Modeling plays a crucial role in various fields by creating accurate representations of real-world systems to predict outcomes and optimize processes. Whether used in fashion, data science, or engineering, effective modeling enhances decision-making and innovation. Explore the rest of the article to discover how modeling techniques can transform your projects and improve results.
Table of Comparison
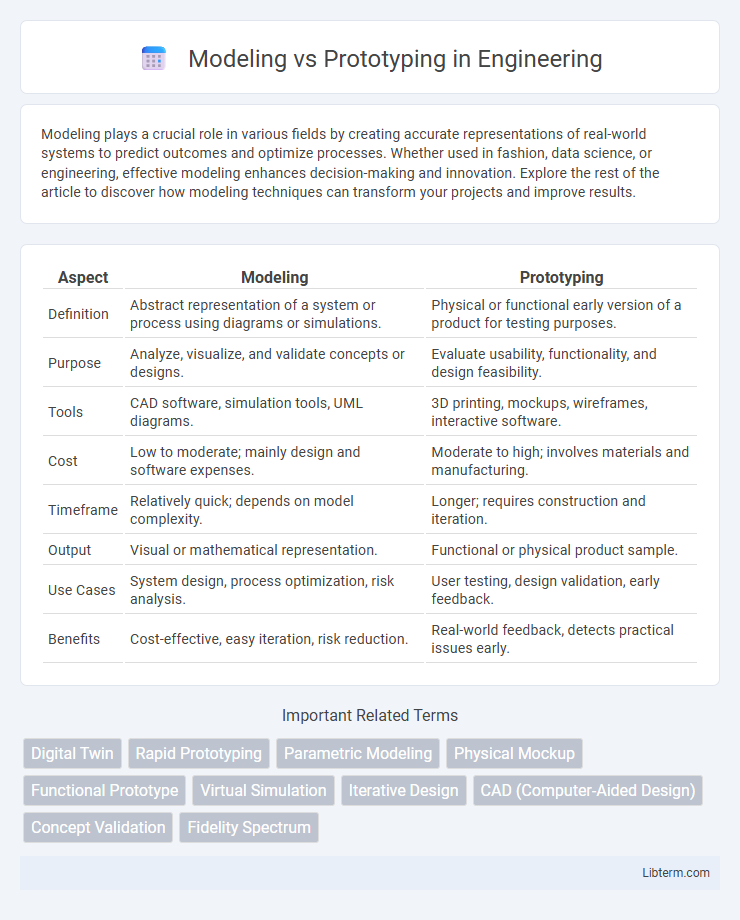
| Aspect | Modeling | Prototyping |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Abstract representation of a system or process using diagrams or simulations. | Physical or functional early version of a product for testing purposes. |
| Purpose | Analyze, visualize, and validate concepts or designs. | Evaluate usability, functionality, and design feasibility. |
| Tools | CAD software, simulation tools, UML diagrams. | 3D printing, mockups, wireframes, interactive software. |
| Cost | Low to moderate; mainly design and software expenses. | Moderate to high; involves materials and manufacturing. |
| Timeframe | Relatively quick; depends on model complexity. | Longer; requires construction and iteration. |
| Output | Visual or mathematical representation. | Functional or physical product sample. |
| Use Cases | System design, process optimization, risk analysis. | User testing, design validation, early feedback. |
| Benefits | Cost-effective, easy iteration, risk reduction. | Real-world feedback, detects practical issues early. |
Understanding Modeling and Prototyping
Modeling involves creating abstract representations of systems to analyze and predict their behavior, while prototyping focuses on building functional versions to test usability and design concepts. Understanding modeling helps clarify system requirements and identify potential issues early through simulations. Prototyping provides tangible feedback from users, enabling iterative improvements before final development.
Key Differences Between Modeling and Prototyping
Modeling creates abstract representations of systems using diagrams and formal methods to analyze requirements, structures, and behaviors, while prototyping builds tangible, interactive versions of a product to explore design and functionality. Modeling emphasizes documentation and theoretical validation, whereas prototyping focuses on user feedback and iterative refinement through practical implementation. Key differences include the purpose--conceptual analysis versus experiential testing--and the deliverable format, with models being non-functional artifacts and prototypes being functional, testable artifacts.
When to Use Modeling in Development
Modeling in development is ideal during the initial phases when defining system requirements and architecture to provide a clear, abstract representation of the project. It helps in visualizing complex systems through UML diagrams, flowcharts, or data models, facilitating communication among stakeholders and ensuring alignment on design specifications. Modeling is particularly useful when precision, documentation, and early error detection are critical to reduce overall project risks and costs.
The Role of Prototyping in Product Design
Prototyping plays a crucial role in product design by enabling designers to create tangible representations of concepts and test functionality early in the development process. This hands-on approach allows for rapid iterations, user feedback, and identification of design flaws before final production. Unlike modeling, which often involves abstract or digital simulations, prototyping provides real-world insights that enhance usability, performance, and overall product quality.
Advantages of Modeling
Modeling enhances project accuracy by providing detailed visual representations that clarify system requirements and design before development. It facilitates early detection of errors and inconsistencies, reducing costly revisions during later stages. By supporting better communication among stakeholders, modeling ensures alignment and streamlines the decision-making process throughout software development.
Benefits of Prototyping
Prototyping accelerates product development by enabling early visualization and testing of design concepts, which reduces costly revisions later. It enhances stakeholder communication through tangible models, facilitating more accurate feedback and aligning expectations. Prototyping also promotes iterative improvement, increasing usability and functionality before final production.
Common Tools for Modeling and Prototyping
Common tools for modeling include UML software such as Enterprise Architect, Visual Paradigm, and IBM Rational Rose, which facilitate creating detailed system diagrams and workflows. Prototyping tools like Figma, Adobe XD, and Axure enable designers to build interactive wireframes and user interface mockups for user testing and feedback. Both sets of tools play crucial roles in software development, with modeling focusing on system structure and prototyping emphasizing user experience validation.
Challenges in Modeling Versus Prototyping
Modeling faces challenges such as abstract representation limitations and difficulty in capturing dynamic user interactions, leading to potential misinterpretations of system behavior. Prototyping struggles with resource intensity and time constraints, often resulting in incomplete or low-fidelity versions that may mislead stakeholders about final functionality. Both approaches require balancing accuracy and feasibility to ensure effective communication and validation during software development.
Industry Applications: Modeling vs Prototyping
Modeling enables industries such as aerospace and automotive to simulate complex systems and predict performance outcomes, reducing risk and development costs. Prototyping in manufacturing and product design allows for tangible testing and validation of physical attributes, facilitating iterative improvements before mass production. Combining modeling with prototyping accelerates innovation cycles by integrating virtual analysis with real-world feedback in industrial applications.
Choosing the Right Approach for Your Project
Choosing the right approach between modeling and prototyping depends on project goals, complexity, and stakeholder involvement. Modeling provides detailed system representations ideal for complex architecture and early validation, while prototyping offers tangible, functional versions useful for user feedback and interface testing. Effective project planning requires assessing whether thorough analysis (modeling) or iterative usability testing (prototyping) better aligns with the development phase and resource availability.
Modeling Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com