Efficient chip evacuation is critical for maintaining tool life and machining accuracy by preventing clogging and overheating. Proper chip removal techniques, including optimized cutting parameters and effective coolant use, ensure smooth production flow and high-quality finishes. Discover the best strategies for your chip evacuation needs in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
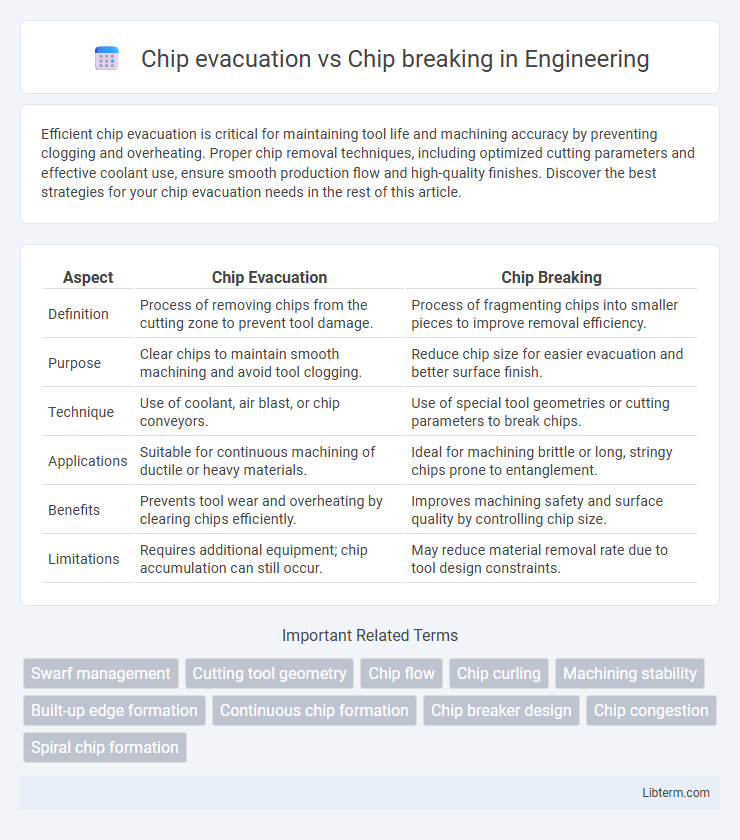
| Aspect | Chip Evacuation | Chip Breaking |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Process of removing chips from the cutting zone to prevent tool damage. | Process of fragmenting chips into smaller pieces to improve removal efficiency. |
| Purpose | Clear chips to maintain smooth machining and avoid tool clogging. | Reduce chip size for easier evacuation and better surface finish. |
| Technique | Use of coolant, air blast, or chip conveyors. | Use of special tool geometries or cutting parameters to break chips. |
| Applications | Suitable for continuous machining of ductile or heavy materials. | Ideal for machining brittle or long, stringy chips prone to entanglement. |
| Benefits | Prevents tool wear and overheating by clearing chips efficiently. | Improves machining safety and surface quality by controlling chip size. |
| Limitations | Requires additional equipment; chip accumulation can still occur. | May reduce material removal rate due to tool design constraints. |
Introduction to Chip Evacuation and Chip Breaking
Chip evacuation and chip breaking are critical processes in machining that enhance tool life and surface finish quality. Chip evacuation refers to the removal of generated chips from the cutting zone to prevent tool clogging and heat buildup, often achieved through coolant flow or chip conveyors. Chip breaking involves fracturing continuous chips into smaller segments, improving chip handling, reducing machine downtime, and ensuring safer operation by minimizing chip entanglement.
Importance of Effective Chip Management
Effective chip management is crucial in machining processes to prevent tool damage, improve surface finish, and maintain operational efficiency. Proper chip evacuation reduces heat buildup and avoids chip recutting, which can degrade tool life and part quality. Implementing efficient chip breaking techniques ensures manageable chip sizes, minimizing machine downtime and enhancing overall productivity.
Mechanisms of Chip Formation in Machining
Chip evacuation involves the removal of continuous chips from the cutting zone to prevent interference with the cutting tool and workpiece, crucial for maintaining machining efficiency and surface quality. Chip breaking refers to the process of fragmenting continuous chips into smaller, manageable segments through tool geometry and cutting conditions, enhancing chip control and safety. Both mechanisms directly influence heat dissipation, tool wear, and machining stability by modulating chip formation dynamics and flow.
What is Chip Evacuation?
Chip evacuation refers to the process of removing metal chips generated during machining operations, ensuring efficient cutting and preventing tool damage. Effective chip evacuation improves surface finish, reduces heat buildup, and maintains machine tool performance by preventing chip re-cutting and clogging. Techniques for chip evacuation include optimized coolant flow, chip conveyors, and chip breakers designed to control chip size and facilitate smooth removal.
Understanding the Process of Chip Breaking
Chip breaking involves fragmenting chips into smaller, manageable pieces to prevent damage to the workpiece and tooling, enhance surface finish, and improve machining efficiency. Various chip breaking techniques include using specialized cutting tool geometries, modifying cutting parameters like feed rate and speed, and employing coolant to facilitate chip control. Effective chip evacuation complements chip breaking by removing the broken chips from the cutting zone, reducing the risk of tool clogging and maintaining optimal cutting conditions.
Key Differences: Chip Evacuation vs Chip Breaking
Chip evacuation involves the removal of chips from the cutting area to prevent tool damage and maintain machining efficiency, whereas chip breaking refers to the process of fragmenting chips into smaller, manageable pieces to facilitate easier evacuation and reduce workpiece surface roughness. Effective chip evacuation relies on optimized coolant flow, tool geometry, and machine setup, while chip breaking is achieved through specific tool designs and cutting parameters that promote chip segmentation. Both processes are critical in maintaining tool life, enhancing machining safety, and improving overall production quality in metalworking operations.
Factors Affecting Chip Evacuation Efficiency
Chip evacuation efficiency in machining is influenced by cutting speed, feed rate, and tool geometry, which directly affect chip size and shape. Proper coolant application and machine tool rigidity also play crucial roles in preventing chip entanglement and ensuring smooth chip flow. Material properties, such as ductility and thermal conductivity, impact chip formation and evacuation, making them essential factors in optimizing machining processes.
Techniques to Achieve Optimal Chip Breaking
Chip evacuation and chip breaking are critical in machining to enhance tool life and surface finish. Effective chip breaking techniques include using specialized tool geometries such as chip breakers, controlling cutting parameters like feed rate and speed, and applying coolant to reduce temperature and prevent chip clogging. Optimizing tool rake angles and incorporating helical or segmented blades further promote efficient chip formation and evacuation, minimizing machine downtime.
Impact on Tool Life and Surface Quality
Chip evacuation significantly improves tool life by preventing chip clogging and reducing heat buildup, which minimizes tool wear during cutting operations. Effective chip breaking enhances surface quality by producing smaller, manageable chips that reduce workpiece damage and promote smoother finishes. Optimizing both chip evacuation and chip breaking is crucial for maintaining tool integrity and achieving high-precision surface results in machining processes.
Best Practices for Improved Chip Control
Effective chip evacuation prevents tool damage and workpiece surface defects by ensuring smooth chip flow away from the cutting zone. Implementing optimized chip breaking techniques, such as selecting appropriate tool geometry and cutting parameters, reduces long chip formation, improving machining stability. Using coolant strategically enhances chip removal, while maintaining correct feed rates and speeds promotes consistent chip size for enhanced tool life and surface finish.
Chip evacuation Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com