Labor mobility refers to the ease with which workers can move between different jobs, industries, or geographic locations to find better employment opportunities. High labor mobility boosts economic growth by allowing your skills to match the demands of the market more efficiently, reducing unemployment and improving overall productivity. Discover how improving labor mobility can impact your career and the economy by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
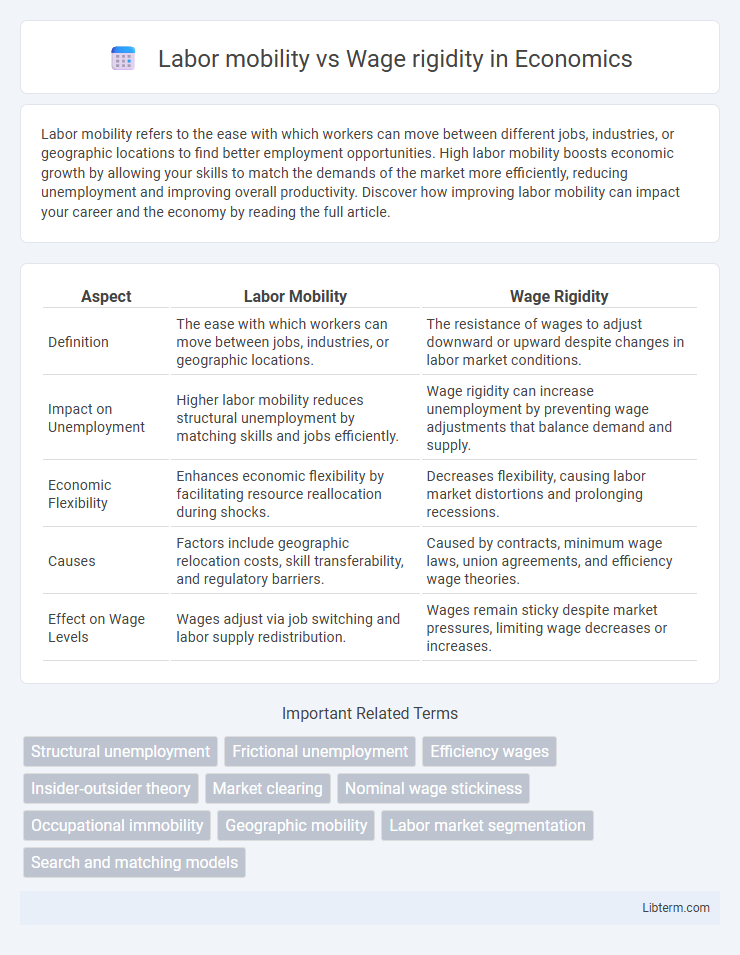
| Aspect | Labor Mobility | Wage Rigidity |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | The ease with which workers can move between jobs, industries, or geographic locations. | The resistance of wages to adjust downward or upward despite changes in labor market conditions. |
| Impact on Unemployment | Higher labor mobility reduces structural unemployment by matching skills and jobs efficiently. | Wage rigidity can increase unemployment by preventing wage adjustments that balance demand and supply. |
| Economic Flexibility | Enhances economic flexibility by facilitating resource reallocation during shocks. | Decreases flexibility, causing labor market distortions and prolonging recessions. |
| Causes | Factors include geographic relocation costs, skill transferability, and regulatory barriers. | Caused by contracts, minimum wage laws, union agreements, and efficiency wage theories. |
| Effect on Wage Levels | Wages adjust via job switching and labor supply redistribution. | Wages remain sticky despite market pressures, limiting wage decreases or increases. |
Understanding Labor Mobility: Definition and Importance
Labor mobility refers to the ability of workers to move between different jobs, industries, or geographic locations in response to economic changes. High labor mobility enables efficient allocation of human resources, reducing unemployment and adapting to market demands. Understanding labor mobility is crucial for policymakers aiming to enhance workforce flexibility and economic growth.
Exploring Wage Rigidity: Causes and Consequences
Wage rigidity stems from factors like long-term labor contracts, minimum wage laws, and efficiency wages, which limit the flexibility of wages to adjust to market conditions. This rigidity can result in higher unemployment rates during economic downturns as employers are unable to reduce wages to retain all workers. Understanding wage rigidity is essential for policymakers to address labor market inefficiencies and support optimal employment levels.
Key Differences Between Labor Mobility and Wage Rigidity
Labor mobility refers to the ease with which workers can move between jobs, industries, or geographic locations, while wage rigidity denotes the resistance of wages to adjust downward despite changes in labor market conditions. Labor mobility enhances employment flexibility and efficiency by matching workers to opportunities, whereas wage rigidity can lead to unemployment or labor market inefficiencies by constraining wage adjustments. The key difference lies in labor mobility's focus on the movement of workers and wage rigidity's emphasis on the inflexibility of wage levels in response to economic shifts.
Economic Theories Explaining Labor Mobility
Economic theories explaining labor mobility emphasize the role of wage flexibility in responding to regional job market disparities and mismatches in labor supply and demand. Models such as the Harris-Todaro framework illustrate how expected wage differentials drive migration decisions despite potential unemployment risks, while dual labor market theory highlights barriers to mobility caused by segmented labor markets and institutional wage rigidity. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for addressing economic inefficiencies related to unemployment concentrations and underutilization of human capital.
Factors Contributing to Wage Rigidity
Wage rigidity is primarily influenced by factors such as long-term employment contracts, minimum wage laws, and strong labor unions that limit wage flexibility. Labor market institutions, including collective bargaining agreements and social norms, contribute to wage stickiness by preventing wages from adjusting quickly to changes in labor supply and demand. Moreover, efficiency wage theories suggest employers may maintain higher wages to increase productivity and reduce turnover, reinforcing rigidity despite fluctuating labor mobility.
Effects of Labor Mobility on Economic Growth
Labor mobility enhances economic growth by enabling workers to relocate to regions with higher labor demand, thereby optimizing resource allocation and increasing productivity. Increased labor mobility reduces wage rigidity by allowing wages to adjust naturally according to regional labor market conditions, fostering competitive labor markets. Studies show that economies with higher interregional labor mobility experience faster GDP growth due to improved labor market efficiency and innovation diffusion.
Impact of Wage Rigidity on Labor Markets
Wage rigidity significantly affects labor markets by limiting employers' ability to adjust wages in response to economic fluctuations, leading to prolonged unemployment during downturns. Fixed or sticky wages reduce labor mobility as workers may be reluctant to move to regions or jobs with uncertain or potentially lower pay, exacerbating regional labor market imbalances. Empirical studies show that high wage rigidity correlates with slower employment recovery and decreased job matching efficiency, intensifying labor market inefficiencies.
Policy Approaches to Enhance Labor Mobility
Policies to enhance labor mobility focus on reducing geographic, occupational, and informational barriers through targeted investments in training programs, affordable housing, and streamlined licensing requirements. Expanding access to remote work technology and portability of benefits facilitates smoother transitions across jobs and locations, mitigating the adverse effects of wage rigidity on unemployment rates. Labor market reforms promoting flexible wage-setting mechanisms complement mobility efforts by aligning wages with local labor market conditions.
Strategies to Address Wage Rigidity
Strategies to address wage rigidity include implementing flexible wage-setting mechanisms that allow salaries to adjust based on labor market conditions and employee performance metrics. Enhancing labor mobility through retraining programs and skills development can reduce dependency on fixed wages by enabling workers to transition to higher-demand sectors. Encouraging decentralized wage negotiations between employers and employees promotes responsiveness to local economic changes, mitigating the negative impact of rigid wage structures.
Labor Mobility vs Wage Rigidity: Comparative Analysis and Future Outlook
Labor mobility enhances economic efficiency by allowing workers to move freely across regions and industries in response to demand fluctuations, while wage rigidity often obstructs this adjustment by fixing wages despite changes in labor supply and demand. Comparative analysis reveals that economies with high labor mobility exhibit lower unemployment rates and faster recovery from economic shocks, whereas those with significant wage rigidity face prolonged joblessness and reduced labor market flexibility. Future outlook suggests that integrating flexible wage policies with supportive labor mobility measures can optimize workforce allocation and promote sustainable economic growth.
Labor mobility Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com