Regulate refers to the act of controlling or maintaining standards through rules or laws to ensure order and safety. Effective regulation helps prevent chaos in industries, protect consumers, and promote fair competition. Explore the full article to understand how regulation impacts your daily life and business environment.
Table of Comparison
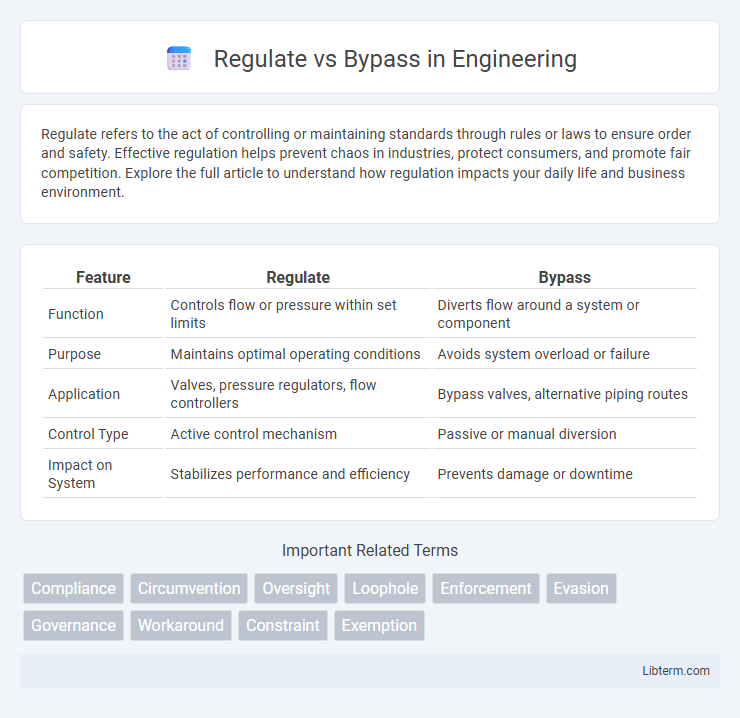
| Feature | Regulate | Bypass |
|---|---|---|
| Function | Controls flow or pressure within set limits | Diverts flow around a system or component |
| Purpose | Maintains optimal operating conditions | Avoids system overload or failure |
| Application | Valves, pressure regulators, flow controllers | Bypass valves, alternative piping routes |
| Control Type | Active control mechanism | Passive or manual diversion |
| Impact on System | Stabilizes performance and efficiency | Prevents damage or downtime |
Introduction to Regulation and Bypass
Regulate involves controlling or managing processes, systems, or behaviors through rules and guidelines to ensure stability and compliance. Bypass refers to the act of circumventing established regulations or controls to achieve a different outcome or gain direct access. Understanding the dynamics between regulation and bypass is essential for managing risk and maintaining operational efficiency in industries such as finance, healthcare, and technology.
Defining Regulation: Purpose and Methods
Regulation refers to the establishment and enforcement of rules or standards by authorities to control behaviors, processes, or technologies within a society or industry. Its purpose is to ensure safety, fairness, and compliance while protecting public interests, typically through methods such as licensing, monitoring, and penalties for violations. Effective regulation balances innovation and risk mitigation by setting clear guidelines and consistent oversight mechanisms.
Understanding Bypass: Techniques and Motivations
Understanding bypass involves exploring techniques that circumvent standard regulatory frameworks to achieve specific goals, often motivated by efficiency, cost reduction, or innovation acceleration. Common bypass methods include leveraging loopholes in existing laws, utilizing offshore jurisdictions, and applying alternative compliance strategies that reduce oversight. These practices are driven by the desire to evade stringent controls while maintaining operational flexibility in competitive markets.
Key Differences Between Regulate and Bypass
Regulate involves controlling or adjusting a system or process to maintain desired levels or outcomes, often through rules or mechanisms. Bypass refers to creating an alternative route or method to avoid the standard pathway, typically to circumvent restrictions or obstacles. Key differences include regulation's emphasis on control and compliance, whereas bypass prioritizes avoidance and alternative solutions.
Legal Implications of Regulation vs Bypass
Regulating a process ensures compliance with established laws, reducing the risk of penalties and legal disputes by adhering to governmental standards and industry-specific regulations. Bypassing regulations can lead to severe legal consequences, including fines, sanctions, and loss of licenses, as it often constitutes a violation of statutory requirements. Legal systems emphasize enforcement mechanisms to uphold regulatory frameworks, highlighting the importance of lawful conduct for organizational legitimacy and risk management.
Ethical Considerations in Regulation and Bypass
Regulating technology ensures accountability, protects user privacy, and upholds societal values by enforcing standards that prevent misuse and discrimination. Bypassing regulations might accelerate innovation but raises ethical concerns such as unchecked data exploitation, increased cybersecurity risks, and erosion of user trust. Balancing ethical considerations requires transparent frameworks that address both the necessity of regulation and the potential consequences of circumventing rules.
Industry Examples: Regulation and Bypass in Action
In the pharmaceutical industry, regulation ensures drug safety and efficacy through rigorous clinical trials and FDA approvals, while companies sometimes bypass regulations by marketing off-label uses or exploiting regulatory loopholes. In the energy sector, government policies regulate emissions standards to curb pollution, yet some firms bypass these by investing in carbon offset projects or relocating operations to countries with looser environmental laws. The financial industry faces strict regulatory frameworks like Dodd-Frank to prevent crises, whereas certain hedge funds may bypass these controls using complex derivatives and offshore structures to avoid scrutiny.
The Impact on Innovation and Progress
Regulate and bypass strategies significantly influence innovation and progress, with regulation often providing structured frameworks that ensure safety, quality, and ethical standards while potentially slowing agility and creative experimentation. Bypass approaches enable rapid development and market entry by avoiding regulatory hurdles, fostering disruptive innovation but raising concerns about untested risks and consumer protection. Balancing regulation and bypass is critical to safeguarding public interest while accelerating technological advancements and fostering competitive markets.
Risks and Consequences of Bypassing Regulations
Bypassing regulations exposes individuals and organizations to significant legal penalties, including fines, sanctions, and potential criminal charges. Ignoring established regulatory frameworks increases operational risks such as safety hazards, financial instability, and damaged reputations. Regulatory compliance ensures accountability and risk mitigation, while evading these rules can lead to severe long-term consequences and loss of stakeholder trust.
Choosing the Right Approach: When to Regulate or Bypass
Choosing the right approach between regulating and bypassing depends on the specific context and desired outcome. Regulating is ideal for ensuring compliance, maintaining safety standards, and protecting public interests in industries such as finance, healthcare, and environmental management. Bypassing may be suitable when innovation or rapid progress is hindered by strict regulations, allowing for agility and experimentation without compromising core ethical or legal standards.
Regulate Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com