The efficient frontier represents the set of optimal investment portfolios offering the highest expected return for a given level of risk, crucial for effective portfolio management. Understanding this concept helps you balance risk and reward to maximize your investment outcomes. Explore the rest of the article to learn how to apply the efficient frontier in your financial strategy.
Table of Comparison
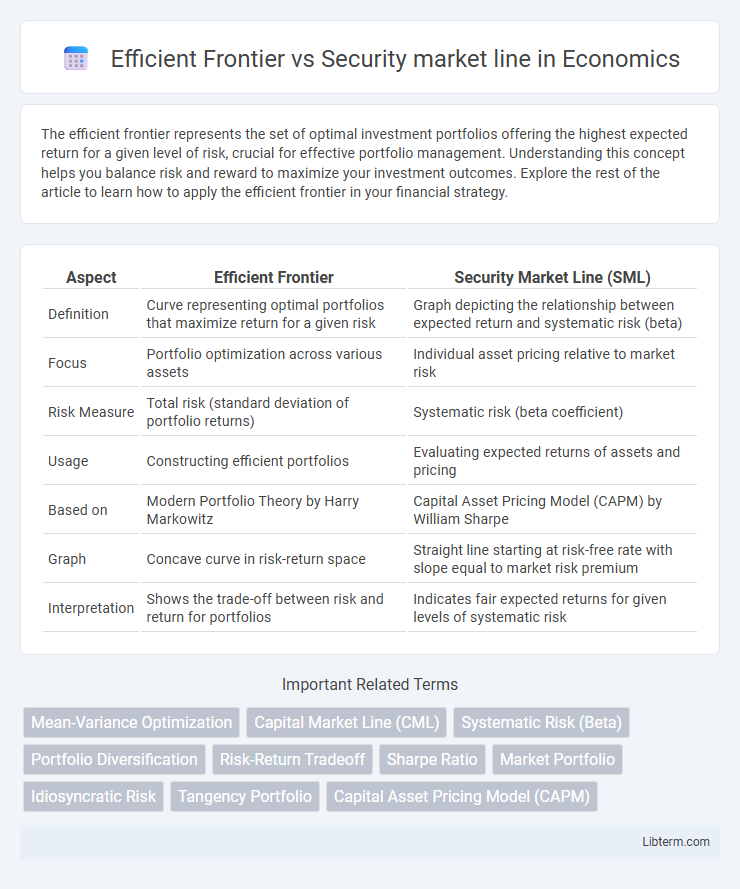
| Aspect | Efficient Frontier | Security Market Line (SML) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Curve representing optimal portfolios that maximize return for a given risk | Graph depicting the relationship between expected return and systematic risk (beta) |
| Focus | Portfolio optimization across various assets | Individual asset pricing relative to market risk |
| Risk Measure | Total risk (standard deviation of portfolio returns) | Systematic risk (beta coefficient) |
| Usage | Constructing efficient portfolios | Evaluating expected returns of assets and pricing |
| Based on | Modern Portfolio Theory by Harry Markowitz | Capital Asset Pricing Model (CAPM) by William Sharpe |
| Graph | Concave curve in risk-return space | Straight line starting at risk-free rate with slope equal to market risk premium |
| Interpretation | Shows the trade-off between risk and return for portfolios | Indicates fair expected returns for given levels of systematic risk |
Introduction to Efficient Frontier and Security Market Line
The Efficient Frontier represents the set of optimal portfolios that offer the highest expected return for a given level of risk, derived from Modern Portfolio Theory. The Security Market Line (SML) illustrates the relationship between systematic risk, measured by beta, and expected return according to the Capital Asset Pricing Model (CAPM). While the Efficient Frontier focuses on risk-return trade-offs through portfolio diversification, the SML provides a benchmark for evaluating individual asset prices based on their market risk.
Key Concepts: Risk, Return, and Portfolio Theory
The Efficient Frontier represents the set of optimal portfolios that offer the highest expected return for a given level of risk, based on Modern Portfolio Theory's principles of diversification and risk minimization. The Security Market Line (SML) illustrates the relationship between systematic risk, measured by beta, and expected return for individual securities or portfolios, serving as a graphical representation of the Capital Asset Pricing Model (CAPM). Together, these concepts highlight the trade-off between risk and return, guiding investors in constructing portfolios that balance market risk and optimize performance.
Defining the Efficient Frontier
The Efficient Frontier represents the set of optimal portfolios offering the highest expected return for a given level of risk, derived from Modern Portfolio Theory. It is graphically depicted as a curve in risk-return space, where portfolios below the curve are suboptimal. The Security Market Line, in contrast, illustrates the relationship between expected return and systematic risk (beta), serving as a benchmark for evaluating individual securities relative to market risk.
Understanding the Security Market Line (SML)
The Security Market Line (SML) represents the relationship between expected return and systematic risk (beta) for individual securities, providing a benchmark for evaluating investment performance relative to the market. Unlike the Efficient Frontier, which illustrates the optimal portfolios offering the highest return for a given level of risk, the SML focuses on pricing single assets based on their market risk exposure. Understanding the SML enables investors to identify undervalued or overvalued securities by comparing actual returns against the expected returns predicted by the Capital Asset Pricing Model (CAPM).
Mathematical Foundations of the Efficient Frontier
The Efficient Frontier is derived from mean-variance optimization, using quadratic programming to minimize portfolio variance for a given expected return. It represents the set of portfolios that offer the highest expected return for each level of risk, mathematically defined by the covariance matrix of asset returns and the vector of expected returns. In contrast, the Security Market Line (SML) is a linear representation of the Capital Asset Pricing Model (CAPM), linking expected return to systematic risk measured by beta, without the portfolio optimization framework that underpins the Efficient Frontier.
CAPM and Its Role in the Security Market Line
The Efficient Frontier represents the set of optimal portfolios offering the highest expected return for a given level of risk, based on Modern Portfolio Theory. The Security Market Line (SML), derived from the Capital Asset Pricing Model (CAPM), illustrates the relationship between systematic risk (beta) and expected return for individual securities. CAPM plays a crucial role in the SML by quantifying expected returns through the risk-free rate, beta, and market risk premium, enabling investors to assess if securities are fairly priced relative to market risk.
Visualizing Efficient Frontier vs Security Market Line
Visualizing the Efficient Frontier highlights the set of optimal portfolios offering the highest expected return for a given level of risk, depicted as a curved line on a risk-return graph. The Security Market Line, shown as a straight line, represents the relationship between expected return and systematic risk (beta) for individual securities or portfolios in the Capital Asset Pricing Model (CAPM). Comparing these visuals emphasizes that while the Efficient Frontier focuses on total portfolio risk and return optimization, the Security Market Line specifically illustrates the risk-return trade-off based on market risk exposure.
Similarities Between Efficient Frontier and SML
Both the Efficient Frontier and Security Market Line (SML) illustrate the relationship between risk and return in portfolio theory, serving as fundamental tools in modern portfolio management. They rely on the Capital Asset Pricing Model (CAPM) framework, emphasizing that investors seek to optimize returns for a given level of risk or minimize risk for a given return. Both concepts use expected return and risk measurement--standard deviation for the Efficient Frontier and beta for the SML--to guide investment decisions and highlight the trade-off between risk and reward.
Differences and Applications in Investment Strategy
The Efficient Frontier represents the set of optimal portfolios offering the highest expected return for a given level of risk, based on Modern Portfolio Theory and asset covariance. The Security Market Line (SML) illustrates the relationship between expected return and systematic risk (beta), derived from the Capital Asset Pricing Model (CAPM), highlighting individual asset pricing rather than portfolio combinations. Investors use the Efficient Frontier to construct diversified portfolios maximizing risk-adjusted returns, while the SML guides asset selection by assessing whether securities provide adequate return for their market risk exposure.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Tool for Portfolio Optimization
The Efficient Frontier provides a visual representation of optimal portfolios offering the highest expected return for a given level of risk, making it essential for identifying diversified asset combinations. The Security Market Line (SML) focuses on individual asset pricing relative to systematic risk through the Capital Asset Pricing Model (CAPM), helping investors evaluate whether assets are fairly valued. Selecting between the two depends on investment goals: use the Efficient Frontier for portfolio construction and risk-return trade-offs, and the SML for assessing individual security performance against market expectations.
Efficient Frontier Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com