Unite captures the essence of bringing people or things together into a single, harmonious whole, fostering collaboration and strength. This concept is vital in building communities, teams, and partnerships that thrive on shared goals and mutual support. Explore the rest of the article to discover how you can effectively unite diverse elements for greater success.
Table of Comparison
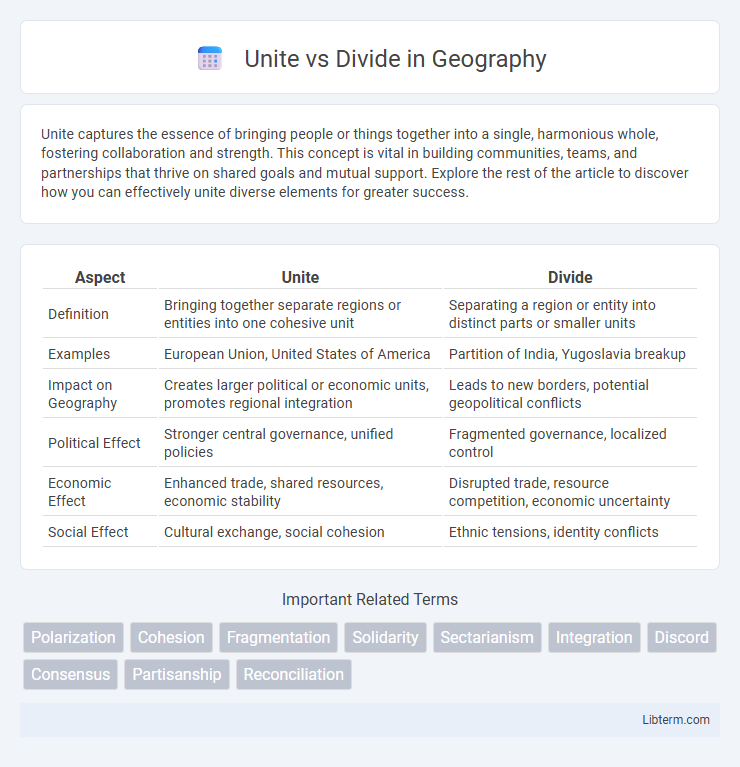
| Aspect | Unite | Divide |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Bringing together separate regions or entities into one cohesive unit | Separating a region or entity into distinct parts or smaller units |
| Examples | European Union, United States of America | Partition of India, Yugoslavia breakup |
| Impact on Geography | Creates larger political or economic units, promotes regional integration | Leads to new borders, potential geopolitical conflicts |
| Political Effect | Stronger central governance, unified policies | Fragmented governance, localized control |
| Economic Effect | Enhanced trade, shared resources, economic stability | Disrupted trade, resource competition, economic uncertainty |
| Social Effect | Cultural exchange, social cohesion | Ethnic tensions, identity conflicts |
Understanding the Concepts: Unite vs Divide
Unite and divide represent opposing forces in social and organizational dynamics, where uniting fosters collaboration, shared goals, and collective strength, while dividing emphasizes separation, conflict, and fragmentation. Understanding these concepts involves recognizing the psychological and sociological mechanisms that drive group cohesion or discord, such as common identity versus perceived differences. Effective leadership and communication strategies often aim to maximize unity by addressing division through empathy, dialogue, and inclusive practices.
Historical Perspectives on Unity and Division
Throughout history, unity has often emerged as a powerful force in nation-building, exemplified by the unification of Germany in 1871 and the American Civil Rights Movement, which fostered social cohesion and collective identity. Conversely, division has frequently led to conflict and fragmentation, as seen in the breakup of Yugoslavia during the 1990s and the sectarian strife in Northern Ireland. These historical perspectives illustrate how unity can drive progress and stability, whereas division often results in political turmoil and social disruption.
Psychological Effects of Unity and Division
Unity fosters a sense of belonging, reduces stress, and enhances overall mental well-being by promoting social support and collective resilience. Division, on the other hand, often triggers feelings of isolation, anxiety, and hostility, which can escalate into chronic psychological distress and weakened community bonds. Research in social psychology highlights that cohesive groups improve emotional regulation and increase individual motivation, while fragmented groups face increased conflict and reduced cooperation.
Factors That Foster Unity
Shared values and common goals are primary factors that foster unity, promoting collaboration and collective purpose among individuals or groups. Effective communication and mutual respect enhance understanding, reducing conflicts and building trust within communities. Inclusive leadership that encourages participation and acknowledges diverse perspectives strengthens unity by creating a sense of belonging and shared responsibility.
Forces That Drive Division
Forces that drive division include misinformation, social inequality, and competing interests, which exacerbate misunderstandings between groups. Psychological phenomena such as in-group bias and confirmation bias reinforce existing divides by promoting favoritism and resistance to opposing views. Political polarization and economic disparities further intensify these forces, creating fragmented societies with diminished social cohesion.
The Role of Leadership in Uniting or Dividing
Effective leadership directly influences whether a group is united or divided by shaping communication, fostering trust, and setting a clear vision. Leaders who promote inclusivity, empathy, and collaboration create a cohesive environment that strengthens collective goals. Conversely, leaders who exhibit divisiveness through favoritism, exclusion, or poor communication deepen rifts and hinder organizational progress.
Social Media: A Tool for Unity or Division?
Social media platforms have become powerful tools that can either unite or divide societies depending on how they are used and regulated. Algorithms often amplify echo chambers and misinformation, intensifying polarization and conflict across communities. However, social media also facilitates global connectivity, grassroots movements, and cross-cultural dialogue that promote understanding and collective action.
Consequences of Unity and Division in Society
Unity fosters social cohesion, economic growth, and political stability by encouraging collective action and shared goals among diverse groups. In contrast, division often leads to social fragmentation, increased conflict, and weakened institutions, undermining trust and cooperation within communities. Societies that prioritize unity experience enhanced resilience and innovation, while divided societies face challenges such as polarization, inequality, and diminished civic engagement.
Strategies to Promote Unity over Division
Effective strategies to promote unity over division include fostering inclusive communication that respects diverse perspectives and encourages collaboration among different groups. Implementing community-building activities and dialogue sessions strengthens social bonds and reduces misunderstandings, creating a shared sense of purpose. Educational programs that emphasize empathy, cultural awareness, and conflict resolution skills empower individuals to embrace common goals and resist divisive rhetoric.
Case Studies: Lessons from United and Divided Communities
Case studies from United and Divided Communities reveal that social cohesion strengthens resilience against economic downturns and enhances collective problem-solving capabilities. Communities with high levels of trust and collaboration experience lower crime rates and improved public health outcomes. In contrast, divided communities often face increased social unrest and reduced access to resources, highlighting the critical impact of unity on sustainable development.
Unite Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com