Lip seals are essential components that prevent fluid leakage in hydraulic systems by creating a tight barrier between moving parts. Their design ensures durability and efficiency, reducing maintenance needs and enhancing system performance. Discover how choosing the right lip seal can protect Your equipment and extend its lifespan by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
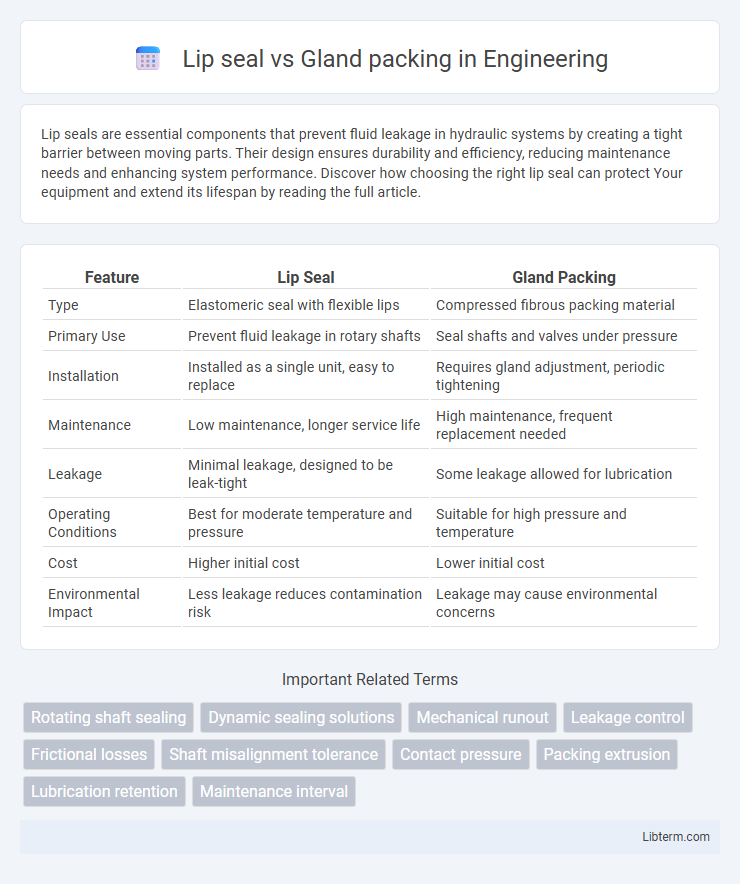
| Feature | Lip Seal | Gland Packing |
|---|---|---|
| Type | Elastomeric seal with flexible lips | Compressed fibrous packing material |
| Primary Use | Prevent fluid leakage in rotary shafts | Seal shafts and valves under pressure |
| Installation | Installed as a single unit, easy to replace | Requires gland adjustment, periodic tightening |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance, longer service life | High maintenance, frequent replacement needed |
| Leakage | Minimal leakage, designed to be leak-tight | Some leakage allowed for lubrication |
| Operating Conditions | Best for moderate temperature and pressure | Suitable for high pressure and temperature |
| Cost | Higher initial cost | Lower initial cost |
| Environmental Impact | Less leakage reduces contamination risk | Leakage may cause environmental concerns |
Introduction to Lip Seal and Gland Packing
Lip seals provide effective sealing for rotary shafts using a flexible elastomer lip that maintains contact with the shaft, minimizing leakage and contamination. Gland packing employs braided or woven materials compressed into a stuffing box around a shaft, creating a seal primarily used in pumps and valves. Both methods are essential for maintaining system integrity but differ in design, application, and maintenance requirements.
How Lip Seals Work
Lip seals function by utilizing a flexible elastomer lip that maintains continuous contact with a rotating or reciprocating shaft, creating a barrier to prevent fluid leakage. The sealing lip is typically supported by a garter spring to ensure consistent pressure against the shaft, adapting to shaft misalignments or wear. This design enables effective sealing in dynamic applications by balancing low friction with high resistance to contaminants.
Mechanism of Gland Packing
Gland packing functions through the compression of braided or woven fibers around a shaft, creating a tight seal that prevents fluid leakage in pumps and valves. The packing material, often impregnated with lubricants, forms a barrier that balances pressure without damaging the rotating shaft. Unlike lip seals, which rely on elastomeric lips to maintain contact, gland packing requires periodic adjustment to maintain compression and sealing efficiency.
Key Differences Between Lip Seal and Gland Packing
Lip seals offer superior sealing performance with less friction and wear compared to gland packing, which requires frequent adjustment and lubrication. Lip seals provide a more compact, maintenance-free solution suitable for high-speed applications, while gland packing is often used in low-speed or heavy-duty equipment where leakage control is less critical. The materials of lip seals typically include elastomers like nitrile or Viton, whereas gland packing utilizes braided fibers or PTFE for sealing.
Advantages of Lip Seals
Lip seals provide superior sealing performance by maintaining constant contact with rotating shafts, effectively preventing fluid leakage and contamination. Their design offers low friction and minimal wear, resulting in longer service life and reduced maintenance costs compared to gland packing. Lip seals are also easier to install and do not require periodic adjustments, enhancing operational efficiency in various industrial applications.
Advantages of Gland Packing
Gland packing offers superior sealing performance in high-pressure and high-temperature applications, providing a reliable solution for dynamic equipment such as pumps and valves. It is cost-effective, easy to install, and maintain, ensuring minimal downtime and extended service life. The adaptability of gland packing materials to various chemical environments enhances its versatility across multiple industrial processes.
Common Applications of Lip Seals
Lip seals are commonly used in automotive engines, hydraulic systems, and pumps due to their efficient sealing against oils and fluids under moderate pressure and speed. These seals are preferred in applications where minimal friction and wear resistance are critical, such as in rotating shafts and gearboxes. Compared to gland packing, lip seals provide superior leakage control and longer service life in dynamic sealing environments.
Typical Uses for Gland Packing
Gland packing is commonly used in industrial applications involving pumps, valves, and compressors where moderate sealing performance is required under varying pressures and temperatures. It is ideal for sealing rotating or reciprocating shafts in chemical, petrochemical, and water treatment plants due to its adaptability and cost-effectiveness. Typical uses of gland packing include sealing slurry pumps, gate valves, and agitators where leakage control and ease of maintenance are critical.
Factors to Consider When Choosing Between Lip Seal and Gland Packing
When choosing between lip seal and gland packing, consider factors such as operating temperature, pressure, and shaft speed, as lip seals typically perform better in high-speed applications with moderate pressure and temperature. Gland packing is preferred for high-pressure environments and slower shaft speeds due to its adjustable compression properties and ability to handle shaft misalignment. Maintenance requirements and leakage tolerance also influence the choice, with lip seals offering lower maintenance and gland packing allowing for controlled leakage to maintain lubrication.
Conclusion: Which Is Right for Your Application?
Lip seals offer superior efficiency with low friction and minimal leakage, making them ideal for high-speed rotary shafts in automotive and industrial machinery. Gland packing provides versatility and reliability for static or slow-moving shafts, accommodating a wide range of temperatures and pressures in pumps and valves. Choosing the right seal depends on your application's speed, pressure, temperature, and maintenance preferences to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
Lip seal Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com