Big-box retail stores significantly impact local economies by drawing large crowds and offering lower prices, which often leads to the decline of small, independent businesses. These retail giants influence urban development patterns and consumer behavior, reshaping shopping habits in both suburban and urban areas. Discover how the big-box retail effect could be shaping Your community and economy throughout the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
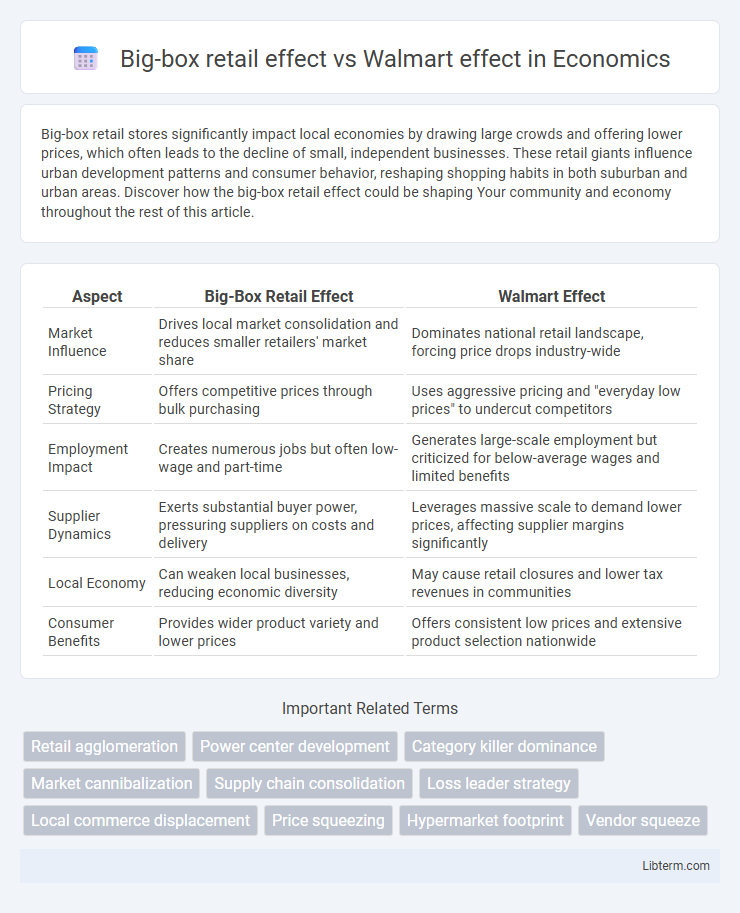
| Aspect | Big-Box Retail Effect | Walmart Effect |
|---|---|---|
| Market Influence | Drives local market consolidation and reduces smaller retailers' market share | Dominates national retail landscape, forcing price drops industry-wide |
| Pricing Strategy | Offers competitive prices through bulk purchasing | Uses aggressive pricing and "everyday low prices" to undercut competitors |
| Employment Impact | Creates numerous jobs but often low-wage and part-time | Generates large-scale employment but criticized for below-average wages and limited benefits |
| Supplier Dynamics | Exerts substantial buyer power, pressuring suppliers on costs and delivery | Leverages massive scale to demand lower prices, affecting supplier margins significantly |
| Local Economy | Can weaken local businesses, reducing economic diversity | May cause retail closures and lower tax revenues in communities |
| Consumer Benefits | Provides wider product variety and lower prices | Offers consistent low prices and extensive product selection nationwide |
Introduction to the Big-Box and Walmart Effects
Big-box retail effects significantly reshape local economies by introducing large-scale stores that drive down prices through economies of scale, impacting small retailers and changing consumer behavior. The Walmart effect specifically highlights how Walmart's aggressive pricing strategies and vast product selection influence market competition, labor wages, and supply chains on a national and global scale. Both phenomena underscore shifts in retail landscapes, with big-box stores emphasizing size and variety, while Walmart's model amplifies these factors through global sourcing and logistical efficiency.
Historical Overview of Big-Box Retail Expansion
The historical expansion of big-box retail began in the mid-20th century, with retailers like Walmart, Home Depot, and Costco pioneering large-scale stores characterized by vast square footage and broad product assortments. This growth transformed suburban and rural retail landscapes, driving significant economic and social changes, including the decline of small independent retailers and shifts in consumer shopping habits. The Walmart effect specifically highlights aggressive pricing strategies and supply chain innovations that set industry standards, while the broader big-box retail effect emphasizes scale economies and consumer convenience.
Defining the Walmart Effect in Retail Economics
The Walmart Effect in retail economics refers to the phenomenon where Walmart's aggressive pricing strategies and supply chain efficiency lead to significant shifts in market dynamics, often driving down prices and forcing competitors to adapt or exit. Unlike the broader Big-box retail effect, which encompasses the impact of large-format stores on consumer behavior and local economies, the Walmart Effect specifically highlights Walmart's role in reshaping retail landscapes through economies of scale and bargaining power over suppliers. This effect results in lower consumer prices but can pressure smaller retailers and alter employment patterns within communities.
Market Disruption: Local Businesses and Competition
Big-box retail stores and Walmart both significantly disrupt local markets by altering competition dynamics and consumer behavior. Big-box retailers often draw customers away from smaller businesses through extensive product variety and lower prices driven by economies of scale, leading to reduced market share for local shops. The Walmart effect intensifies this disruption by leveraging aggressive pricing strategies and supply chain efficiencies, often forcing local competitors to downsize or shut down, fundamentally reshaping community economic landscapes.
Employment Patterns and Wage Impacts
Big-box retail stores often lead to shifts in local employment patterns, with increased demand for low-wage, part-time positions that can reduce overall job stability. The Walmart effect, specifically, has been linked to wage suppression in surrounding areas due to aggressive cost-cutting and labor practices, resulting in slower wage growth for competing retailers. Both phenomena contribute to reshaping labor markets by prioritizing cost efficiency over employee compensation, impacting local economies and worker livelihoods.
Supply Chain Innovations and Pressures
Big-box retail formats accelerate supply chain innovations by emphasizing centralized distribution centers and advanced inventory management systems to optimize stock levels and reduce delivery times. The Walmart effect specifically drives pressure on suppliers to lower costs and increase efficiency through practices such as just-in-time inventory and data-driven demand forecasting. Both phenomena reshape supply chains by incentivizing collaboration, technological adoption, and cost reduction strategies across the retail ecosystem.
Pricing Strategies and Consumer Benefits
Big-box retail stores implement economies of scale to offer lower prices through bulk purchasing and streamlined supply chains, enhancing overall consumer savings. Walmart's pricing strategy emphasizes everyday low prices (EDLP) to maintain consistent affordability, driving competitive pressure across retail markets. Both models improve consumer benefits by expanding product access and reducing costs, though Walmart's targeted pricing approach often leads to more aggressive market penetration and price matching.
Community Transformation and Urban Development
Big-box retail stores like Target and Costco often drive community transformation by attracting diverse businesses and enhancing local infrastructure, which fosters urban development through job creation and increased property values. The Walmart effect, characterized by aggressive price competition and market dominance, can lead to the closure of smaller retailers, impacting economic diversity and altering the social fabric of communities. While both influence urban landscapes, big-box retailers generally promote broader economic revitalization, whereas Walmart's presence tends to centralize commerce and reshape community dynamics.
Policy Responses and Regulatory Challenges
Policy responses to the big-box retail effect often involve zoning reforms and antitrust regulations to address market concentration and community impact, whereas Walmart-specific challenges prompt tailored measures targeting supplier practices and labor standards. Regulatory approaches must balance promoting competitive markets while mitigating negative outcomes like small business displacement and reduced wage growth. Enforcement complexities arise due to varying state and local jurisdictions, requiring coordinated frameworks to effectively oversee retail giants' economic influence.
Future Trends: E-commerce, Big-Box, and Walmart Evolution
E-commerce continues to reshape the retail landscape by driving convenience and expanding product accessibility, challenging both traditional big-box stores and Walmart's market dominance. Big-box retailers adapt by integrating omnichannel strategies, enhancing in-store experiences, and leveraging data analytics to compete with digital-first competitors. Walmart evolves through investments in technology, online grocery delivery, and partnerships, aiming to sustain growth amid shifting consumer preferences and the rise of direct-to-consumer brands.
Big-box retail effect Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com