Effective human resources management drives organizational success by aligning talent strategies with business goals and fostering a positive workplace culture. It encompasses recruitment, employee development, performance management, and compliance with labor laws to maximize workforce potential. Explore the full article to understand how optimizing your human resources can transform your company.
Table of Comparison
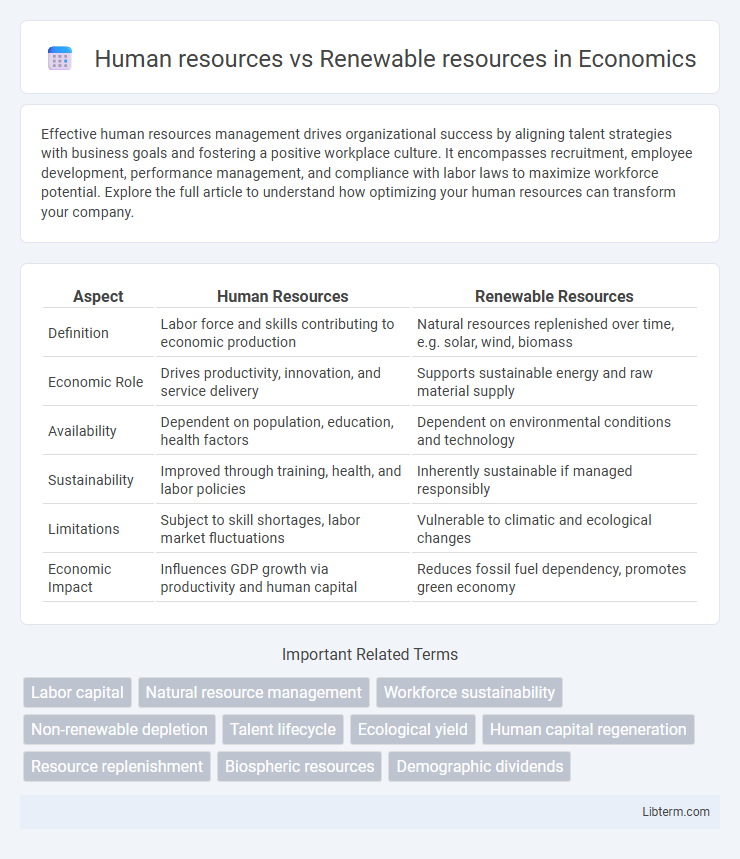
| Aspect | Human Resources | Renewable Resources |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Labor force and skills contributing to economic production | Natural resources replenished over time, e.g. solar, wind, biomass |
| Economic Role | Drives productivity, innovation, and service delivery | Supports sustainable energy and raw material supply |
| Availability | Dependent on population, education, health factors | Dependent on environmental conditions and technology |
| Sustainability | Improved through training, health, and labor policies | Inherently sustainable if managed responsibly |
| Limitations | Subject to skill shortages, labor market fluctuations | Vulnerable to climatic and ecological changes |
| Economic Impact | Influences GDP growth via productivity and human capital | Reduces fossil fuel dependency, promotes green economy |
Understanding Human Resources: Definition and Scope
Human resources refer to the workforce within an organization or economy, encompassing employees' skills, knowledge, and abilities essential for productivity and growth. Unlike renewable resources, which are natural assets capable of replenishment such as solar energy or wind power, human resources are intangible assets critical for innovation, management, and operational success. Understanding human resources involves analyzing recruitment, training, development, and employee engagement to maximize organizational effectiveness and sustain competitive advantage.
Renewable Resources Explained: Key Characteristics
Renewable resources are natural assets that replenish naturally over short periods, including solar energy, wind power, hydroelectricity, and biomass. These resources exhibit sustainability through continuous regeneration, low environmental impact, and the capacity to support long-term energy needs without depletion. Unlike human resources, which refer to workforce skills and capabilities, renewable resources primarily contribute to ecological balance and energy production.
Core Differences Between Human and Renewable Resources
Human resources refer to the workforce and skills available within an organization or economy, emphasizing intellectual capabilities and labor input. Renewable resources, such as solar energy, wind, and biomass, are natural assets replenished continuously through ecological processes, highlighting sustainability and environmental regeneration. Core differences lie in the intangible nature of human resources involving knowledge and productivity, contrasted with the physical, naturally replenished characteristics of renewable resources essential for long-term ecological balance.
The Role of Human Resources in Economic Development
Human resources drive economic development by enhancing productivity, innovation, and labor quality through education, training, and health improvements. Skilled human capital attracts investment and supports technological advancement, which fuels sustainable growth and income generation. Unlike renewable resources that replenish naturally, human resources require continuous development to maximize their economic contribution.
Environmental Importance of Renewable Resources
Renewable resources, such as solar, wind, and biomass energy, play a crucial role in reducing environmental degradation by lowering greenhouse gas emissions and minimizing reliance on finite fossil fuels. Unlike human resources, which pertain to workforce capabilities and management, renewable resources provide sustainable energy solutions that support long-term ecological balance and biodiversity conservation. Prioritizing renewable resource development is essential for mitigating climate change impacts and ensuring clean air, water, and soil quality for future generations.
Sustainability: Comparing Human and Renewable Resources
Human resources encompass skills, labor, and expertise essential for organizational success, while renewable resources such as solar, wind, and biomass offer sustainable energy solutions with minimal environmental impact. Sustainable management of human resources involves investing in education, health, and well-being to enhance productivity and long-term economic growth. Renewable resources contribute to sustainability by reducing carbon emissions and preserving ecosystems, ensuring availability for future generations while supporting global efforts to combat climate change.
Management Strategies for Human vs Renewable Resources
Human resource management strategies emphasize talent acquisition, employee development, and retention to maximize workforce productivity and organizational growth. Renewable resource management focuses on sustainable harvesting, resource regeneration, and environmental impact monitoring to ensure long-term availability and ecosystem balance. Effective planning in both sectors requires integrating data analytics and adaptive frameworks to optimize resource utilization while minimizing waste and depletion.
Challenges in Harnessing Human and Renewable Resources
Challenges in harnessing human resources revolve around skills mismatches, workforce diversity, and employee motivation, which impact organizational productivity and innovation. Renewable resources face technological limitations, high initial costs, and intermittency issues, hindering consistent energy supply and economic viability. Effective strategies must address skill development, technology integration, and sustainable management to optimize the benefits of both human and renewable resources.
Technological Impacts on Human and Renewable Resources
Technological advancements significantly enhance human resources by automating repetitive tasks and enabling remote collaboration, thereby increasing productivity and skill development. In renewable resources, technology improves efficiency in energy harvesting through innovations like advanced solar panels and smart grid systems, reducing environmental impact and supporting sustainable resource management. The integration of artificial intelligence and data analytics optimizes resource allocation and predictive maintenance, ensuring both human and renewable assets are utilized effectively to meet growing economic and environmental demands.
Future Trends: Human Resources and Renewable Resources Collaboration
Future trends highlight increasing collaboration between human resources and renewable resources sectors to drive sustainable development and workforce transformation. Integrating advanced training programs on renewable energy technologies prepares human capital for emerging green jobs, boosting economic growth and environmental stewardship. Strategic partnerships focused on innovation, diversity, and skill development are essential to successfully transition towards a low-carbon economy.
Human resources Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com