McDonaldization describes the process by which principles of fast-food restaurants, such as efficiency, calculability, predictability, and control, dominate various sectors of society. This concept highlights how standardized processes can shape experiences and reduce uniqueness in services and products. Dive into the rest of the article to explore how McDonaldization impacts your daily life and broader societal dynamics.
Table of Comparison
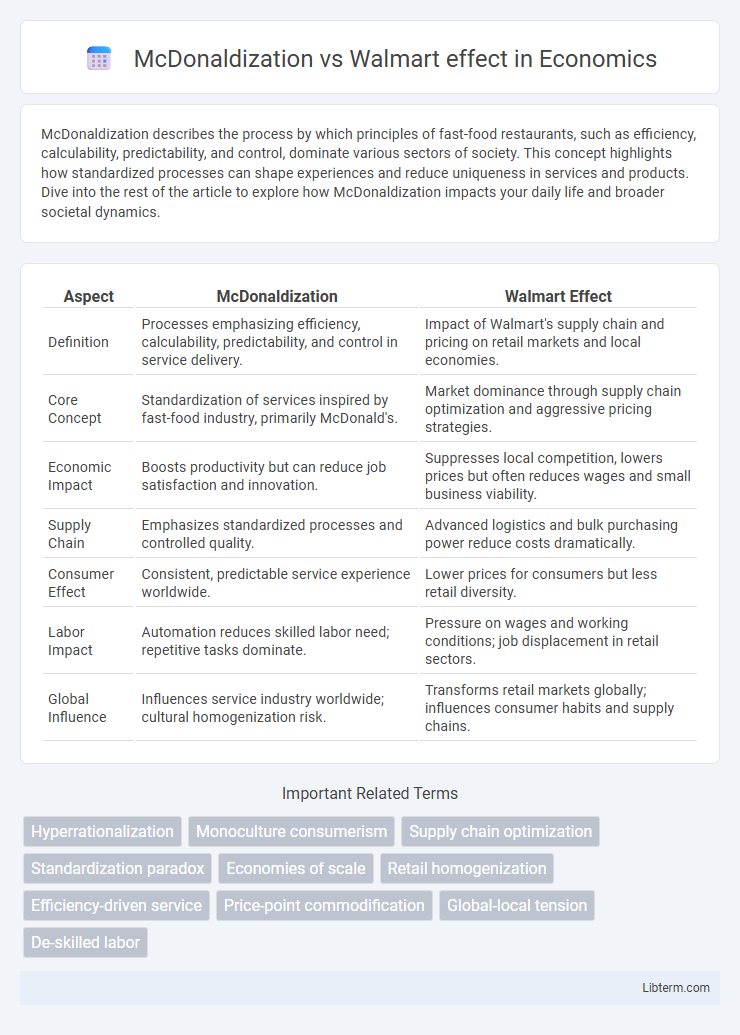
| Aspect | McDonaldization | Walmart Effect |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Processes emphasizing efficiency, calculability, predictability, and control in service delivery. | Impact of Walmart's supply chain and pricing on retail markets and local economies. |
| Core Concept | Standardization of services inspired by fast-food industry, primarily McDonald's. | Market dominance through supply chain optimization and aggressive pricing strategies. |
| Economic Impact | Boosts productivity but can reduce job satisfaction and innovation. | Suppresses local competition, lowers prices but often reduces wages and small business viability. |
| Supply Chain | Emphasizes standardized processes and controlled quality. | Advanced logistics and bulk purchasing power reduce costs dramatically. |
| Consumer Effect | Consistent, predictable service experience worldwide. | Lower prices for consumers but less retail diversity. |
| Labor Impact | Automation reduces skilled labor need; repetitive tasks dominate. | Pressure on wages and working conditions; job displacement in retail sectors. |
| Global Influence | Influences service industry worldwide; cultural homogenization risk. | Transforms retail markets globally; influences consumer habits and supply chains. |
Understanding McDonaldization: Key Concepts
McDonaldization, a concept coined by sociologist George Ritzer, describes the process by which principles of fast-food restaurants--efficiency, calculability, predictability, and control--dominate various sectors of society. This model emphasizes streamlined operations, standardized products, and a focus on quantifiable outcomes to maximize productivity and reduce uncertainty. Understanding these core concepts reveals how McDonaldization shapes consumer behavior, organizational structures, and cultural norms in both retail and service industries.
The Walmart Effect: Definition and Core Principles
The Walmart Effect describes the significant impact Walmart has on local economies, retail markets, and supply chains by leveraging economies of scale, aggressive pricing strategies, and a vast network of suppliers to deliver low prices. Core principles include driving down costs through operational efficiency, exerting bargaining power to influence supplier pricing and practices, and shaping consumer behavior by emphasizing convenience and affordability. This effect often leads to the consolidation of retail sectors, disruption of small businesses, and shifts in labor market dynamics.
Efficiency and Standardization in Modern Business
McDonaldization emphasizes efficiency and standardization by streamlining processes into predictable, uniform services, minimizing time spent on each task to maximize customer throughput. Walmart's effect similarly drives modern business toward cost reduction and operational efficiency through vast supply chain integration and standardized inventory management. Both models prioritize scalability and predictability, leveraging uniform procedures to enhance productivity and reduce variability across locations.
Globalization: How McDonaldization and the Walmart Effect Spread
McDonaldization spreads globalization by standardizing consumer experiences geographically through uniform products, services, and efficient processes across diverse cultures. The Walmart Effect promotes globalization by leveraging massive supply chain networks and economies of scale, pressuring global suppliers to adopt cost-cutting practices and streamline production. Both phenomena drive global market integration, reshaping local economies and consumer behaviors worldwide.
Impact on Consumer Behavior and Choices
McDonaldization shapes consumer behavior by emphasizing efficiency, predictability, and uniformity, leading customers to favor convenience and standardized products. The Walmart effect influences choices through aggressive pricing strategies and extensive product variety, encouraging consumers to prioritize cost savings and one-stop shopping experiences. Both phenomena drive consumers toward homogenized purchasing patterns, reducing differentiation in retail preferences and shopping habits.
Workplace Transformation: Employees Under McDonaldization and the Walmart Effect
Workplace transformation under McDonaldization results in standardized tasks, repetitive workflows, and increased efficiency but often leads to employee alienation and reduced autonomy. The Walmart Effect intensifies labor cost control through aggressive supply chain management and low wages, further pressuring workers with unpredictable schedules and minimal benefits. Together, these models drive a labor environment characterized by high turnover, limited skill development, and constrained worker empowerment.
Economic Consequences for Local Communities
McDonaldization and the Walmart effect both drive economic homogenization in local communities, often leading to reduced diversity in small businesses and job opportunities. McDonaldization emphasizes efficiency and standardized services, which can suppress local entrepreneurship and cultural uniqueness. The Walmart effect results in competitive pricing that undermines local retailers, causing job displacement and altering community economic landscapes.
Cultural Homogenization: Loss of Uniqueness
McDonaldization and the Walmart Effect contribute significantly to cultural homogenization by standardizing consumer experiences and diminishing local uniqueness across global markets. McDonaldization enforces uniformity through predictable, efficiency-driven service models, while the Walmart Effect suppresses local businesses by promoting mass-produced, low-cost goods, eroding regional diversity. Together, these forces accelerate the loss of distinct cultural identities and traditions, leading to a homogenized global consumer culture.
Resistance and Critiques of McDonaldization and Walmartization
Resistance to McDonaldization and Walmartization highlights concerns about cultural homogenization, loss of local businesses, and exploitative labor practices. Critics argue that McDonaldization's emphasis on efficiency and predictability leads to dehumanization and reduced consumer choice, while Walmartization exacerbates income inequality and undermines small retailers through aggressive price competition. Both phenomena face pushback from communities advocating for sustainable local economies and fair labor standards.
The Future of Global Commerce: McDonaldization vs. Walmart Effect
The future of global commerce hinges on the interplay between McDonaldization's emphasis on efficiency, predictability, and control, and the Walmart Effect's drive for cost leadership through massive scale and supply chain optimization. McDonaldization standardizes experiences across markets, promoting uniform consumer expectations, while the Walmart Effect pressures suppliers for ever-lower costs, reshaping global production networks. Together, these forces accelerate globalization, transforming retail landscapes by prioritizing affordability and operational consistency.
McDonaldization Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com