Idle time refers to periods when resources, equipment, or personnel are not actively engaged in productive activities, leading to potential inefficiencies in operations. Managing idle time effectively can improve productivity, reduce operational costs, and enhance overall workflow efficiency. Explore the rest of the article to discover strategies to minimize idle time and optimize your business performance.
Table of Comparison
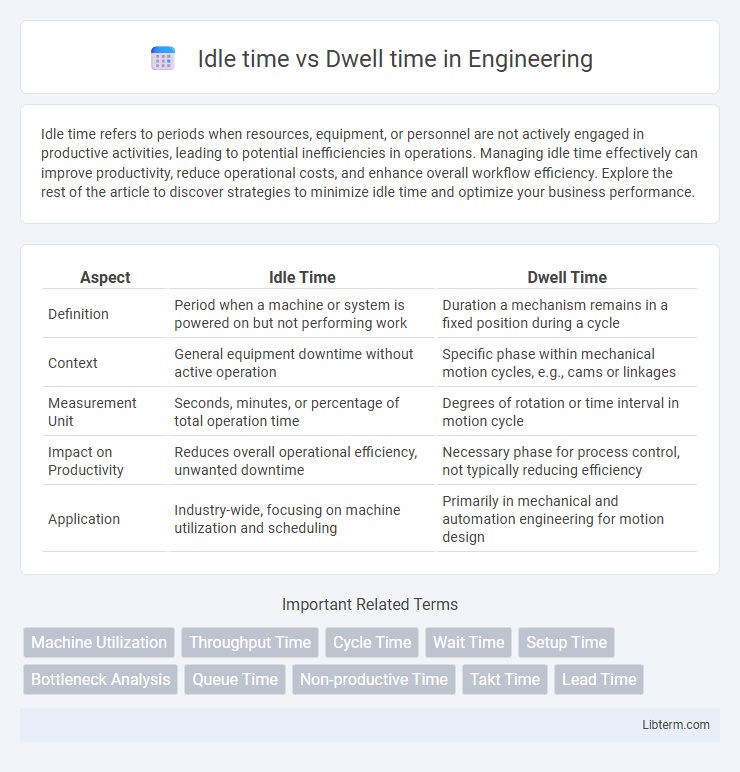
| Aspect | Idle Time | Dwell Time |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Period when a machine or system is powered on but not performing work | Duration a mechanism remains in a fixed position during a cycle |
| Context | General equipment downtime without active operation | Specific phase within mechanical motion cycles, e.g., cams or linkages |
| Measurement Unit | Seconds, minutes, or percentage of total operation time | Degrees of rotation or time interval in motion cycle |
| Impact on Productivity | Reduces overall operational efficiency, unwanted downtime | Necessary phase for process control, not typically reducing efficiency |
| Application | Industry-wide, focusing on machine utilization and scheduling | Primarily in mechanical and automation engineering for motion design |
Understanding Idle Time and Dwell Time
Idle time refers to periods when equipment or personnel are not actively engaged in productive tasks, often caused by delays or waiting times during operations. Dwell time specifically measures the duration an asset, such as a vehicle or container, remains stationary at a particular location, like a loading dock or warehouse, before proceeding to the next activity. Understanding idle time and dwell time is critical for optimizing operational efficiency, reducing bottlenecks, and improving resource utilization in logistics and manufacturing environments.
Key Differences Between Idle Time and Dwell Time
Idle time refers to the period when resources, such as machinery or employees, are available but not actively engaged in productive tasks, causing potential inefficiencies. Dwell time specifically measures the duration a vehicle or container remains stationary at a location, often impacting logistics and supply chain performance. The key difference lies in idle time being a broader concept of non-productive waiting across various industries, whereas dwell time is focused on transportation and material handling contexts.
Causes of Idle Time in Operations
Idle time in operations primarily results from equipment breakdowns, lack of raw materials, and workforce shortages, which halt production and reduce efficiency. Inefficient scheduling and machine setup delays further contribute to idle periods, impacting overall throughput. Addressing these causes through preventive maintenance, supply chain optimization, and workforce management is essential to minimize idle time and improve operational performance.
Factors Leading to Increased Dwell Time
Factors leading to increased dwell time include prolonged loading of web pages due to large multimedia content, slow server response times, and inefficient site navigation that causes users to spend more time searching for information. High dwell time can also result from engaging or complex content that requires additional reading or interaction. Optimizing page speed, improving user interface design, and providing clear content structure are essential to manage dwell time effectively.
Measuring Idle Time: Methods and Metrics
Measuring idle time involves tracking periods when equipment or employees are available but not actively productive, using methods like time studies, sensor data, and automated tracking software. Key metrics include total idle time, idle time percentage relative to total operational time, and frequency of idle instances, which help identify inefficiencies and optimize resource allocation. Accurate measurement of idle time enables better scheduling, maintenance planning, and overall productivity improvements in manufacturing and service environments.
Calculating Dwell Time: Tools and Techniques
Calculating dwell time involves analyzing user engagement metrics through tools such as Google Analytics, heatmaps, and session replay software to track the precise duration users spend actively interacting with a webpage or application. Techniques like event tracking and time-stamped logs enable businesses to distinguish between idle time and true engagement, providing a clearer understanding of user behavior. Advanced methods including machine learning algorithms can further refine dwell time calculation by filtering out inactive periods, thereby improving the accuracy of performance insights.
The Impact of Idle Time vs Dwell Time on Productivity
Idle time, often characterized by unproductive periods where workers or machines are unable to perform tasks, directly reduces operational efficiency and overall productivity in manufacturing and service environments. Dwell time, referring to the interval between process steps or the duration a product remains idle at a workstation, can indicate bottlenecks or inefficiencies in workflow management, leading to increased cycle times and lower throughput. Minimizing both idle and dwell times through optimized scheduling, predictive maintenance, and process redesign significantly enhances productivity by maximizing resource utilization and reducing delays.
Strategies to Minimize Idle Time
To minimize idle time in manufacturing or service operations, businesses implement strategies such as optimizing workforce scheduling, deploying real-time monitoring systems, and enhancing equipment maintenance routines. Leveraging predictive analytics helps identify bottlenecks before they occur, ensuring smoother transitions between tasks and reducing unnecessary delays. Efficient material handling and streamlined communication among teams also contribute significantly to lowering idle time and increasing overall productivity.
Approaches to Reduce Dwell Time
Reducing dwell time involves optimizing process flow through techniques such as lean manufacturing and Just-In-Time (JIT) inventory management, which minimize waiting periods and streamline operations. Implementing predictive analytics and IoT sensors enables real-time monitoring and proactive maintenance, preventing bottlenecks and equipment idle time. Enhancing workforce training and scheduling ensures tasks are completed efficiently, further decreasing overall dwell time in production or logistics environments.
Optimizing Processes: Balancing Idle and Dwell Time
Optimizing processes requires balancing idle time and dwell time to enhance operational efficiency and reduce waste. Idle time represents periods when resources or equipment are not in use, while dwell time indicates the duration items or materials remain stationary within a process. Minimizing idle time through predictive maintenance and streamlining workflows, alongside reducing dwell time by accelerating transitions and improving inventory management, leads to smoother production cycles and increased throughput.
Idle time Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com