Salmon is a nutrient-rich fish packed with omega-3 fatty acids that promote heart health and brain function. Its versatile flavor and texture make it ideal for grilling, baking, or incorporating into salads and pasta dishes. Discover more about the benefits, cooking tips, and sustainable sourcing options of salmon in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
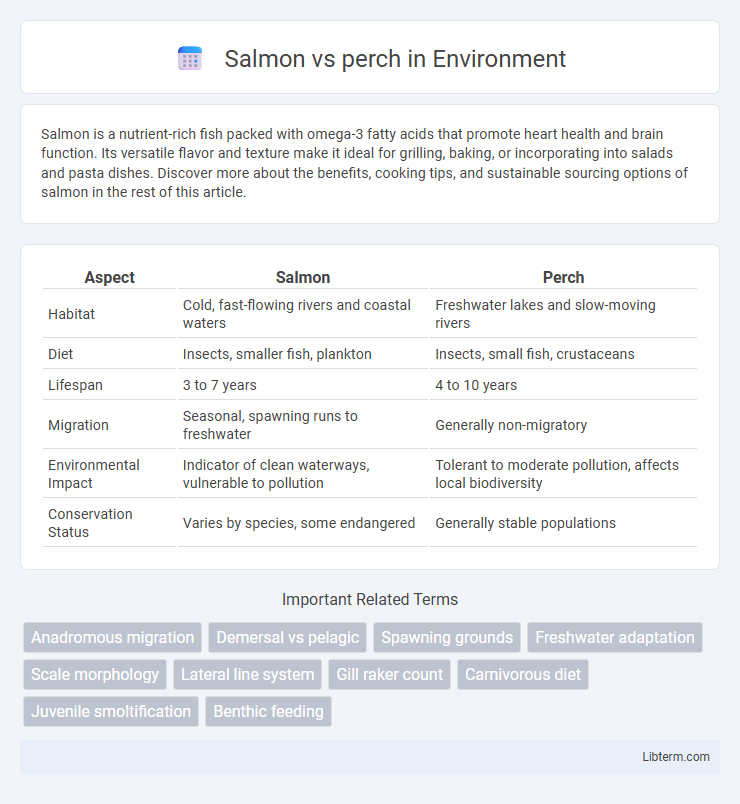
| Aspect | Salmon | Perch |
|---|---|---|
| Habitat | Cold, fast-flowing rivers and coastal waters | Freshwater lakes and slow-moving rivers |
| Diet | Insects, smaller fish, plankton | Insects, small fish, crustaceans |
| Lifespan | 3 to 7 years | 4 to 10 years |
| Migration | Seasonal, spawning runs to freshwater | Generally non-migratory |
| Environmental Impact | Indicator of clean waterways, vulnerable to pollution | Tolerant to moderate pollution, affects local biodiversity |
| Conservation Status | Varies by species, some endangered | Generally stable populations |
Introduction to Salmon and Perch
Salmon and perch are distinct freshwater and saltwater fish species known for their ecological and culinary importance. Salmon, belonging to the family Salmonidae, are anadromous fish that migrate from the ocean to freshwater rivers for spawning, characterized by their rich, omega-3 fatty acid content and vibrant pink flesh. Perch, primarily from the family Percidae, inhabit freshwater environments and are prized for their mild, flaky white meat and adaptability to diverse aquatic habitats.
Taxonomy and Species Overview
Salmon belong to the family Salmonidae and are primarily classified under the genus Salmo and Oncorhynchus, encompassing species like Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) and Chinook salmon (Oncorhynchus tshawytscha). Perch belong to the family Percidae, with the most studied species being the European perch (Perca fluviatilis) and Yellow perch (Perca flavescens). Both fish exhibit diverse ecological adaptations but differ significantly in their taxonomic classifications and evolutionary lineage.
Habitat and Geographic Distribution
Salmon primarily inhabit the cold waters of the North Atlantic and Pacific Oceans, migrating between freshwater rivers for spawning and the open ocean for feeding. Perch are commonly found in freshwater lakes, rivers, and ponds across North America and Europe, favoring slower-moving or still waters with ample vegetation. The distinct habitats and geographic distribution highlight salmon's anadromous life cycle versus perch's more localized freshwater residency.
Physical Characteristics Comparison
Salmon exhibit streamlined, torpedo-shaped bodies adapted for fast swimming in open waters, with a silvery coloration and small scales that reduce friction, while perch display a more robust, laterally compressed body with distinct dark vertical stripes and larger, rougher scales suited for maneuvering in freshwater habitats. Salmon have a prominent adipose fin and forked tail that enhance propulsion during migration, contrasted with perch's spiny dorsal fins and rounded tail aiding in stability and quick directional changes. The size difference is notable, as salmon commonly reach lengths of 28 to 30 inches and weigh up to 30 pounds, whereas perch typically measure 6 to 12 inches with a slender build.
Nutritional Value: Salmon vs Perch
Salmon offers a richer nutritional profile with higher omega-3 fatty acids, essential for heart and brain health, compared to perch, which contains moderate amounts. Perch provides a leaner protein source with fewer calories and fat, making it ideal for low-fat diets. Both fish supply valuable vitamins and minerals, but salmon's vitamin D and B12 levels significantly surpass those found in perch.
Taste and Culinary Uses
Salmon offers a rich, buttery flavor with a tender, flaky texture that makes it ideal for grilling, smoking, and sashimi preparations, while its high-fat content enhances moisture and taste. Perch features a mild, slightly sweet flavor with a firmer, flaky texture, commonly used in frying, baking, or pan-searing dishes that highlight its delicate taste. Both fish provide versatile culinary options, but salmon's stronger flavor and higher omega-3 levels cater to heartier recipes, whereas perch suits lighter, more subtle pairings.
Fishing Methods and Availability
Salmon fishing primarily employs methods such as trolling, fly fishing, and netting in both freshwater rivers and coastal marine environments, with seasonal availability peaking during their spawning runs from late spring to early fall. Perch fishing typically utilizes baitcasting and float fishing techniques in freshwater lakes and slow-moving rivers, with year-round accessibility, especially abundant in temperate regions during warmer months. The targeted use of specific lures and natural baits allows anglers to maximize catch rates based on the differing behaviors and habitats of salmon and perch.
Health Benefits and Risks
Salmon is rich in omega-3 fatty acids, protein, and vitamin D, which promote heart health, reduce inflammation, and support brain function, while perch contains moderate protein and fewer omega-3s but offers a leaner option with lower calories. Consuming salmon regularly may reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease and improve cognitive function, but potential mercury exposure and farmed salmon contaminants pose health concerns. Perch is generally considered safer with lower mercury levels, making it a favorable choice for individuals seeking a lean protein source with fewer dietary risks.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Salmon farming often raises concerns about environmental impact due to issues like habitat disruption, water pollution, and the spread of diseases to wild fish populations. Perch farming typically has a lower ecological footprint since perch require less feed and are often raised in more controlled, freshwater environments that reduce the risk of pollution. Sustainable practices in perch aquaculture, such as recirculating systems, support conservation efforts better than many conventional salmon farming techniques.
Which Fish is Better: Final Verdict
Salmon stands out as the better fish due to its rich omega-3 fatty acids, high protein content, and essential vitamins like B12 and D, promoting heart health and brain function. Perch, while lean and lower in calories, contains fewer omega-3s and essential nutrients compared to salmon, making it less beneficial for those seeking a nutrient-dense fish option. For optimal health benefits, salmon remains the superior choice between the two.
Salmon Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com