Understanding your consumption patterns helps identify areas where you can reduce waste and save money. Efficient use of resources not only benefits the environment but also improves your overall lifestyle. Explore the following insights to optimize your consumption habits effectively.
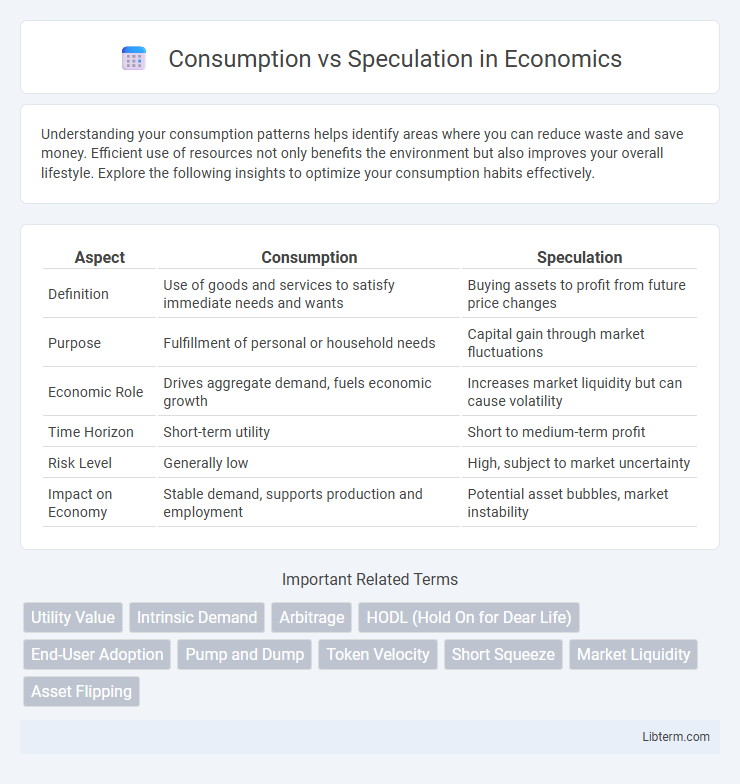
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Consumption | Speculation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Use of goods and services to satisfy immediate needs and wants | Buying assets to profit from future price changes |
| Purpose | Fulfillment of personal or household needs | Capital gain through market fluctuations |
| Economic Role | Drives aggregate demand, fuels economic growth | Increases market liquidity but can cause volatility |
| Time Horizon | Short-term utility | Short to medium-term profit |
| Risk Level | Generally low | High, subject to market uncertainty |
| Impact on Economy | Stable demand, supports production and employment | Potential asset bubbles, market instability |
Understanding Consumption and Speculation
Understanding consumption involves recognizing it as the use of goods and services for immediate satisfaction and fulfillment of needs or wants. Speculation refers to the act of purchasing assets primarily to profit from future price changes rather than for direct utility. Distinguishing consumption from speculation is crucial for analyzing economic behaviors and market dynamics.
Defining Key Differences
Consumption involves using goods and services to satisfy immediate needs or desires, driving demand in everyday markets. Speculation centers on purchasing assets primarily to profit from price fluctuations, often creating market volatility. Understanding these distinctions clarifies economic behaviors and their impact on resource allocation and financial stability.
Historical Perspectives on Consumption and Speculation
Historical perspectives reveal that consumption traditionally served as a means to satisfy immediate needs and enhance daily living, while speculation emerged as an economic strategy aimed at profiting from market fluctuations. In ancient and medieval economies, consumption drove production cycles, whereas speculation gained prominence with the development of financial markets during the Renaissance and early modern period. The evolution of speculative activities significantly influenced the growth of capitalism, shaping investment behaviors and economic policies throughout history.
Economic Impacts of Consumption
Consumption drives economic growth by increasing demand for goods and services, encouraging production, and generating employment opportunities. High consumer spending boosts businesses' revenues, which leads to investments in innovation and infrastructure. This multiplier effect stimulates GDP growth and stabilizes markets by supporting steady cash flow within the economy.
Speculation’s Role in Financial Markets
Speculation plays a critical role in financial markets by providing liquidity and enabling price discovery, which helps in the efficient allocation of resources. Speculators assume risks that others may avoid, thus stabilizing markets by smoothing out price volatility. Their activity influences asset prices based on expectations of future events rather than immediate consumption needs, differentiating speculative investment from consumption-driven behaviors.
Risks and Rewards: A Comparative Analysis
Consumption drives immediate utility by satisfying present needs but risks depletion of resources and diminished future value. Speculation aims for profit through market fluctuations, offering higher rewards at the cost of increased volatility and potential financial loss. Balancing consumption and speculation strategies requires assessing risk tolerance and time horizons to optimize overall economic outcomes.
Consumer Behavior vs. Investor Psychology
Consumer behavior centers on fulfilling immediate needs and desires, driven by emotional satisfaction, brand loyalty, and perceived value. Investor psychology involves risk assessment, market sentiment, and cognitive biases influencing decisions in speculative markets. While consumers prioritize utility and experience, investors weigh potential returns and losses, reflecting fundamentally different motivational frameworks.
Regulatory Approaches to Curb Speculation
Regulatory approaches to curb speculation often include implementing transaction taxes, position limits, and enhanced reporting requirements to increase market transparency and reduce excessive volatility. Authorities may enforce stricter capital requirements and leverage caps on speculative trading to minimize systemic risks and discourage destabilizing behaviors. These measures aim to distinguish between genuine consumption-driven transactions and speculative activities, promoting market stability and protecting consumers.
Long-Term Effects on Market Stability
Excessive speculation in financial markets often leads to increased volatility and price bubbles, undermining long-term market stability. In contrast, consumption-driven demand contributes to sustainable growth by reflecting genuine economic activity and support for productive assets. Markets dominated by consumption trends tend to experience steadier price movements, reduced systemic risk, and enhanced investor confidence over extended periods.
Striking a Balance: Toward Sustainable Growth
Striking a balance between consumption and speculation is crucial for sustainable economic growth as excessive consumption can deplete resources while unchecked speculation may lead to market volatility and financial instability. Sustainable growth requires integrating responsible consumer behavior with prudent investment strategies that promote long-term value creation rather than short-term gains. Policies that encourage savings, investments in productive assets, and consumer spending aligned with environmental and social goals support a resilient and balanced economy.
Consumption Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com