Frame action captures dynamic movements within a scene, emphasizing visual storytelling through carefully composed shots. Effective framing directs the viewer's attention, enhancing the emotional impact and clarity of the narrative. Explore the rest of this article to master techniques that will elevate your visual storytelling skills.
Table of Comparison
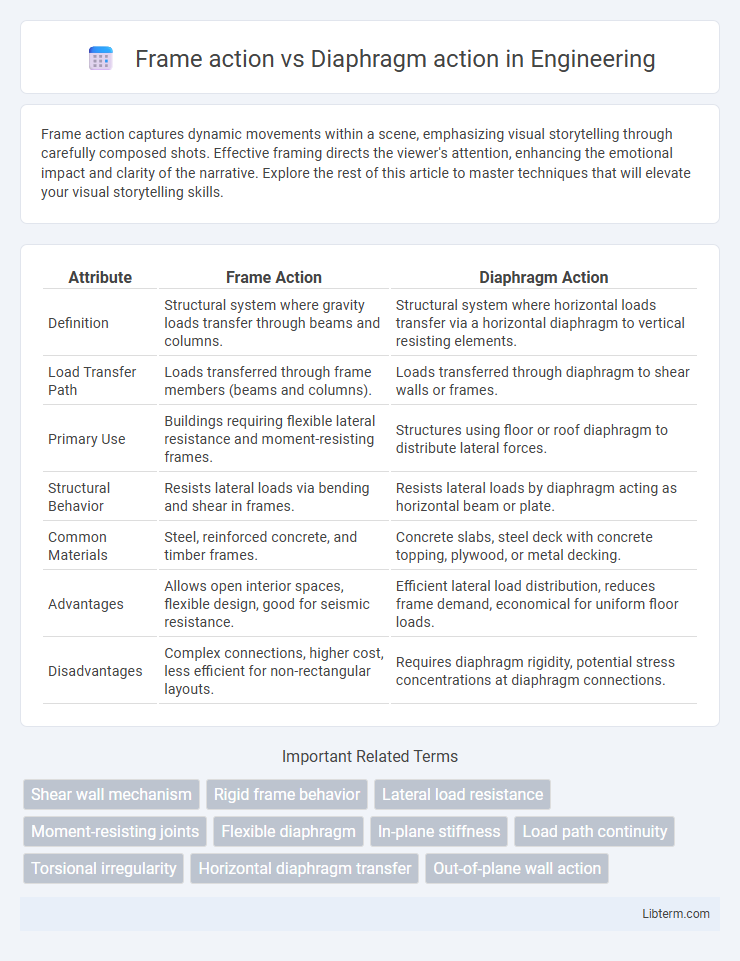
| Attribute | Frame Action | Diaphragm Action |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Structural system where gravity loads transfer through beams and columns. | Structural system where horizontal loads transfer via a horizontal diaphragm to vertical resisting elements. |
| Load Transfer Path | Loads transferred through frame members (beams and columns). | Loads transferred through diaphragm to shear walls or frames. |
| Primary Use | Buildings requiring flexible lateral resistance and moment-resisting frames. | Structures using floor or roof diaphragm to distribute lateral forces. |
| Structural Behavior | Resists lateral loads via bending and shear in frames. | Resists lateral loads by diaphragm acting as horizontal beam or plate. |
| Common Materials | Steel, reinforced concrete, and timber frames. | Concrete slabs, steel deck with concrete topping, plywood, or metal decking. |
| Advantages | Allows open interior spaces, flexible design, good for seismic resistance. | Efficient lateral load distribution, reduces frame demand, economical for uniform floor loads. |
| Disadvantages | Complex connections, higher cost, less efficient for non-rectangular layouts. | Requires diaphragm rigidity, potential stress concentrations at diaphragm connections. |
Understanding Frame Action: Definition and Fundamentals
Frame action refers to the mechanical system in firearms where the trigger and hammer are integrated within the frame, allowing for a consistent and often smoother trigger pull. This design contrasts with diaphragm action by emphasizing the alignment and interaction of internal components within a rigid frame structure, enhancing reliability and ease of maintenance. Understanding frame action fundamentals involves recognizing the role of the trigger mechanism, sear engagement, and hammer movement enclosed by the firearm's frame.
Diaphragm Action Explained: Basics and Importance
Diaphragm action in valves utilizes a flexible membrane to regulate fluid flow, ensuring a tight seal and reducing leakage risks compared to frame action valves. This type of valve is crucial in industries requiring sterile and contamination-free environments, such as pharmaceuticals and food processing. Its design allows efficient control of corrosive or abrasive fluids, enhancing operational longevity and reliability.
Structural Roles: Frame Action vs Diaphragm Action
Frame action transfers lateral loads through a building's skeleton of beams and columns, relying on the rigidity and connections of the frame to resist forces such as wind and seismic activity. Diaphragm action involves horizontal structural elements like floors and roofs acting as rigid planes that distribute lateral loads to vertical resisting components, ensuring load path continuity. Combining frame and diaphragm actions enhances overall structural stability and load distribution efficiency in multi-story buildings.
Load Distribution Mechanisms in Buildings
Frame action in buildings distributes loads primarily through interconnected beams and columns that transfer forces vertically and horizontally, providing rigidity and resistance to bending and shear. Diaphragm action involves horizontal structural elements, such as floors or roofs, which distribute lateral loads to vertical resisting systems like shear walls or frames by acting as rigid or semi-rigid plates. Effective load distribution mechanisms in frame action rely on moment-resisting connections, while diaphragm action depends on the stiffness and continuity of the horizontal planes to ensure lateral stability.
Key Differences Between Frame and Diaphragm Actions
Frame action guitars feature a solid wood center block that reduces feedback and provides sustain, making them ideal for rock and jazz genres. Diaphragm action, or chambered body guitars, utilize hollowed cavities within the body to enhance resonance and produce a warmer, more acoustic-like tone. The key difference lies in construction: frame actions emphasize stability and sustain through a solid block, while diaphragm actions prioritize resonance and tonal depth via chambered design.
Applications of Frame Action in Structural Design
Frame action in structural design is commonly applied in multi-story buildings and bridges where load distribution through rigid connections enhances overall stability and stiffness. It efficiently transfers lateral loads such as wind and seismic forces, making it ideal for high-rise construction and infrastructure requiring robust earthquake resistance. The interconnected beams and columns in frame action systems provide flexibility in architectural design while ensuring structural integrity under dynamic conditions.
Diaphragm Action in Seismic and Wind Resistance
Diaphragm action in seismic and wind resistance involves the horizontal structural component, such as floors or roofs, acting as a stiff diaphragm to transfer lateral loads to vertical resisting elements like shear walls or frames. This action ensures the distribution of wind or seismic forces across the structure, reducing differential movement and enhancing overall stability. Compared to frame action, diaphragm action effectively coordinates load transfer over large areas, minimizing torsional effects and improving the building's dynamic response under lateral loading conditions.
Material Selection Impact on Frame and Diaphragm Actions
Material selection critically influences frame and diaphragm actions in structural engineering, dictating stiffness, strength, and overall load distribution. Steel frames, due to their high ductility and tensile strength, enhance frame action by effectively resisting lateral loads through bending and shear. In contrast, diaphragms composed of reinforced concrete or composite materials provide rigidity essential for transferring lateral loads to vertical resisting elements, with material stiffness directly affecting shear transfer efficiency and deformation behavior.
Common Design Challenges and Solutions
Frame action and diaphragm action valves both face common design challenges such as achieving optimal sealing performance under varying pressure and temperature conditions. Addressing these issues involves selecting resilient seat materials and precise machining to ensure tight shutoff and minimize leakage. Incorporating flexible diaphragm materials and robust frame structures enhances durability, allowing valves to maintain reliable operation in demanding industrial environments.
Choosing the Right Structural System: Practical Considerations
Choosing between frame action and diaphragm action depends on factors such as building height, lateral load intensity, and architectural layout. Frame action offers rigidity and flexibility for taller structures, efficiently resisting wind and seismic forces through moment-resisting frames. Diaphragm action relies on horizontal diaphragms like floors or roofs to transfer lateral loads to vertical resisting elements, making it ideal for low to mid-rise buildings with well-distributed load paths.
Frame action Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com