Teacher-centered learning focuses on the instructor as the primary source of knowledge, directing the flow of information and controlling the learning environment to ensure content mastery. This approach emphasizes structured lessons, clear objectives, and rigorous assessment to measure student understanding effectively. Discover how this traditional method can impact Your educational experience by exploring the detailed insights in the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
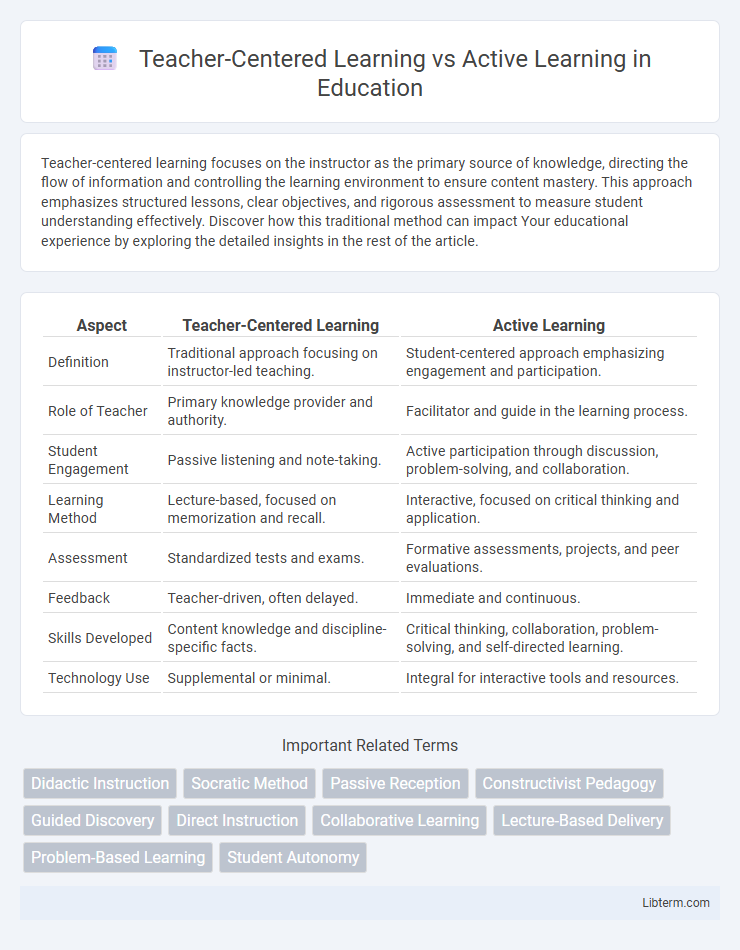
| Aspect | Teacher-Centered Learning | Active Learning |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Traditional approach focusing on instructor-led teaching. | Student-centered approach emphasizing engagement and participation. |
| Role of Teacher | Primary knowledge provider and authority. | Facilitator and guide in the learning process. |
| Student Engagement | Passive listening and note-taking. | Active participation through discussion, problem-solving, and collaboration. |
| Learning Method | Lecture-based, focused on memorization and recall. | Interactive, focused on critical thinking and application. |
| Assessment | Standardized tests and exams. | Formative assessments, projects, and peer evaluations. |
| Feedback | Teacher-driven, often delayed. | Immediate and continuous. |
| Skills Developed | Content knowledge and discipline-specific facts. | Critical thinking, collaboration, problem-solving, and self-directed learning. |
| Technology Use | Supplemental or minimal. | Integral for interactive tools and resources. |
Introduction to Teaching Methodologies
Teacher-Centered Learning emphasizes direct instruction where educators control content delivery, prioritizing structured lessons and standardized assessments. Active Learning engages students through participation, collaboration, and critical thinking activities, fostering deeper understanding and retention. Modern teaching methodologies advocate integrating active learning strategies to enhance student motivation and real-world skill application.
Defining Teacher-Centered Learning
Teacher-centered learning is an educational approach where the instructor holds primary authority, delivering content through lectures and direct instruction to students who play a passive role. This method emphasizes structured curriculum, uniform assessment, and teacher control over learning pace and content. The focus lies on knowledge transmission from teacher to student rather than collaborative or experiential learning processes.
What is Active Learning?
Active learning is an educational approach that engages students directly in the learning process through activities such as discussions, problem-solving, and hands-on projects, promoting deeper understanding and retention of knowledge. Unlike teacher-centered learning, where instruction is primarily lecture-based and passive, active learning encourages collaboration, critical thinking, and real-time feedback. Research shows that active learning improves academic performance, increases student motivation, and develops essential skills for lifelong learning.
Key Differences Between Teacher-Centered and Active Learning
Teacher-centered learning emphasizes direct instruction where the teacher controls the content delivery, focusing on memorization and passive reception of information. Active learning prioritizes student engagement through discussions, problem-solving, and collaboration, fostering critical thinking and deeper understanding. The key difference lies in the role of the student: passive recipient in teacher-centered learning versus active participant in active learning.
Advantages of Teacher-Centered Learning
Teacher-centered learning offers structured guidance, ensuring consistent delivery of core content aligned with curriculum standards, which enhances knowledge retention and clarity. This approach facilitates efficient classroom management and allows teachers to address diverse student needs through direct instruction and immediate feedback. It supports standardized assessment preparation by providing a clear framework and pacing for learning objectives.
Benefits of Active Learning Strategies
Active learning strategies enhance student engagement, improve retention, and foster critical thinking by involving learners in interactive activities such as discussions, problem-solving, and collaborative projects. Unlike teacher-centered learning, active learning shifts the focus from passive reception to active participation, promoting deeper understanding and practical application of knowledge. Research shows that classrooms implementing active learning techniques see increased student motivation and higher academic performance across various subjects.
Challenges of Each Approach
Teacher-centered learning often faces challenges such as limited student engagement and reliance on passive information absorption, which can hinder critical thinking development. Active learning demands significant preparation time, classroom management skills, and can lead to inconsistent learning outcomes if not properly facilitated. Both approaches require balancing content delivery and student participation to optimize educational effectiveness.
Classroom Examples: Teacher-Centered vs Active Learning
Teacher-centered learning often involves lectures where the teacher delivers content while students take notes passively, such as in a traditional history class focused on memorizing dates and events. In contrast, active learning engages students through group discussions, problem-solving activities, or hands-on experiments, like a science class where students collaborate to test hypotheses and analyze results. These classroom examples demonstrate how active learning promotes critical thinking and retention more effectively than passive reception in teacher-centered settings.
Impact on Student Engagement and Outcomes
Teacher-centered learning often results in passive student participation, limiting critical thinking and problem-solving skills development. Active learning strategies, including collaborative projects and interactive discussions, significantly enhance student engagement and improve retention of knowledge. Studies indicate that classrooms implementing active learning report higher academic achievement and increased motivation compared to traditional lecture-based settings.
Choosing the Right Approach for Your Classroom
Teacher-centered learning emphasizes structured instruction and direct guidance, ideal for delivering foundational knowledge efficiently. Active learning fosters student engagement and critical thinking through collaboration and hands-on activities, promoting deeper understanding and retention. Selecting the right approach depends on your classroom goals, student needs, and content complexity to balance structure and participation effectively.
Teacher-Centered Learning Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com