, quantitative, and trend-based analysis. | Goal-driven, qualitative, and scenario-based analysis. |
| Application | Short to medium term economic planning and risk assessment. | Long-term policy design and sustainability planning. |
| Outcome | Probable economic scenarios and forecasts. | Actionable pathways and strategies to reach target economic futures. |
Introduction to Forecasting and Backcasting
Forecasting uses historical data and trend analysis to predict future outcomes, enabling businesses to anticipate market changes and make informed decisions. Backcasting starts with defining a desirable future and works backward to identify necessary steps and policies to achieve that vision. Both methods are essential for strategic planning, with forecasting focusing on probable futures and backcasting emphasizing goal-oriented pathways.
Defining Forecasting: Concepts and Applications
Forecasting involves predicting future trends and outcomes based on historical data and statistical models, enabling businesses and policymakers to make informed decisions. Common applications include sales projections, financial planning, and demand forecasting, which help optimize resource allocation and mitigate risks. Advanced forecasting techniques utilize machine learning algorithms and time-series analysis to improve accuracy across various industries.
Understanding Backcasting: Principles and Uses
Backcasting is a strategic planning method that starts with defining a desirable future and then works backward to identify policies and actions needed to achieve that future. It is widely used in sustainability and long-term urban planning to create pathways that align current decisions with future goals. This approach highlights the gap between present conditions and intended outcomes, enabling stakeholders to develop innovative solutions tailored to specific future scenarios.
Key Differences Between Forecasting and Backcasting
Forecasting projects future outcomes based on current trends and historical data, while backcasting starts with defining a desirable future and works backward to identify pathways to achieve that future. Forecasting relies heavily on quantitative models to predict probable scenarios, whereas backcasting emphasizes qualitative assessments and strategic planning for transformative change. The key difference lies in forecasting's focus on predicting what is likely to happen versus backcasting's focus on planning what should happen to reach a specific goal.
Advantages of Forecasting in Strategic Planning
Forecasting in strategic planning enables organizations to anticipate future trends by analyzing historical data and current market conditions, facilitating proactive decision-making. It enhances resource allocation efficiency and risk management by providing quantifiable predictions that guide long-term goals. Forecasting improves agility in responding to industry shifts, ensuring competitive advantage and sustained growth.
Benefits of Backcasting for Long-Term Vision
Backcasting enables organizations to establish a clear long-term vision by starting with desired future outcomes and working backward to identify necessary steps, reducing uncertainty in strategic planning. This approach fosters innovative solutions by encouraging consideration of transformative changes rather than incremental adjustments typical of forecasting. Backcasting benefits sustainability initiatives by aligning short-term actions with ambitious future goals, ensuring trajectory consistency over extended periods.
Methodologies Involved in Forecasting and Backcasting
Forecasting methodologies primarily involve trend analysis, time series modeling, and extrapolation techniques that use historical data to predict future outcomes, incorporating statistical tools like regression analysis and machine learning algorithms. Backcasting methodologies focus on defining desired future goals first and then working backward to identify the necessary steps, utilizing scenario planning, normative modeling, and participatory approaches to design strategic pathways. Both methods integrate quantitative data and qualitative insights but differ in their starting points and analytical frameworks for decision-making.
Common Challenges in Forecasting and Backcasting
Forecasting and backcasting both face challenges such as uncertainty in data accuracy and the difficulty of predicting complex system behaviors over time. In forecasting, limited historical data and volatile variables can lead to unreliable future projections. Backcasting struggles with setting realistic long-term goals and identifying actionable steps amid changing socio-economic and technological conditions.
Real-World Examples: Forecasting vs Backcasting
Forecasting predicts future outcomes based on current trends, such as weather forecasts using historical climate data and models to anticipate conditions. Backcasting starts with defining a desired future goal and works backward to identify steps needed to achieve it, exemplified by cities planning carbon neutrality by 2050, mapping policies required today. In energy planning, forecasting estimates future demand growth, while backcasting designs long-term sustainable energy systems aligned with decarbonization targets.
Choosing the Right Approach: Forecasting or Backcasting?
Choosing the right approach between forecasting and backcasting depends on your project's goals and time horizon. Forecasting uses historical data and trends to predict future outcomes, ideal for short- to medium-term planning in dynamic environments. Backcasting starts with defining a desired future state and works backward to identify necessary steps, making it effective for long-term sustainability and transformative change initiatives.
Forecasting Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com