Efficient allocation ensures resources are distributed to maximize productivity and minimize waste, enhancing overall operational success. Understanding how to allocate your resources effectively can lead to reduced costs and improved project outcomes. Discover key strategies for efficient allocation by exploring the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
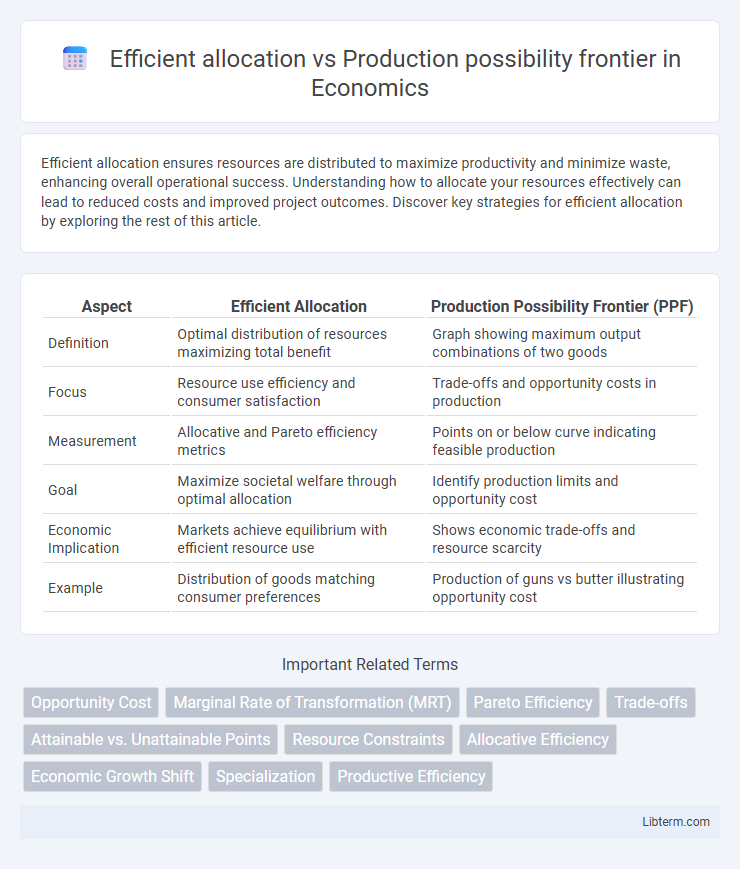
| Aspect | Efficient Allocation | Production Possibility Frontier (PPF) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Optimal distribution of resources maximizing total benefit | Graph showing maximum output combinations of two goods |
| Focus | Resource use efficiency and consumer satisfaction | Trade-offs and opportunity costs in production |
| Measurement | Allocative and Pareto efficiency metrics | Points on or below curve indicating feasible production |
| Goal | Maximize societal welfare through optimal allocation | Identify production limits and opportunity cost |
| Economic Implication | Markets achieve equilibrium with efficient resource use | Shows economic trade-offs and resource scarcity |
| Example | Distribution of goods matching consumer preferences | Production of guns vs butter illustrating opportunity cost |
Understanding Efficient Allocation in Economics
Efficient allocation in economics refers to the optimal distribution of resources where no individual can be made better off without making someone else worse off, known as Pareto efficiency. This concept is closely illustrated by points on the Production Possibility Frontier (PPF), which represents the maximum feasible output combinations of two goods given available resources and technology. Understanding efficient allocation involves recognizing that any point on the PPF curve reflects productive efficiency, but only those points where resources meet consumer preferences represent allocative efficiency.
The Fundamentals of the Production Possibility Frontier (PPF)
The Production Possibility Frontier (PPF) illustrates the maximum feasible output combinations of two goods that an economy can produce given fixed resources and technology, highlighting opportunity costs and trade-offs. Efficient allocation occurs when resources are fully utilized on the PPF curve, indicating no waste and optimal production levels. Points inside the PPF represent inefficiency, while points outside are unattainable with existing resources and technology.
Opportunity Cost Illustrated by the PPF
The Production Possibility Frontier (PPF) visually represents the trade-offs and opportunity costs involved in efficient allocation of resources between two goods. Points on the PPF curve illustrate maximum production capabilities, where any shift from one good to another incurs an opportunity cost quantified by the slope of the frontier. Efficient allocation occurs when resources are fully utilized on the PPF, highlighting the economic principle that producing more of one good results in the forgone output of another.
Efficient vs. Inefficient Use of Resources
Efficient allocation occurs when resources are distributed to maximize output on the production possibility frontier (PPF), representing full utilization without waste. Inefficient use of resources is demonstrated by points inside the PPF, indicating underutilization or misallocation that leads to lower production levels. The PPF visually distinguishes efficient production (on the curve) from inefficiency (below the curve), emphasizing optimal resource allocation's role in achieving maximum possible output combinations.
Attaining Productive Efficiency on the PPF Curve
Attaining productive efficiency on the Production Possibility Frontier (PPF) curve means resources are allocated efficiently to maximize output without waste, placing production points directly on the curve rather than inside it. Efficient allocation aligns with producing combinations of goods where increasing one good's output requires a proportional sacrifice in another, reflecting opportunity costs dictated by the PPF. Points on the PPF represent productive efficiency because all resources are fully employed, maximizing production potential given current technology and resource constraints.
Shifts in the PPF: Causes and Implications
Shifts in the Production Possibility Frontier (PPF) occur due to changes in resource availability, technological advancements, or improvements in labor productivity, directly impacting production capacity and economic growth. Efficient allocation entails utilizing these enhanced resources optimally to achieve maximum output combinations along the new frontier without waste. Recognizing these shifts helps policymakers and businesses adjust strategies to sustain efficiency and capitalize on expanded production possibilities.
Trade-Offs Between Goods: Navigating the Frontier
Efficient allocation occurs when resources are distributed along the Production Possibility Frontier (PPF), maximizing output without waste. The PPF illustrates trade-offs between goods, showing potential combinations of two products that an economy can produce given fixed resources and technology. Moving along the frontier highlights opportunity costs, where increasing production of one good reduces the output of the other, requiring careful decisions to balance priorities and optimize resource use.
The Role of Technology in Expanding the PPF
Technological advancements shift the Production Possibility Frontier (PPF) outward by enabling higher output with the same input resources, thereby improving overall efficiency in resource allocation. By integrating cutting-edge technology, firms can produce more goods and services, reducing opportunity costs and optimizing productive capabilities. This expansion of the PPF reflects the economy's increased capacity to produce due to innovation and improved methods of production.
Economic Growth and Changes in Efficient Allocation
Efficient allocation occurs when resources are distributed in a way that maximizes output without waste, aligning production points on the Production Possibility Frontier (PPF). Economic growth shifts the PPF outward, reflecting an increased capacity to produce goods and services due to improvements in technology, capital, or labor. Changes in efficient allocation during this growth phase optimize resource use between sectors, pushing the economy toward points on the new frontier rather than inside it.
Real-World Applications of PPF and Efficient Allocation
The Production Possibility Frontier (PPF) illustrates the maximum feasible output combinations of two goods, guiding efficient resource allocation in sectors such as agriculture and manufacturing. Real-world applications of the PPF help policymakers identify optimal production points, minimize opportunity costs, and achieve economic efficiency by avoiding underutilization or overextension of resources. Efficient allocation ensures resources are directed toward producing goods and services that maximize societal welfare, as demonstrated in energy production trade-offs and public health resource distribution.
Efficient allocation Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com