A delta squeeze occurs in options trading when rapid buying of options forces market makers to buy the underlying stock to hedge their positions, driving the stock price higher. This phenomenon can amplify price movements sharply, creating significant volatility and opportunities for traders. Discover how understanding delta squeezes can enhance your trading strategy by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
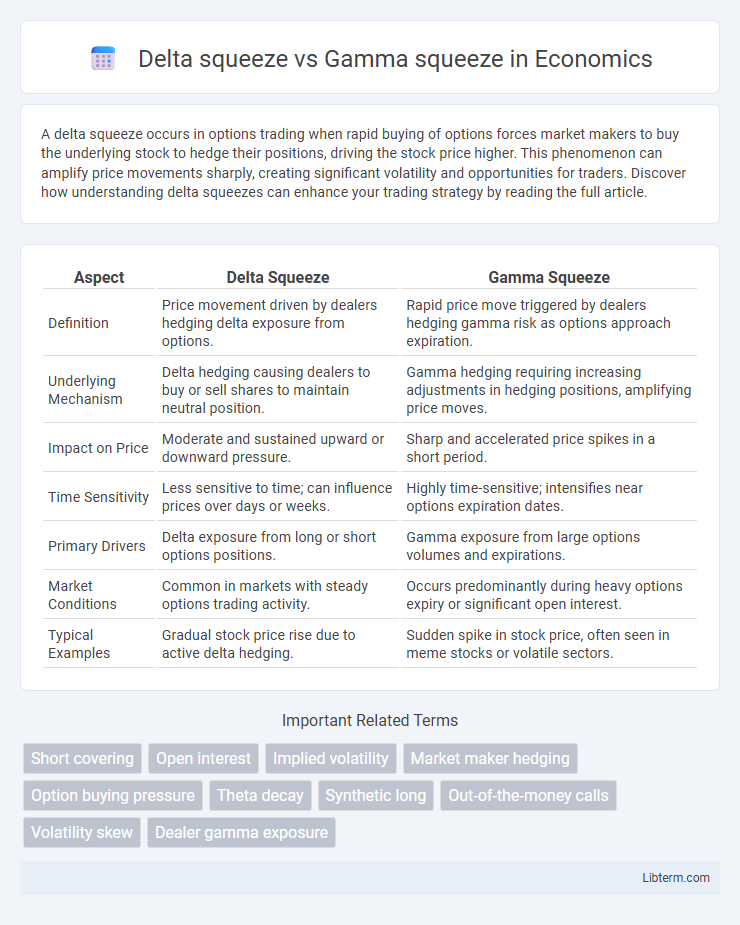
| Aspect | Delta Squeeze | Gamma Squeeze |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Price movement driven by dealers hedging delta exposure from options. | Rapid price move triggered by dealers hedging gamma risk as options approach expiration. |
| Underlying Mechanism | Delta hedging causing dealers to buy or sell shares to maintain neutral position. | Gamma hedging requiring increasing adjustments in hedging positions, amplifying price moves. |
| Impact on Price | Moderate and sustained upward or downward pressure. | Sharp and accelerated price spikes in a short period. |
| Time Sensitivity | Less sensitive to time; can influence prices over days or weeks. | Highly time-sensitive; intensifies near options expiration dates. |
| Primary Drivers | Delta exposure from long or short options positions. | Gamma exposure from large options volumes and expirations. |
| Market Conditions | Common in markets with steady options trading activity. | Occurs predominantly during heavy options expiry or significant open interest. |
| Typical Examples | Gradual stock price rise due to active delta hedging. | Sudden spike in stock price, often seen in meme stocks or volatile sectors. |
Understanding Delta Squeeze: A Brief Overview
Delta squeeze occurs when options traders aggressively buy calls, compelling market makers to purchase the underlying stock to hedge their delta exposure, intensifying upward price pressure. This phenomenon contrasts with a gamma squeeze, where rapid changes in delta force market makers to adjust their hedges dynamically, amplifying volatility. Understanding delta squeeze involves recognizing its role in driving swift price movements due to hedging demands linked to option deltas rather than changes in gamma sensitivity.
What is a Gamma Squeeze?
A Gamma squeeze occurs when traders buying options force market makers to hedge by purchasing the underlying stock, causing a rapid price increase. This dynamic is driven by the options' gamma, which measures the rate of change in delta, leading to amplified buying activity as the stock price moves. The resulting feedback loop can significantly escalate volatility and push the stock price higher in a short period.
Key Differences Between Delta Squeeze and Gamma Squeeze
Delta squeeze occurs when hedgers rapidly buy or sell the underlying asset to maintain a neutral delta position as option prices change, causing significant price moves. Gamma squeeze happens when increases in the underlying price cause option dealers to buy more of the asset to hedge their gamma exposure, accelerating the price rise. Key differences include delta squeeze primarily involving adjustments in delta hedging, while gamma squeeze intensifies due to accelerating gamma-related hedging demands.
How Delta Squeezes Impact Stock Prices
Delta squeezes significantly impact stock prices by increasing demand for options as the underlying asset's price moves, forcing market makers to rapidly buy or sell shares to hedge their positions. This dynamic creates a feedback loop, amplifying price volatility and causing sharp upward or downward movements in the stock. Unlike gamma squeezes, delta squeezes primarily stem from the directional exposure and hedging adjustments related to the delta of options rather than rapid changes in gamma sensitivity.
The Mechanics Behind a Gamma Squeeze
A gamma squeeze occurs when market makers hedge their exposure by buying underlying shares as option prices rise, driven by high call option volume and increasing stock prices. This dynamic causes accelerated stock price movement, as the need to buy shares to maintain delta neutrality intensifies, fueling further price increases. Unlike a delta squeeze that focuses on option deltas, a gamma squeeze is rooted in the gamma exposure of options, influencing the rate of delta change and causing more aggressive hedging behavior.
Real-World Examples of Delta and Gamma Squeezes
Delta squeezes occur when rapid buying or selling of options forces hedgers to adjust the underlying stock positions, leading to significant price moves, as seen in Tesla's 2020 volatility spikes driven by heavy call option activity. Gamma squeezes involve the acceleration of these price movements due to increasing gamma exposure, evident in the 2021 GameStop frenzy where market makers rapidly bought shares to hedge rising gamma risk from soaring call option volumes. Real-world examples highlight how delta squeezes initiate price momentum, while gamma squeezes amplify the intensity and speed of stock price changes during intense options market activity.
Indicators That Signal a Potential Squeeze
Indicators that signal a potential delta squeeze include rapid increases in open interest and call option volume, highlighting aggressive bullish betting on underlying asset price movements. In contrast, gamma squeeze indicators often involve elevated implied volatility alongside sharp price spikes, reflecting market makers' hedging activity to manage their gamma exposure. Monitoring shifts in options' delta and gamma values alongside trading volume provides critical insights for anticipating these squeezes.
Risks and Rewards for Traders in Squeeze Scenarios
Delta squeeze and gamma squeeze both present unique risks and rewards for traders. Delta squeeze risks include rapid stock price movements driven by hedging needs of option sellers, causing high volatility but potential for quick profits if timed correctly. Gamma squeeze amplifies price swings due to accelerated hedging as option expiration nears, increasing the potential reward through intensified momentum while posing risks of sharp reversals and liquidity challenges.
Strategies for Navigating Delta and Gamma Squeezes
Effective strategies for navigating delta squeezes involve monitoring option deltas to anticipate rapid price movements and adjusting option positions to manage directional risk. Gamma squeeze mitigation requires careful tracking of gamma exposure and employing hedging techniques, such as dynamic rebalancing or spreading options, to limit the impact of sharp volatility spikes. Combining delta and gamma risk management with real-time analytics enables traders to optimize entry and exit points, minimizing losses during forced buying or selling pressures.
Delta Squeeze vs Gamma Squeeze: Which Moves Markets More?
Delta squeeze occurs when rapid hedging of options by market makers forces large stock price moves as they buy or sell shares to maintain a neutral position. Gamma squeeze intensifies this effect by accelerating delta changes, causing even more aggressive buying or selling of the underlying asset due to increased option sensitivity as expiry approaches. Gamma squeeze often moves markets more significantly because it compounds delta adjustments, leading to sharper and faster price spikes during periods of heavy option activity.
Delta squeeze Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com