Planetary gears offer compact, efficient, and high-torque transmission in various mechanical systems, making them essential in automotive, aerospace, and industrial applications. Their unique design allows load distribution across multiple gears, enhancing durability and performance under heavy loads. Explore the rest of the article to understand how planetary gear systems can optimize your machinery's operation.
Table of Comparison
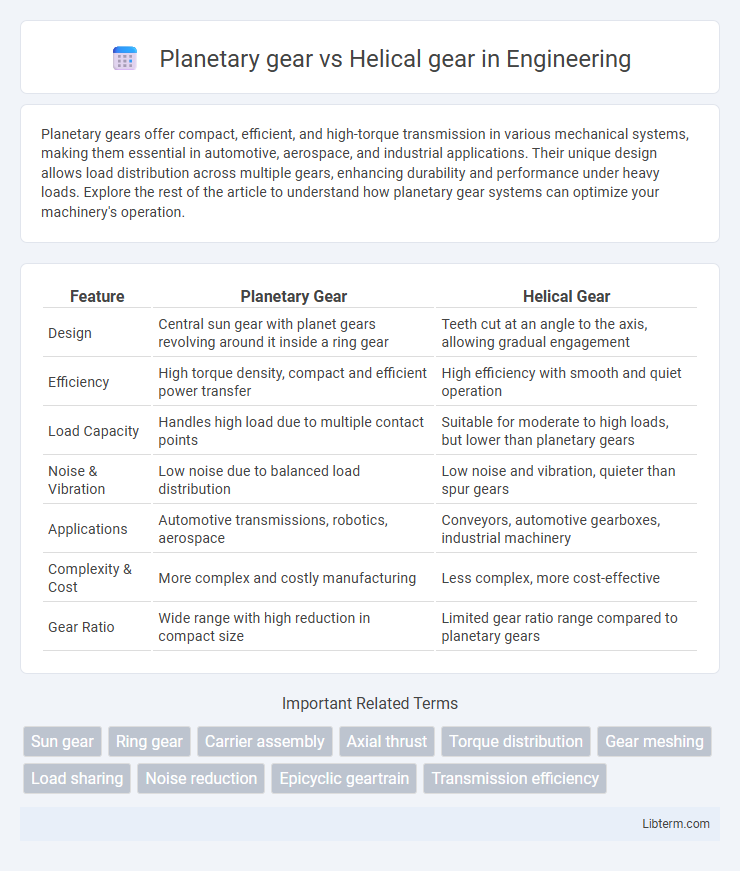
| Feature | Planetary Gear | Helical Gear |
|---|---|---|
| Design | Central sun gear with planet gears revolving around it inside a ring gear | Teeth cut at an angle to the axis, allowing gradual engagement |
| Efficiency | High torque density, compact and efficient power transfer | High efficiency with smooth and quiet operation |
| Load Capacity | Handles high load due to multiple contact points | Suitable for moderate to high loads, but lower than planetary gears |
| Noise & Vibration | Low noise due to balanced load distribution | Low noise and vibration, quieter than spur gears |
| Applications | Automotive transmissions, robotics, aerospace | Conveyors, automotive gearboxes, industrial machinery |
| Complexity & Cost | More complex and costly manufacturing | Less complex, more cost-effective |
| Gear Ratio | Wide range with high reduction in compact size | Limited gear ratio range compared to planetary gears |
Introduction to Gear Systems
Planetary gears offer compact design and high torque transmission through a central sun gear, multiple planet gears, and a ring gear, optimizing load distribution and efficiency in gear systems. Helical gears feature angled teeth that engage gradually, providing smoother operation and higher load capacity compared to spur gears, ideal for high-speed applications. Both gear types play crucial roles in industrial machinery, automotive transmissions, and robotics, selected based on space constraints, load requirements, and noise reduction needs.
Overview of Planetary Gears
Planetary gears consist of a central sun gear, multiple planet gears, and an outer ring gear working together to provide high torque density and compact design. These gears enable smooth power transmission with high efficiency and load distribution across multiple contact points, making them ideal for applications requiring high torque and compact size. Their configuration allows for varied gear ratios within a single stage, enhancing flexibility in mechanical systems like automatic transmissions and industrial machinery.
Fundamentals of Helical Gears
Helical gears feature angled teeth that engage gradually, resulting in smoother and quieter operation compared to planetary gears with their radial tooth arrangement. The fundamental design of helical gears allows for higher load capacity and efficient power transmission due to increased tooth contact area. These gears are commonly used in automotive transmissions and industrial machinery where reducing noise and enhancing durability are essential.
Key Working Principles Compared
Planetary gears operate with a central sun gear, multiple planet gears, and an outer ring gear, distributing load evenly and enabling high torque transmission within a compact design. Helical gears feature angled teeth that engage gradually, providing smoother and quieter operation with higher load capacity compared to spur gears. The planetary gear system allows simultaneous power distribution through multiple contact points, while helical gears rely on meshing angled teeth for continuous and efficient power transfer.
Efficiency and Power Transmission
Planetary gears provide higher power transmission efficiency due to their load distribution across multiple planet gears, reducing stress and improving torque density compared to helical gears. Helical gears have good efficiency but experience axial thrust losses and sliding friction that slightly reduce their performance in high-torque applications. Planetary systems excel in compact designs requiring high efficiency and torque, while helical gears are preferred for smoother, quieter operation in moderate power transmission scenarios.
Load Capacity and Durability
Planetary gears offer higher load capacity due to their multiple gear engagements distributing torque evenly across the system, enhancing durability under heavy loads and shock conditions. Helical gears, while providing smooth and quiet operation with good load capacity, typically bear stress on fewer teeth at a time, which may reduce durability in extreme load scenarios compared to planetary configurations. The inherent design of planetary gearsets allows for better heat dissipation and balanced load sharing, making them more suitable for high-torque and heavy-duty applications.
Space and Weight Considerations
Planetary gears offer a compact design with a high power-to-weight ratio, making them ideal for applications with limited space and strict weight constraints. Helical gears, while efficient and smooth in operation, generally require more axial space and have a heavier structure due to their larger gear teeth and longer shafts. In aerospace and robotics, planetary gear systems are preferred for their space-saving configuration and reduced mass, which directly contribute to performance optimization and fuel efficiency.
Noise and Vibration Analysis
Planetary gears typically exhibit lower noise and vibration levels due to their multiple teeth sharing the load and continuous contact, which distributes forces more evenly compared to helical gears. Helical gears generate higher noise and vibration because of the angled teeth that produce axial thrust and sliding friction during meshing, leading to increased operational noise. Advanced noise and vibration analysis shows planetary gear systems are preferable for applications demanding quiet operation and reduced mechanical stress.
Typical Applications and Industries
Planetary gears are extensively used in automotive transmissions, robotics, and aerospace systems due to their compact design and high torque capacity, making them ideal for applications requiring precise motion control and durability. Helical gears find typical applications in industrial machinery, conveyors, and power plants, where smooth and quiet operation is critical, especially under high load and high-speed conditions. Industries such as manufacturing, automotive, and energy heavily rely on helical gears for efficient power transmission, while planetary gears dominate sectors demanding compactness and high efficiency, like robotics and aerospace.
Choosing the Right Gear for Your Needs
Planetary gears offer high torque density and compact design, making them ideal for applications requiring precise motion control and load distribution, such as robotics and automotive transmissions. Helical gears provide smoother operation and higher load capacity due to angled teeth engagement, which reduces noise and vibration, suitable for high-speed machinery and heavy-duty equipment. Selecting between planetary and helical gears depends on factors like space constraints, torque requirements, noise levels, and operational speed to ensure optimal gear performance.
Planetary gear Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com