Modular curriculum breaks down subjects into independent units, allowing for flexible learning paths tailored to individual needs. This approach enhances comprehension by focusing on specific topics without the constraints of a fixed syllabus. Discover how modular curriculum can transform Your educational experience by exploring the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
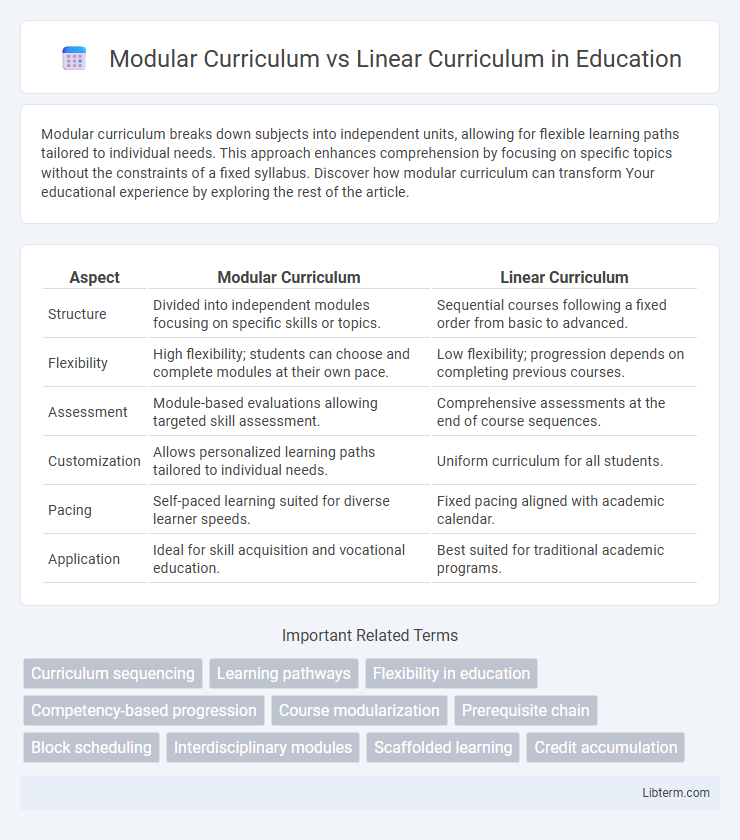
| Aspect | Modular Curriculum | Linear Curriculum |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Divided into independent modules focusing on specific skills or topics. | Sequential courses following a fixed order from basic to advanced. |
| Flexibility | High flexibility; students can choose and complete modules at their own pace. | Low flexibility; progression depends on completing previous courses. |
| Assessment | Module-based evaluations allowing targeted skill assessment. | Comprehensive assessments at the end of course sequences. |
| Customization | Allows personalized learning paths tailored to individual needs. | Uniform curriculum for all students. |
| Pacing | Self-paced learning suited for diverse learner speeds. | Fixed pacing aligned with academic calendar. |
| Application | Ideal for skill acquisition and vocational education. | Best suited for traditional academic programs. |
Introduction to Curriculum Structures
Modular curriculum breaks down subjects into independent units that can be tailored and combined flexibly to meet diverse learning needs, promoting personalized education paths. Linear curriculum follows a sequential, fixed progression where each topic builds on the previous one, ensuring a structured and cumulative knowledge development. Understanding these fundamental curriculum structures helps educators design effective learning experiences aligned with specific educational goals.
Defining Modular Curriculum
Modular Curriculum organizes learning content into independent, self-contained units or modules, allowing students to focus on specific skills or topics at their own pace. Each module is designed to be standalone with clear objectives, assessments, and outcomes, enabling flexible progression through the curriculum. This contrasts with Linear Curriculum, which follows a fixed sequential order where concepts build progressively from one lesson to the next.
Understanding Linear Curriculum
Linear curriculum follows a structured, sequential approach where concepts build progressively from simple to complex, ensuring foundational knowledge before advancing. This method supports consistent skill development by emphasizing a fixed order of topics and clear learning objectives. Understanding linear curriculum is crucial for designing educational programs that prioritize continuity and systematic mastery of content.
Key Differences Between Modular and Linear Approaches
Modular curriculum divides content into independent units allowing flexible learning paths, whereas linear curriculum follows a fixed sequence designed for progressive skill development. Modular approach supports personalized learning and easier updating of individual modules, contrasting with the linear method's emphasis on cumulative knowledge building and structured pacing. Assessment in modular curricula targets specific competencies within modules, while linear curricula rely on comprehensive evaluations after sequential topic completion.
Flexibility and Personalization in Learning
Modular curriculum enhances flexibility by allowing learners to engage with individual modules independently, tailoring their learning paths according to personal interests and pace. Linear curriculum follows a fixed sequence, limiting personalization but ensuring structured progression through topics. Emphasizing modular design supports adaptive learning environments, fostering greater student autonomy and customized educational experiences.
Impact on Student Engagement and Motivation
Modular curriculum enhances student engagement by offering flexible, self-paced learning units that cater to individual interests and learning styles, thereby increasing motivation through personalized progression. In contrast, linear curriculum follows a fixed, sequential structure that may limit students' autonomy, potentially reducing motivation and engagement for those who struggle with or excel beyond the set pace. Research indicates that modular systems promote active learning and deeper involvement, while linear curricula can lead to disengagement when content feels repetitive or misaligned with student needs.
Curriculum Design and Implementation Challenges
Modular curriculum design allows for flexible, self-contained units that students can complete in varying sequences, posing challenges in ensuring consistent learning outcomes and seamless integration across modules. In contrast, linear curriculum follows a fixed, sequential progression that simplifies planning but may limit adaptability and fail to address diverse learner needs. Implementation hurdles for modular curricula include aligning assessment standards and coordinating instructor collaboration, while linear curricula often struggle with student engagement and pacing difficulties.
Assessing Learning Outcomes in Both Models
Assessing learning outcomes in a modular curriculum allows for targeted evaluation of specific skills and knowledge within each module, enabling more precise measurement of student progress and immediate feedback. In contrast, linear curriculum assessment typically evaluates cumulative understanding at the end of a sequence, often emphasizing comprehensive exams or final projects that reflect overall mastery. Modular assessments facilitate flexibility and adaptation to individual learner needs, while linear assessments provide a structured overview of content retention and sequential skill development.
Suitability for Different Educational Contexts
Modular curriculum offers flexibility and adaptability, making it ideal for diverse educational contexts such as vocational training, adult education, and interdisciplinary studies, where learners need customized pacing and content. Linear curriculum suits traditional K-12 and standardized education systems by providing structured progression and clear learning objectives across sequential grade levels. Institutions often select curriculum types based on learner autonomy, subject complexity, and institutional goals to optimize educational outcomes.
Future Trends in Curriculum Development
Future trends in curriculum development emphasize flexible learning pathways, with modular curriculum gaining prominence for its adaptability and personalized learning experiences. Modular design enables integration of interdisciplinary content and micro-credentials, supporting rapid skill acquisition aligned with evolving workforce demands. Linear curriculum remains relevant for foundational knowledge but is increasingly supplemented by modular components to address diverse learner needs in digital and hybrid education environments.
Modular Curriculum Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com