Fault tolerance ensures your systems remain operational despite hardware or software failures by detecting and handling errors seamlessly. Implementing robust fault tolerance strategies minimizes downtime and data loss, enhancing overall reliability and user experience. Discover how integrating fault tolerance can safeguard your infrastructure by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
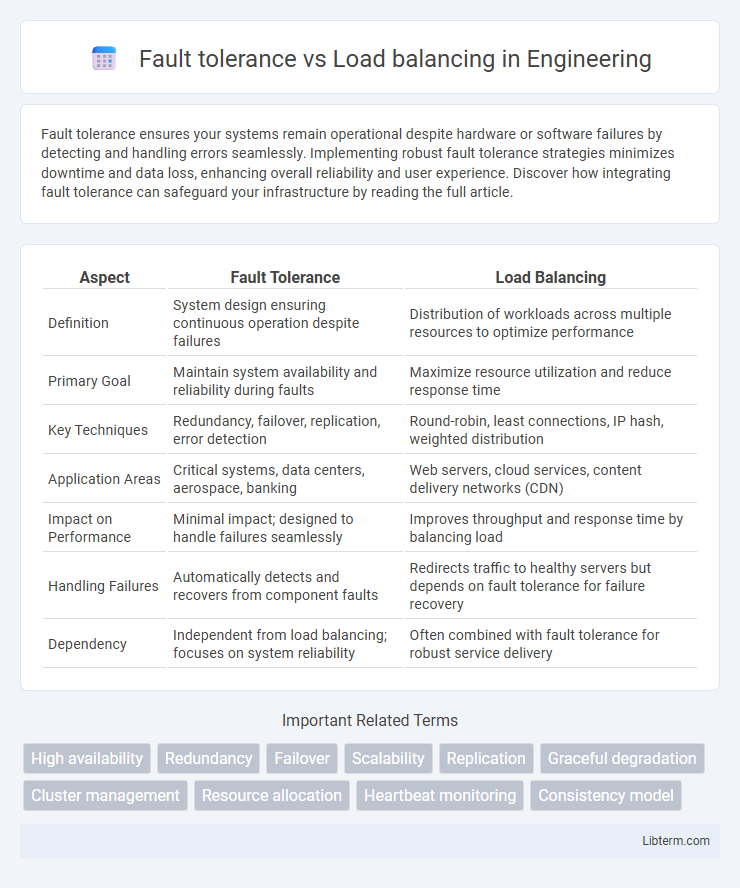
| Aspect | Fault Tolerance | Load Balancing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | System design ensuring continuous operation despite failures | Distribution of workloads across multiple resources to optimize performance |
| Primary Goal | Maintain system availability and reliability during faults | Maximize resource utilization and reduce response time |
| Key Techniques | Redundancy, failover, replication, error detection | Round-robin, least connections, IP hash, weighted distribution |
| Application Areas | Critical systems, data centers, aerospace, banking | Web servers, cloud services, content delivery networks (CDN) |
| Impact on Performance | Minimal impact; designed to handle failures seamlessly | Improves throughput and response time by balancing load |
| Handling Failures | Automatically detects and recovers from component faults | Redirects traffic to healthy servers but depends on fault tolerance for failure recovery |
| Dependency | Independent from load balancing; focuses on system reliability | Often combined with fault tolerance for robust service delivery |
Introduction to Fault Tolerance and Load Balancing
Fault tolerance ensures system reliability by allowing continuous operation despite hardware or software failures, using techniques such as redundancy and error detection. Load balancing distributes network or application traffic across multiple servers to optimize resource use, enhance performance, and prevent overload on any single server. Both fault tolerance and load balancing are critical in maintaining high availability and seamless user experience in cloud computing and distributed systems.
Core Concepts: Fault Tolerance Defined
Fault tolerance is the system's ability to continue operating properly in the event of the failure of some of its components, ensuring uninterrupted service and data integrity. It involves redundant hardware, software, or network pathways to detect and recover from faults automatically without human intervention. Load balancing, while distributing workloads evenly across servers to optimize resource use and prevent overload, primarily addresses performance and scalability rather than system failure resilience.
Core Concepts: What is Load Balancing?
Load balancing is the process of distributing network or application traffic across multiple servers to ensure no single server becomes overwhelmed, thereby optimizing resource use and minimizing response time. It enhances system availability and reliability by efficiently managing workloads and preventing server bottlenecks. Core techniques include round-robin, least connections, and IP hash, each designed to balance traffic based on different criteria to maintain seamless user experiences.
Key Differences Between Fault Tolerance and Load Balancing
Fault tolerance ensures system reliability by automatically detecting and recovering from hardware or software failures, maintaining continuous operation without service disruption. Load balancing distributes network or application traffic evenly across multiple servers or resources to optimize performance, prevent overload, and improve response times. Unlike fault tolerance, which focuses on redundancy and failover mechanisms, load balancing centers on efficient resource utilization and traffic management.
How Fault Tolerance Ensures System Reliability
Fault tolerance ensures system reliability by automatically detecting hardware or software failures and switching to backup resources without interrupting operations. It uses redundant components and error-correcting mechanisms to maintain continuous service and prevent data loss. Effective fault tolerance minimizes downtime and sustains performance despite unexpected faults in distributed systems or cloud infrastructures.
Role of Load Balancing in Performance Optimization
Load balancing plays a critical role in performance optimization by efficiently distributing incoming network traffic across multiple servers, ensuring no single server becomes a bottleneck. This distribution enhances system responsiveness, reduces latency, and maximizes resource utilization, leading to improved application throughput. Fault tolerance complements load balancing by providing system resilience through redundancy, but load balancing specifically targets optimal performance under varying workloads.
Common Techniques for Fault Tolerance
Fault tolerance relies on techniques such as redundancy, failover systems, data replication, and checkpointing to ensure continuous system operation despite hardware or software failures. Load balancing distributes incoming network traffic across multiple servers to optimize resource use, maximize throughput, and prevent any single server from becoming a bottleneck. Common fault tolerance mechanisms include using redundant power supplies, RAID configurations for storage, and heartbeat protocols that monitor system health to trigger automatic failover.
Popular Load Balancing Strategies Explained
Fault tolerance ensures system reliability by automatically detecting and recovering from failures, while load balancing optimizes resource use by distributing workloads across multiple servers. Popular load balancing strategies include Round Robin, which evenly allocates requests; Least Connections, directing traffic to the server with the fewest active sessions; and IP Hash, assigning clients to servers based on their IP addresses for session persistence. These techniques enhance application performance, reduce latency, and maintain uptime in distributed computing environments.
Real-world Applications: When to Use Each Approach
Fault tolerance is crucial in mission-critical systems like aerospace or healthcare, where uptime and error-free operation are mandatory to prevent catastrophic failures. Load balancing is essential in web services and e-commerce platforms to distribute user traffic efficiently across servers, ensuring optimal response times and preventing resource overload. Choosing fault tolerance is ideal for applications requiring continuous availability despite hardware or software faults, whereas load balancing best suits environments needing scalability and performance under varying user loads.
Choosing Between Fault Tolerance and Load Balancing
Choosing between fault tolerance and load balancing depends on system priorities and architecture. Fault tolerance emphasizes system reliability by ensuring continuous operation despite failures using redundancy and failover mechanisms, ideal for mission-critical applications. Load balancing optimizes resource use and response times by distributing workloads across multiple servers, best suited for performance and scalability in high-traffic environments.
Fault tolerance Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com