Isolation transformers enhance electrical safety by separating your equipment from the main power source, reducing electrical noise and preventing shock hazards. They are essential in sensitive environments such as medical and industrial settings, where stable and clean power is crucial. Discover how an isolation transformer can protect your devices and improve performance by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
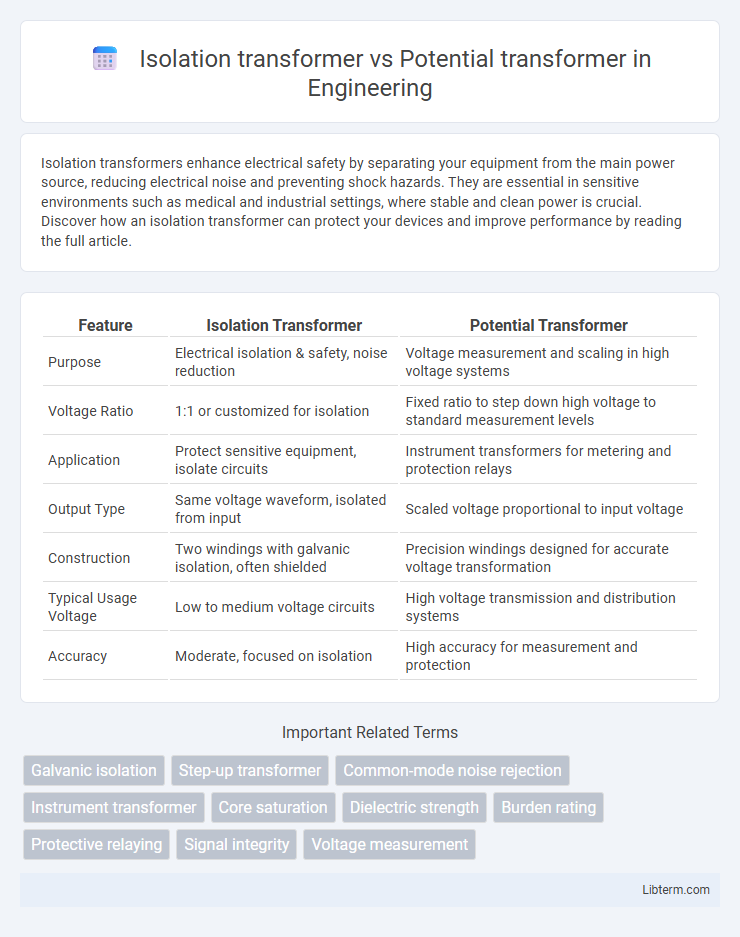
| Feature | Isolation Transformer | Potential Transformer |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Electrical isolation & safety, noise reduction | Voltage measurement and scaling in high voltage systems |
| Voltage Ratio | 1:1 or customized for isolation | Fixed ratio to step down high voltage to standard measurement levels |
| Application | Protect sensitive equipment, isolate circuits | Instrument transformers for metering and protection relays |
| Output Type | Same voltage waveform, isolated from input | Scaled voltage proportional to input voltage |
| Construction | Two windings with galvanic isolation, often shielded | Precision windings designed for accurate voltage transformation |
| Typical Usage Voltage | Low to medium voltage circuits | High voltage transmission and distribution systems |
| Accuracy | Moderate, focused on isolation | High accuracy for measurement and protection |
Introduction to Isolation Transformers and Potential Transformers
Isolation transformers are designed to transfer electrical power while providing galvanic isolation between the input and output, enhancing safety and reducing noise interference in sensitive equipment. Potential transformers, also known as voltage transformers, step down high volttage to a lower, measurable level for monitoring and protection in power systems. Both transformers play essential roles in electrical power distribution, with isolation transformers focusing on safety and noise reduction, and potential transformers enabling accurate voltage measurement and system control.
Core Functions: Isolation vs Voltage Measurement
Isolation transformers primarily serve to isolate electrical circuits for safety and noise reduction by transferring power without a direct electrical connection, using magnetic coupling in the core. Potential transformers are designed specifically for voltage measurement by accurately stepping down high voltages to standardized, lower levels for metering and protection equipment, ensuring precise voltage representation. The core function of an isolation transformer is electrical isolation, while a potential transformer focuses on voltage transformation and measurement accuracy.
Construction Differences
Isolation transformers feature identical primary and secondary windings separated by an insulated core to eliminate ground loops and provide electrical isolation. Potential transformers utilize a step-down ratio with a single primary winding and a precisely designed secondary winding to accurately measure high voltages at lower levels. The core material and winding techniques differ significantly, with isolation transformers prioritizing insulation and safety, whereas potential transformers emphasize measurement accuracy and voltage scaling.
Working Principles Explained
Isolation transformers operate by magnetically coupling the primary and secondary windings through a core, providing electrical isolation while maintaining the same voltage level, which protects circuits from surges and noise. Potential transformers, designed to step down high voltages to standardized, lower values for metering and protection, function by inducing a proportional voltage in the secondary winding relative to the primary voltage using electromagnetic induction. Both transformers rely on Faraday's law of electromagnetic induction but serve distinct purposes: isolation transformers for safety and noise reduction, and potential transformers for accurate voltage measurement.
Key Applications in Electrical Systems
Isolation transformers are primarily used in electrical systems for safety applications, providing galvanic isolation to protect equipment and personnel from electric shock and to reduce noise in sensitive devices. Potential transformers are designed for accurate voltage measurement and monitoring in high-voltage power systems, enabling precise metering and protection relay operation. Key applications of isolation transformers include medical equipment, industrial control systems, and testing laboratories, while potential transformers are essential in substations, power distribution networks, and energy management systems.
Safety Features and Benefits
Isolation transformers provide galvanic isolation between input and output, significantly reducing the risk of electric shock and preventing ground loops, enhancing operator safety in sensitive environments. Potential transformers step down high voltages to standardized lower levels, enabling safe measurement and monitoring while maintaining accuracy and insulation from hazardous circuits. Both transformers improve safety by isolating equipment from dangerous voltages, but isolation transformers specifically protect personnel from direct contact with live circuits, whereas potential transformers focus on safe voltage scaling for instrumentation.
Signal Integrity and Noise Reduction
Isolation transformers provide galvanic isolation, effectively minimizing ground loops and reducing electromagnetic interference, which enhances signal integrity in sensitive electronic equipment. Potential transformers primarily serve voltage measurement purposes and have limited noise reduction capabilities, making them less effective for preserving signal quality in noisy environments. For applications demanding superior signal integrity and noise mitigation, isolation transformers are the preferred choice.
Voltage Accuracy and Performance
Isolation transformers provide voltage accuracy by maintaining electrical separation between input and output, minimizing noise and voltage spikes, which ensures stable performance in sensitive equipment. Potential transformers accurately step down high voltages to standard measuring levels with precise ratio values, essential for metering and protection in power systems. Performance-wise, isolation transformers excel in safety and noise reduction, while potential transformers deliver high voltage measurement precision and reliability.
Typical Industries and Use Cases
Isolation transformers are widely used in medical equipment manufacturing, industrial automation, and power supply systems to provide electrical safety by isolating circuits and reducing noise. Potential transformers find application primarily in electrical utilities, power generation plants, and substations, where they step down high voltage for metering and protective relays. Both transformers support energy management and equipment protection, but isolation transformers emphasize electrical isolation, while potential transformers focus on voltage measurement and control.
Choosing the Right Transformer for Your Needs
Selecting the right transformer depends on application requirements: isolation transformers provide galvanic isolation and reduce noise in sensitive equipment, ideal for protecting against electrical faults and ensuring safety. Potential transformers (PTs) are designed to step down high voltage to measurable levels for metering and protection devices, prioritizing accuracy and voltage scaling over isolation. Understanding the purpose--safety and noise reduction versus accurate voltage measurement--guides effective transformer choice in electrical systems.
Isolation transformer Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com