Peer assessment enhances critical thinking and fosters collaborative learning by allowing you to evaluate and reflect on others' work. This process builds constructive feedback skills and promotes deeper understanding of the subject matter. Explore the rest of the article to discover effective strategies for implementing meaningful peer assessments.
Table of Comparison
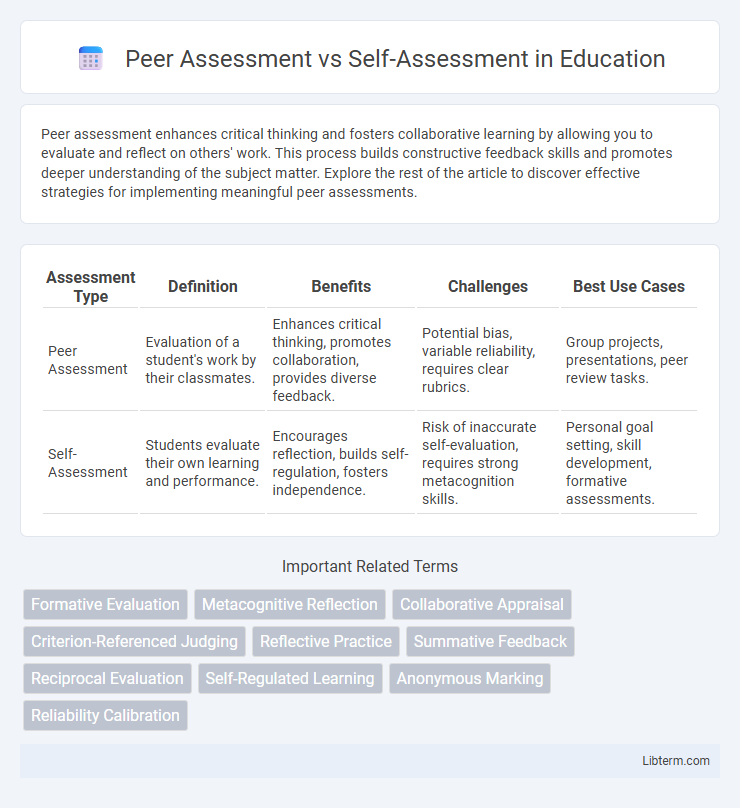
| Assessment Type | Definition | Benefits | Challenges | Best Use Cases |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Peer Assessment | Evaluation of a student's work by their classmates. | Enhances critical thinking, promotes collaboration, provides diverse feedback. | Potential bias, variable reliability, requires clear rubrics. | Group projects, presentations, peer review tasks. |
| Self-Assessment | Students evaluate their own learning and performance. | Encourages reflection, builds self-regulation, fosters independence. | Risk of inaccurate self-evaluation, requires strong metacognition skills. | Personal goal setting, skill development, formative assessments. |
Understanding Peer Assessment: Definition and Purpose
Peer assessment is a collaborative evaluation process where individuals review and provide feedback on each other's work, fostering critical thinking and improving learning outcomes. Its primary purpose is to enhance students' understanding through exposure to diverse perspectives, promote accountability, and develop evaluative skills. This method encourages active engagement and reflection by requiring learners to analyze criteria and apply standards objectively.
What is Self-Assessment? Concepts and Benefits
Self-assessment is a reflective process where individuals evaluate their own work, skills, and learning progress against established criteria or goals. This method enhances metacognitive awareness, encourages autonomy in learning, and fosters critical thinking by allowing individuals to identify strengths and areas for improvement independently. Benefits of self-assessment include increased motivation, personalized feedback, and the development of lifelong learning skills essential for academic and professional growth.
Key Differences Between Peer and Self-Assessment
Peer assessment involves evaluating the work or performance of others, providing external feedback that can reveal new perspectives and identify blind spots. Self-assessment requires individuals to reflect on their own work critically, fostering self-awareness and promoting personal growth through introspection. Key differences include the source of feedback--external in peer assessment versus internal in self-assessment--the potential for bias, with peers offering more objective critique while self-assessments may suffer from over- or underestimation, and the development focus, where peer assessment emphasizes collaborative learning, and self-assessment enhances individual metacognitive skills.
Advantages of Peer Assessment in Learning
Peer assessment enhances learning by promoting critical thinking and deeper understanding as students evaluate others' work, encouraging active engagement with the material. It fosters collaborative skills and diverse perspectives, improving communication and teamwork in academic settings. This method also provides timely, varied feedback, which can be more relatable and motivating than instructor-only evaluation.
Benefits of Self-Assessment for Personal Growth
Self-assessment fosters personal growth by promoting self-awareness, enabling individuals to identify strengths and weaknesses accurately. It encourages reflective thinking, which enhances critical thinking skills and supports continuous learning. This process empowers learners to take ownership of their development, leading to improved motivation and goal-setting capabilities.
Challenges Faced in Peer Assessment
Peer assessment often faces challenges such as bias, where students may grade peers based on personal relationships rather than objective criteria, and inconsistency in evaluation due to varying levels of understanding of the assessment rubric. Difficulties in providing constructive feedback also arise, as peers may lack confidence or the skills needed for clear and helpful critiques. Ensuring fairness and reliability in peer grading systems requires well-structured guidelines and comprehensive training for assessors.
Common Pitfalls in Self-Assessment
Common pitfalls in self-assessment include biases such as overestimation of abilities, lack of objectivity, and difficulty in identifying personal weaknesses accurately. Individuals often struggle with maintaining a realistic perspective, which can lead to inflated self-ratings or overlooking critical areas for improvement. These challenges underscore the importance of combining self-assessment with peer assessment to achieve a more balanced and comprehensive evaluation.
Best Practices for Effective Peer Assessment
Effective peer assessment relies on clear criteria, structured guidelines, and constructive feedback to enhance learning outcomes. Encouraging anonymity and training students in evaluation skills improves objectivity and reduces bias in peer reviews. Implementing iterative peer assessments, combined with teacher oversight, ensures accuracy and promotes deeper engagement with the material.
Enhancing Accuracy in Self-Assessment
Peer assessment offers external feedback that can reveal blind spots, while self-assessment promotes critical reflection by individuals on their own performance. Enhancing accuracy in self-assessment involves training individuals to recognize criteria, use rubrics effectively, and calibrate judgments against established standards. Combining peer insights with systematic self-evaluation techniques leads to more reliable and valid self-assessment outcomes.
Integrating Peer and Self-Assessment: A Balanced Approach
Integrating peer and self-assessment fosters a balanced approach to evaluative feedback by combining external perspectives with personal reflection, enhancing overall learning outcomes. Peer assessment promotes critical thinking and collaborative skills, while self-assessment encourages metacognition and self-regulated learning, creating a complementary dynamic. Research in educational psychology reveals that this integration improves accuracy in grading and deepens student engagement and responsibility for their own progress.
Peer Assessment Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com