Process time refers to the duration required to complete a specific task or operation within a system or workflow. Efficient management of process time can significantly enhance productivity and reduce costs in various industries. Discover how optimizing your process time can transform your business by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
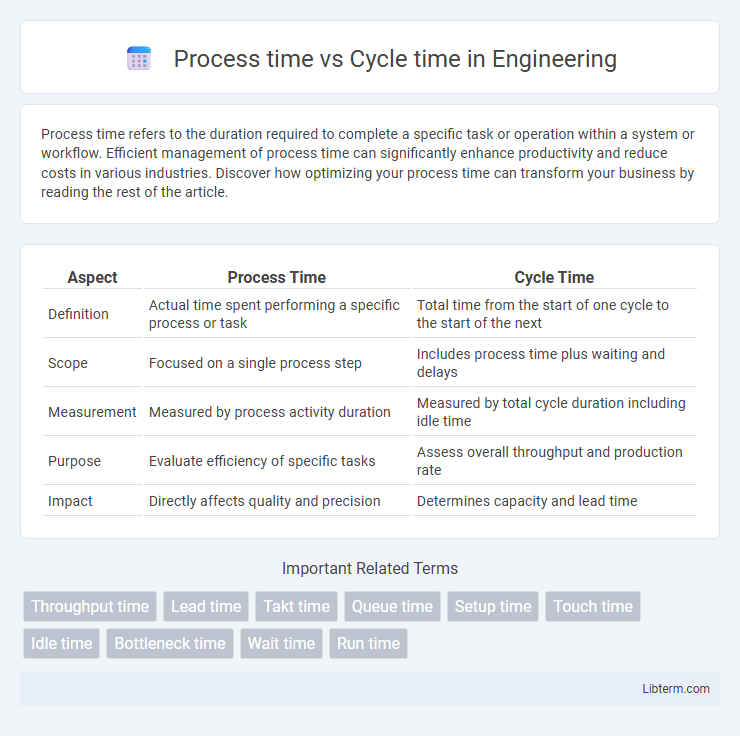
| Aspect | Process Time | Cycle Time |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Actual time spent performing a specific process or task | Total time from the start of one cycle to the start of the next |
| Scope | Focused on a single process step | Includes process time plus waiting and delays |
| Measurement | Measured by process activity duration | Measured by total cycle duration including idle time |
| Purpose | Evaluate efficiency of specific tasks | Assess overall throughput and production rate |
| Impact | Directly affects quality and precision | Determines capacity and lead time |
Understanding Process Time and Cycle Time
Process time refers to the actual duration spent on executing a specific task within a workflow, excluding any waiting or idle periods. Cycle time encompasses the total elapsed time from the beginning to the end of a process, including both processing time and any delays or wait times between tasks. Understanding the distinction between process time and cycle time is crucial for optimizing operational efficiency and identifying bottlenecks in production or service delivery.
Key Differences Between Process Time and Cycle Time
Process time measures the total duration required to complete a specific task or operation within a workflow, highlighting the active work period on a single unit. Cycle time represents the entire elapsed time from the start of one unit to the start of the next unit, including both processing and waiting times between units. Key differences between process time and cycle time include that process time focuses solely on active work, while cycle time encompasses all delays and idle times, directly impacting throughput and efficiency in manufacturing and service processes.
Importance of Measuring Time in Operations
Measuring process time and cycle time is critical for optimizing operational efficiency and identifying bottlenecks in production workflows. Process time captures the duration required to complete a specific task, while cycle time measures the total time to produce one unit from start to finish, enabling accurate throughput analysis. Accurate time measurement enhances resource allocation, reduces lead times, and supports continuous improvement initiatives in manufacturing and service industries.
How Process Time Impacts Workflow Efficiency
Process time directly influences workflow efficiency by determining the duration each task occupies within a cycle, with shorter process times enabling faster task completion and higher throughput. Reducing process time minimizes bottlenecks and idle periods, thereby improving overall productivity and resource utilization. Accurate measurement and optimization of process time help streamline operations, leading to enhanced efficiency and cost savings in manufacturing and business processes.
The Role of Cycle Time in Production Optimization
Cycle time directly impacts production optimization by defining the total time required to complete one production cycle, including processing and waiting times. Minimizing cycle time enhances throughput, reduces bottlenecks, and improves overall equipment effectiveness (OEE). Accurate measurement and continuous reduction of cycle time contribute to cost efficiency and faster market delivery.
Advantages of Reducing Process and Cycle Times
Reducing process time and cycle time enhances operational efficiency by minimizing delays and increasing throughput, enabling faster product delivery and improved customer satisfaction. Shorter times also lead to lower operational costs and better resource utilization, fostering competitive advantage and higher profitability. Streamlined processes contribute to agility in responding to market changes, allowing businesses to innovate and adapt rapidly.
Methods for Calculating Process Time
Process time refers to the actual time spent working on a product or service, excluding waiting or idle periods, and can be calculated by summing the durations of all active work steps within a workflow. Methods for calculating process time include time studies, where direct observation and stopwatch measurements capture work activities, and analysis of process logs or digital timestamps that record start and end times of tasks. Process time differs from cycle time, which encompasses the total elapsed time from the start to the end of a process, including both active work and waiting intervals.
Techniques to Measure Cycle Time Accurately
Accurately measuring cycle time involves techniques such as time tracking with digital timers, video analysis for observing each specific task, and using software tools that automate data collection in manufacturing or service processes. Implementing value stream mapping helps identify bottlenecks and inefficiencies within the cycle, ensuring precise measurement of process phases. Statistical process control (SPC) charts also monitor variations in cycle time, enabling continuous improvement in operational workflows.
Process Time vs Cycle Time: Real-World Examples
Process time measures the total duration required to complete a specific task, while cycle time represents the interval between the start of one process and the start of the next. In manufacturing, a machining process with a process time of 10 minutes may have a cycle time of 15 minutes due to setup and wait times. Real-world applications in software development show process time as actual coding duration, whereas cycle time includes code review and deployment delays, affecting overall project flow.
Best Practices to Balance Process and Cycle Times
Balancing process time and cycle time requires streamlining workflows to eliminate bottlenecks and reduce non-value-added activities. Utilize process mapping and time-tracking tools to identify inefficiencies and standardize procedures that align cycle times with desired output rates. Implement continuous improvement methodologies like Lean and Six Sigma to optimize both throughput and quality, ensuring that process time supports consistent, predictable cycle times.
Process time Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com