Efficient markets quickly incorporate all available information into asset prices, ensuring that securities are fairly valued and eliminating opportunities for consistent excess returns. Understanding how this efficiency impacts your investment strategy can help you make more informed decisions. Explore the rest of the article to learn how market efficiency shapes trading and portfolio management.
Table of Comparison
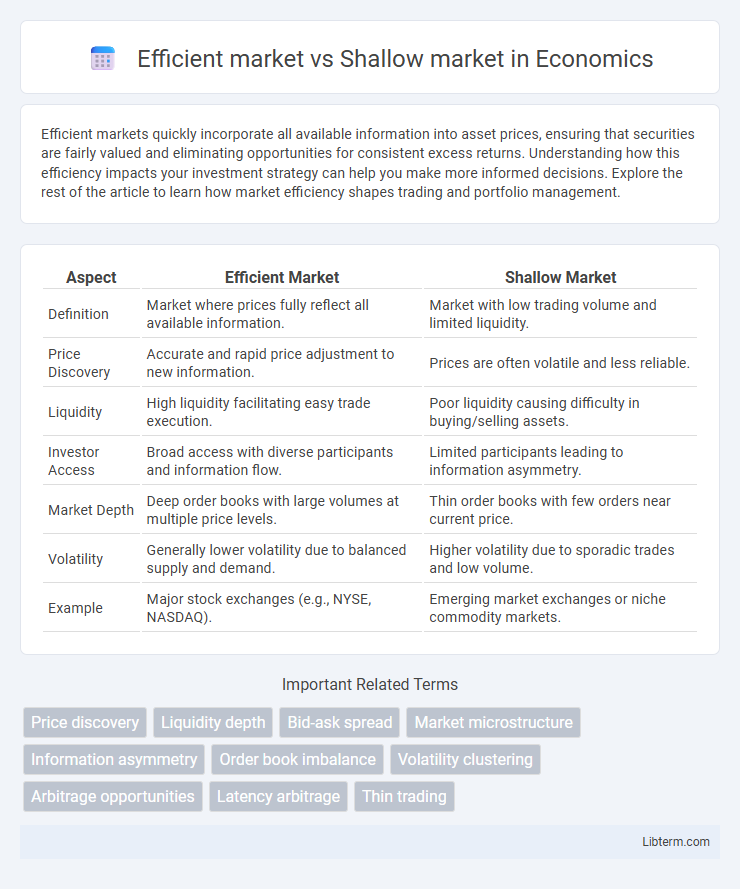
| Aspect | Efficient Market | Shallow Market |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Market where prices fully reflect all available information. | Market with low trading volume and limited liquidity. |
| Price Discovery | Accurate and rapid price adjustment to new information. | Prices are often volatile and less reliable. |
| Liquidity | High liquidity facilitating easy trade execution. | Poor liquidity causing difficulty in buying/selling assets. |
| Investor Access | Broad access with diverse participants and information flow. | Limited participants leading to information asymmetry. |
| Market Depth | Deep order books with large volumes at multiple price levels. | Thin order books with few orders near current price. |
| Volatility | Generally lower volatility due to balanced supply and demand. | Higher volatility due to sporadic trades and low volume. |
| Example | Major stock exchanges (e.g., NYSE, NASDAQ). | Emerging market exchanges or niche commodity markets. |
Understanding Efficient Markets
Efficient markets reflect all available information in asset prices, ensuring that securities are fairly valued and that investors cannot consistently achieve abnormal returns through information-based trading. In contrast, shallow markets exhibit limited liquidity and information flow, leading to price inefficiencies and increased volatility. Understanding efficient markets is crucial for investors as it highlights the challenges of outperforming the market and emphasizes the importance of diversified portfolios and passive investment strategies.
Defining Shallow Markets
Shallow markets are characterized by low liquidity, limited trading volume, and wide bid-ask spreads, making them prone to higher price volatility and inefficiency. Unlike efficient markets, where prices fully reflect all available information due to active participation and deep liquidity, shallow markets struggle to provide accurate price signals and facilitate smooth asset transactions. These markets often suffer from information asymmetry and higher transaction costs, hindering optimal capital allocation and investor confidence.
Key Features of Efficient Markets
Efficient markets are characterized by rapid information dissemination, ensuring asset prices fully reflect all available information, leading to fair valuation and minimal opportunities for excess returns. Key features include high liquidity, tight bid-ask spreads, and numerous active participants contributing to optimal price discovery. In contrast, shallow markets lack depth and liquidity, causing price inefficiencies and higher volatility.
Characteristics of Shallow Markets
Shallow markets exhibit low liquidity with limited trading volumes and wide bid-ask spreads, resulting in higher price volatility and increased susceptibility to manipulation. These markets often lack depth, meaning fewer buy and sell orders at varying price levels, which impedes efficient price discovery. Investors in shallow markets face challenges such as higher transaction costs and difficulty executing large trades without significantly impacting prices.
Liquidity Comparison: Efficient vs Shallow Markets
Efficient markets exhibit high liquidity characterized by narrow bid-ask spreads, rapid trade execution, and ample buyer-seller participation, ensuring price stability and quick absorption of new information. In contrast, shallow markets suffer from low liquidity with wide spreads, limited trading volume, and higher price volatility due to fewer participants and less frequent transactions. This liquidity disparity impacts market efficiency, where efficient markets facilitate smoother price discovery while shallow markets often experience price distortions and increased transaction costs.
Price Discovery in Both Market Types
Efficient markets facilitate rapid and accurate price discovery due to high liquidity and transparent information flow, allowing asset prices to quickly reflect all available information. In contrast, shallow markets exhibit slower price discovery as limited trading volume and fewer participants result in price distortions and greater volatility. The depth of an efficient market ensures that prices serve as reliable signals for resource allocation, whereas shallow markets often experience price inefficiencies and increased risk premia.
Impact on Investors and Traders
Efficient markets provide accurate price discovery based on vast information, enabling investors to make well-informed decisions and reducing opportunities for arbitrage. In contrast, shallow markets exhibit low liquidity and wider bid-ask spreads, increasing transaction costs and causing greater price volatility that can mislead traders. Investors in efficient markets benefit from fair pricing and lower risks, while participants in shallow markets face higher uncertainty and potential difficulties in executing large trades without impacting prices.
Risks Associated with Shallow Markets
Shallow markets are characterized by low liquidity and limited trading volume, which amplifies price volatility and increases the risk of significant bid-ask spreads. Unlike efficient markets, where information is quickly integrated into asset prices reducing systemic risks, shallow markets expose investors to heightened execution risk and potential manipulation. These risks can lead to sudden price swings, making it challenging to enter or exit positions without substantial slippage or loss.
Case Studies: Efficient vs Shallow Market Scenarios
Case studies of efficient markets, such as the New York Stock Exchange, demonstrate high liquidity, rapid information dissemination, and minimal arbitrage opportunities, reflecting strong market efficiency. In contrast, shallow markets like frontier stock exchanges often experience low trading volumes, wider bid-ask spreads, and significant price volatility due to limited investor participation and information asymmetry. These scenarios highlight how market depth and efficiency directly influence price discovery, transaction costs, and investor confidence.
Strategies for Navigating Market Types
Efficient markets require strategies that leverage rapid information processing and minimal advantage from insider knowledge, emphasizing passive investing and low-cost index funds to match market returns. In contrast, shallow markets demand active strategies focused on exploiting liquidity gaps, price inefficiencies, and higher volatility through tactical trading, market making, or arbitrage opportunities. Tailoring approaches to market depth ensures optimized portfolio performance, risk management, and capital allocation across diverse trading environments.
Efficient market Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com