Autonomy empowers individuals to make independent decisions, enhancing personal growth and self-confidence. It fosters responsibility by encouraging you to take control of your actions and outcomes. Discover how embracing autonomy can transform your life by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
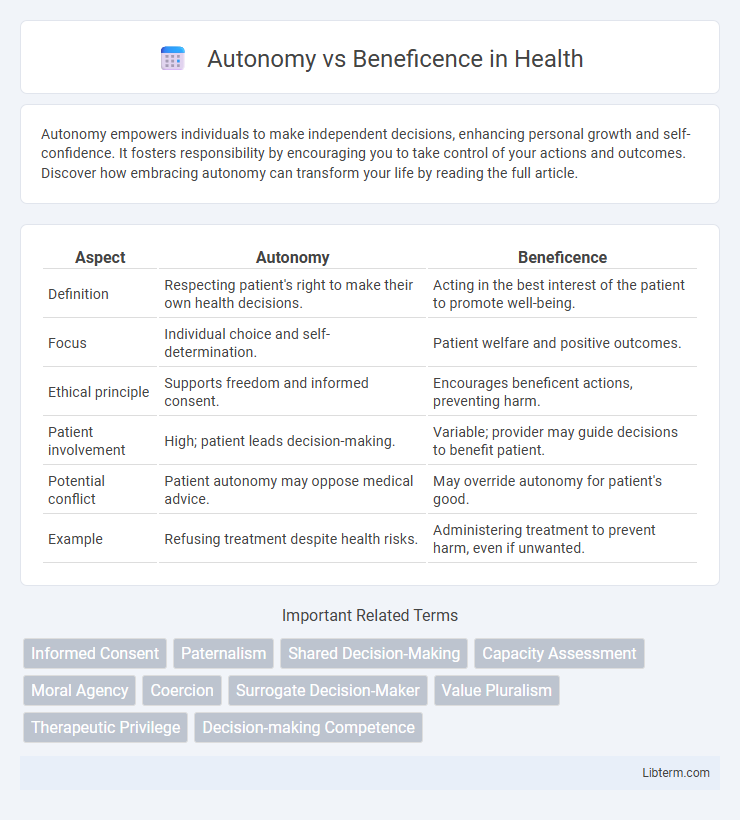
| Aspect | Autonomy | Beneficence |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Respecting patient's right to make their own health decisions. | Acting in the best interest of the patient to promote well-being. |
| Focus | Individual choice and self-determination. | Patient welfare and positive outcomes. |
| Ethical principle | Supports freedom and informed consent. | Encourages beneficent actions, preventing harm. |
| Patient involvement | High; patient leads decision-making. | Variable; provider may guide decisions to benefit patient. |
| Potential conflict | Patient autonomy may oppose medical advice. | May override autonomy for patient's good. |
| Example | Refusing treatment despite health risks. | Administering treatment to prevent harm, even if unwanted. |
Understanding Autonomy: The Right to Self-Determination
Autonomy represents an individual's fundamental right to self-determination, enabling them to make informed decisions about their own life and body without external coercion. It emphasizes respect for personal values, preferences, and the capacity for rational choice in healthcare and ethical contexts. Ensuring patient autonomy requires transparent communication, informed consent, and supporting individuals in exercising control over their treatment options.
Defining Beneficence in Ethical Practice
Beneficence in ethical practice refers to the moral obligation to act for the benefit of others, promoting their well-being and preventing harm. It requires healthcare professionals to prioritize patients' best interests by providing effective treatments and compassionate care. Balancing beneficence with patient autonomy ensures ethical decisions respect individual rights while maximizing positive health outcomes.
Historical Evolution of Autonomy and Beneficence
The historical evolution of autonomy in medical ethics traces back to the shift from paternalistic models towards patient-centered care, emphasizing individuals' rights to make informed decisions about their own health. Beneficence, rooted in Hippocratic traditions, has long underscored the moral obligation of healthcare providers to act in the best interest of patients, promoting well-being and preventing harm. The dynamic interplay between autonomy and beneficence reflects an ongoing ethical balance between respecting patient self-determination and ensuring compassionate, outcome-focused care.
Key Conflicts Between Autonomy and Beneficence
Key conflicts between autonomy and beneficence arise when respecting a patient's right to make independent decisions clashes with the healthcare provider's duty to act in the patient's best interest. Situations such as refusal of life-saving treatments or non-adherence to medical advice exemplify this ethical tension. Balancing informed consent with the imperative to prevent harm remains a central challenge in medical ethics.
Real-World Scenarios: Balancing Individual Choice and Welfare
In healthcare, autonomy emphasizes respecting patients' rights to make informed decisions about their treatments, while beneficence focuses on acting in the patients' best interest to promote well-being. Real-world scenarios, such as end-of-life care or vaccination mandates, often require balancing these principles by weighing individual freedom against public health benefits and safety concerns. Ethical decision-making frameworks guide practitioners in navigating conflicts, ensuring both personal choice and overall welfare are considered.
Cultural Perspectives on Autonomy and Beneficence
Cultural perspectives significantly influence the balance between autonomy and beneficence in ethical decision-making, with Western societies often prioritizing individual autonomy, while many Eastern and Indigenous cultures emphasize community welfare and collective beneficence. Variations in cultural values affect notions of informed consent, decision-making authority, and the role of family or community in healthcare and social services. Recognizing these cultural differences is essential for culturally competent care and ethical practices that respect both individual rights and community responsibilities.
Legal Frameworks Shaping Ethical Decisions
Legal frameworks prioritize autonomy by enforcing informed consent laws that require healthcare providers to respect patients' decision-making rights. Beneficence is codified through statutes mandating standard-of-care practices to promote patient well-being and prevent harm. The interplay between these frameworks creates ethical dilemmas, necessitating clear guidelines for balancing patient self-determination and professional responsibility.
Patient-Centered Care: Prioritizing Autonomy or Beneficence?
Patient-centered care requires balancing autonomy and beneficence by respecting patients' rights to make informed decisions while promoting their well-being through evidence-based recommendations. Emphasizing autonomy prioritizes informed consent and individual values, whereas beneficence focuses on actions that maximize health outcomes, sometimes necessitating paternalistic interventions. Ethical clinical practice integrates both principles to support patient empowerment and optimal care quality.
Resolving Ethical Dilemmas in Practice
Resolving ethical dilemmas involving autonomy versus beneficence requires balancing patient self-determination with the healthcare provider's duty to promote well-being. Effective strategies include clear communication, shared decision-making, and respecting informed consent while considering potential harm minimization. Ethical frameworks, such as principlism, guide practitioners in prioritizing patient values alongside clinical expertise to achieve optimal outcomes.
Future Trends in Ethics: Towards Harmonizing Autonomy and Beneficence
Future trends in ethics emphasize integrating autonomy and beneficence through advanced decision-making frameworks that balance individual rights with collective welfare. Emerging technologies such as AI-driven ethics tools enable nuanced assessments, promoting personalized autonomy while safeguarding beneficent outcomes in healthcare and policy. Interdisciplinary research and participatory approaches foster ethical harmonization, ensuring evolving societal values inform both autonomous choices and beneficent interventions.
Autonomy Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com