DeviceNet is an industrial network protocol designed for communication between control devices and sensors in automation systems. It simplifies device integration and enhances real-time data exchange, improving overall manufacturing efficiency. Explore the rest of this article to understand how DeviceNet can optimize your industrial communication needs.
Table of Comparison
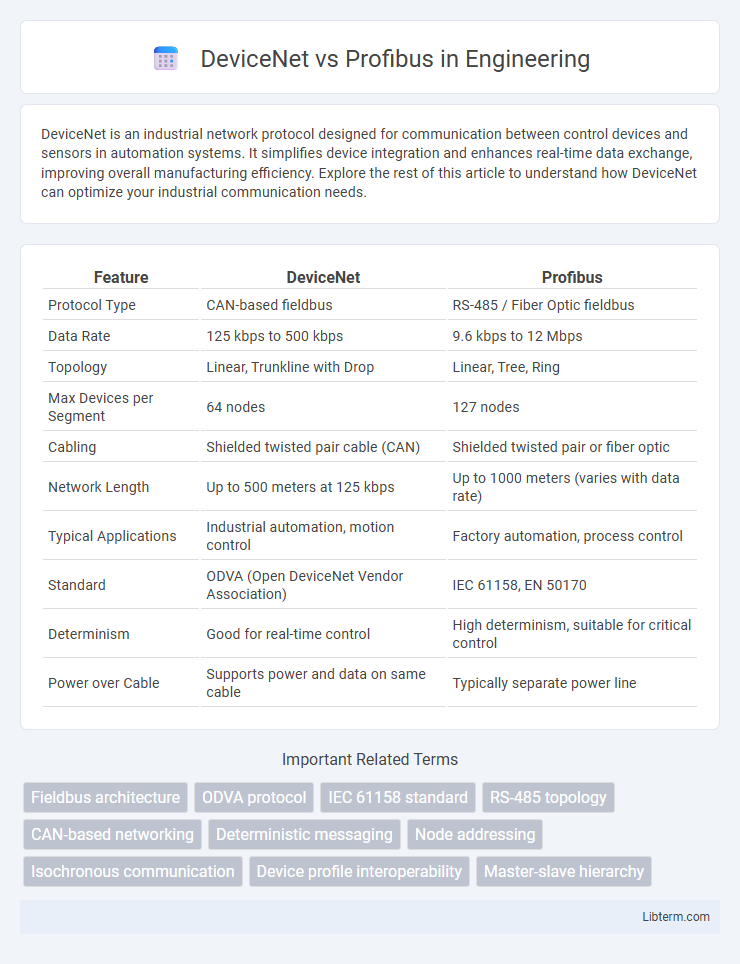
| Feature | DeviceNet | Profibus |
|---|---|---|
| Protocol Type | CAN-based fieldbus | RS-485 / Fiber Optic fieldbus |
| Data Rate | 125 kbps to 500 kbps | 9.6 kbps to 12 Mbps |
| Topology | Linear, Trunkline with Drop | Linear, Tree, Ring |
| Max Devices per Segment | 64 nodes | 127 nodes |
| Cabling | Shielded twisted pair cable (CAN) | Shielded twisted pair or fiber optic |
| Network Length | Up to 500 meters at 125 kbps | Up to 1000 meters (varies with data rate) |
| Typical Applications | Industrial automation, motion control | Factory automation, process control |
| Standard | ODVA (Open DeviceNet Vendor Association) | IEC 61158, EN 50170 |
| Determinism | Good for real-time control | High determinism, suitable for critical control |
| Power over Cable | Supports power and data on same cable | Typically separate power line |
Introduction to Industrial Communication Protocols
DeviceNet and Profibus are industrial communication protocols extensively used for automation and control systems in manufacturing environments. DeviceNet, based on CAN (Controller Area Network) technology, offers fast and reliable communication primarily for device-level networking, facilitating simple integration of sensors and actuators. Profibus supports both process and factory automation with a broader range of communication speeds and topologies, providing robust interoperability between controllers, field devices, and instrumentation across complex industrial networks.
Overview of DeviceNet
DeviceNet is an open industrial network protocol based on the Controller Area Network (CAN) standard, widely used for real-time control and communication between automation devices such as sensors, actuators, and programmable logic controllers (PLCs). It supports a maximum data rate of 500 kbps and allows for simple device integration and network scalability with its multi-master architecture. DeviceNet excels in environments requiring robust communication with low wiring complexity and cost efficiency, making it suitable for discrete manufacturing applications.
Overview of Profibus
Profibus is a robust industrial communication protocol widely used in automation for high-speed data exchange between controllers and field devices. It supports various network topologies such as line, tree, and star, enabling flexible and scalable system design. Profibus provides real-time performance and deterministic communication, making it ideal for complex manufacturing processes and process control applications.
DeviceNet vs Profibus: Technical Specifications
DeviceNet operates on a CAN (Controller Area Network) protocol with data rates up to 500 kbps and supports a maximum network length of 500 meters at 125 kbps, using a simple wiring topology with up to 64 nodes per network segment. Profibus, specifically Profibus DP, utilizes a token-passing protocol with data rates reaching 12 Mbps and allows network lengths up to 1.2 kilometers depending on the baud rate, supporting up to 126 devices per segment with more complex cabling options like RS-485 or fiber optic. DeviceNet is optimized for device-level communication with robust peer-to-peer messaging and simplified wiring, whereas Profibus excels in factory automation requiring higher data throughput and deterministic cycle times.
Network Topologies and Scalability
DeviceNet supports a linear bus topology that simplifies wiring and reduces installation costs, making it ideal for smaller, less complex networks. Profibus offers greater flexibility with star, tree, and ring topologies, enhancing redundancy and fault tolerance in large industrial environments. Scalability in Profibus exceeds DeviceNet due to its support for longer distances, higher node counts, and faster data rates, enabling extensive automation networks.
Data Transmission Speed and Performance Comparison
DeviceNet operates at data transmission speeds up to 500 kbps, suitable for simple control applications with moderate performance requirements. Profibus offers significantly higher speeds, reaching up to 12 Mbps, enabling faster communication and improved performance for complex and real-time industrial automation systems. The higher data rate of Profibus supports extensive device networks and time-critical processes, making it more efficient for large-scale or high-speed applications compared to DeviceNet.
Compatibility and Integration
DeviceNet and Profibus differ significantly in compatibility and integration, as DeviceNet is primarily designed for seamless integration with Rockwell Automation components, using a Controller Area Network (CAN) protocol ideal for simple device networks. Profibus offers broader compatibility across various manufacturers and supports more complex network topologies, utilizing a token-passing protocol suited for industrial automation environments requiring extensive device integration. Integration efforts favor DeviceNet in Rockwell-centric systems for ease of use, while Profibus excels in heterogeneous networks demanding versatile interoperability.
Diagnostics, Monitoring, and Maintenance
DeviceNet excels in real-time diagnostics with extensive network status indicators and error diagnostic messages, enabling quick fault isolation and corrective action. Profibus offers comprehensive network monitoring tools with detailed diagnostics, including device-specific alerts and performance data, facilitating predictive maintenance and reducing downtime. Both protocols enhance maintenance efficiency, but Profibus provides deeper insight into device conditions and communication integrity for complex industrial environments.
Cost Considerations and Implementation
DeviceNet typically offers lower installation and maintenance costs due to its simpler wiring system and compatibility with standard industrial Ethernet components. Profibus requires specialized cabling and connectors, which can increase upfront expenses and complexity during setup. Implementation of DeviceNet tends to be faster and more cost-effective for small to medium-sized networks, while Profibus suits larger, more complex automation systems with higher integration needs.
Choosing the Right Protocol for Your Application
Choosing the right industrial communication protocol depends on factors like network size, data speed, and device compatibility. DeviceNet excels in smaller networks with simpler wiring and moderate speed requirements, while Profibus suits larger, more complex systems needing high-speed data transfer and extensive device integration. Evaluating application-specific needs such as real-time performance, scalability, and existing infrastructure ensures optimal protocol selection.
DeviceNet Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com