Monetary policy shapes economic stability by controlling interest rates and money supply to influence inflation and employment levels. Central banks implement these strategies to manage economic growth and maintain price stability. Explore the rest of the article to understand how monetary policy impacts your financial well-being.
Table of Comparison
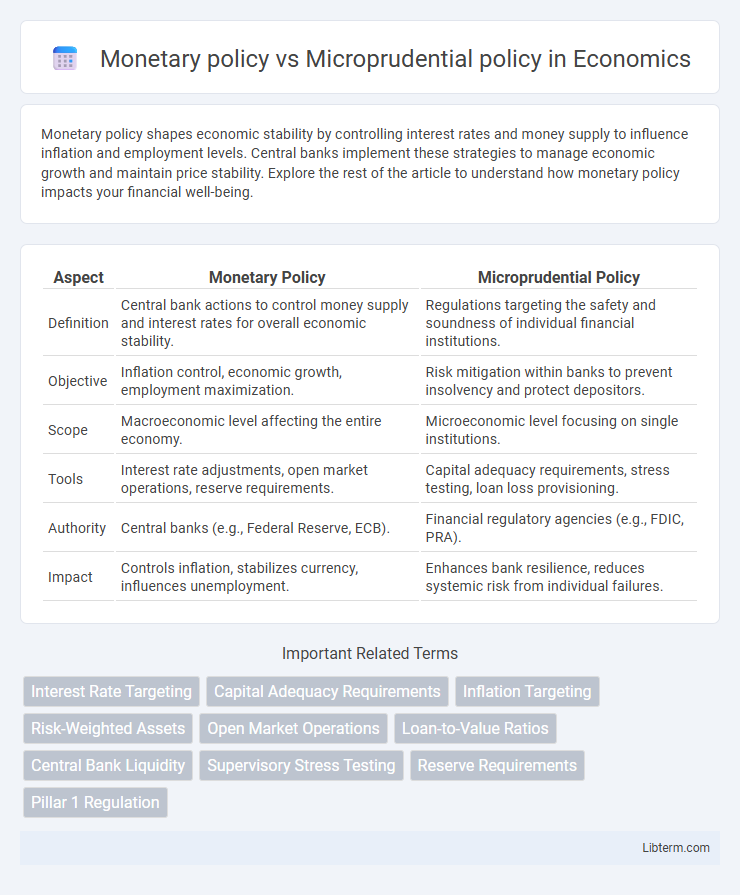
| Aspect | Monetary Policy | Microprudential Policy |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Central bank actions to control money supply and interest rates for overall economic stability. | Regulations targeting the safety and soundness of individual financial institutions. |
| Objective | Inflation control, economic growth, employment maximization. | Risk mitigation within banks to prevent insolvency and protect depositors. |
| Scope | Macroeconomic level affecting the entire economy. | Microeconomic level focusing on single institutions. |
| Tools | Interest rate adjustments, open market operations, reserve requirements. | Capital adequacy requirements, stress testing, loan loss provisioning. |
| Authority | Central banks (e.g., Federal Reserve, ECB). | Financial regulatory agencies (e.g., FDIC, PRA). |
| Impact | Controls inflation, stabilizes currency, influences unemployment. | Enhances bank resilience, reduces systemic risk from individual failures. |
Introduction to Monetary and Microprudential Policies
Monetary policy involves controlling the money supply and interest rates to achieve macroeconomic objectives such as inflation targeting, employment maximization, and economic growth. Microprudential policy focuses on the regulation and supervision of individual financial institutions to ensure their solvency and protect depositors, thereby maintaining financial stability at the micro-level. Together, these policies address broader economic stability by targeting systemic risks and institutional soundness.
Core Objectives: Stability vs. Soundness
Monetary policy primarily targets economic stability by managing inflation, controlling unemployment, and fostering sustainable growth through interest rate adjustments and money supply regulation. Microprudential policy focuses on the soundness of individual financial institutions by ensuring their resilience to shocks through risk assessment, capital requirements, and regulatory supervision. The core distinction lies in monetary policy's macroeconomic stability objective versus microprudential policy's goal of maintaining individual bank safety and preventing systemic risk.
Key Instruments and Tools Used
Monetary policy primarily utilizes interest rate adjustments, open market operations, and reserve requirements to influence inflation, economic growth, and employment levels. Microprudential policy employs capital adequacy ratios, liquidity coverage ratios, and stress testing to ensure individual financial institutions maintain solvency and manage risks effectively. Both policies use distinct instruments targeting macroeconomic stability and individual bank resilience, respectively, to promote overall financial system health.
Scope and Areas of Implementation
Monetary policy primarily targets macroeconomic objectives such as controlling inflation, managing employment levels, and stabilizing currency through tools like interest rates and open market operations. Microprudential policy focuses on the stability and soundness of individual financial institutions by enforcing capital adequacy, risk management, and regulatory compliance to prevent insolvency and protect depositors. While monetary policy operates at the broader economy level influencing aggregate demand, microprudential measures concentrate on mitigating risks within single entities to ensure overall financial system resilience.
Impact on Financial Institutions
Monetary policy primarily influences financial institutions by adjusting interest rates and liquidity, affecting lending, borrowing, and overall credit conditions. Microprudential policy targets the stability of individual financial institutions through capital requirements, risk management, and supervisory measures, reducing the likelihood of insolvency and promoting resilience. Both policies indirectly shape institutional behavior but differ in scale, with monetary policy affecting systemic liquidity and microprudential policy ensuring firm-level soundness.
Policy Transmission Mechanisms
Monetary policy transmits effects primarily through interest rate adjustments, influencing aggregate demand, inflation, and economic growth, while microprudential policy operates by enhancing individual financial institutions' resilience to shocks, thus maintaining systemic stability. The transmission mechanism of monetary policy relies on changes in credit availability, consumption, and investment, whereas microprudential policy uses regulatory tools such as capital requirements and stress testing to prevent bank failures and contain risk. Effective coordination between both policies ensures smooth financial conditions and mitigates the risk of financial crises.
Role in Economic Cycles
Monetary policy primarily influences economic cycles by adjusting interest rates and controlling money supply to stabilize inflation and promote growth. Microprudential policy targets the health of individual financial institutions to prevent systemic risks and maintain financial stability during economic fluctuations. Together, these policies manage economic cycles by balancing macroeconomic objectives with financial sector resilience.
Coordination and Conflicts Between Policies
Monetary policy, aimed at stabilizing inflation and promoting economic growth, often focuses on interest rates and money supply, while microprudential policy targets the stability of individual financial institutions through regulations and supervision. Coordination between these policies is crucial to prevent conflicts, such as monetary easing potentially increasing financial risks that microprudential measures must counterbalance. Misalignment can lead to regulatory arbitrage or financial vulnerabilities, highlighting the importance of integrated frameworks and communication between central banks and regulatory bodies to ensure overall financial stability.
Recent Trends and Case Studies
Monetary policy, driven by central banks like the Federal Reserve and European Central Bank, focuses on controlling inflation and stabilizing economic growth through interest rate adjustments and liquidity management, recently emphasizing accommodative stances post-COVID-19 to support recovery. Microprudential policy targets the resilience of individual financial institutions by enforcing capital adequacy and risk management standards, with recent trends highlighting stress testing and enhanced supervisory frameworks observed in case studies from the 2023 banking sector reforms in the UK and Germany. The interplay between these policies is evident in responses to financial instability, where coordinated efforts during episodes such as the 2022 regional bank failures in the US demonstrate evolving regulatory approaches to mitigate systemic risks while maintaining economic momentum.
Challenges and Future Outlook
Monetary policy faces the challenge of balancing inflation control with economic growth amid global uncertainties and evolving financial markets. Microprudential policy must adapt to complex risk assessments and enhance supervisory frameworks to prevent systemic risks while ensuring financial institutions remain resilient. The future outlook emphasizes integrating digital innovation and real-time data analytics to improve responsiveness and coordination between these policies for financial stability.
Monetary policy Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com