Confidentiality protects sensitive information from unauthorized access, ensuring privacy and trust in personal or professional relationships. It plays a crucial role in safeguarding your data, maintaining legal compliance, and upholding ethical standards. Explore the rest of the article to understand how confidentiality impacts you and the best practices to maintain it.
Table of Comparison
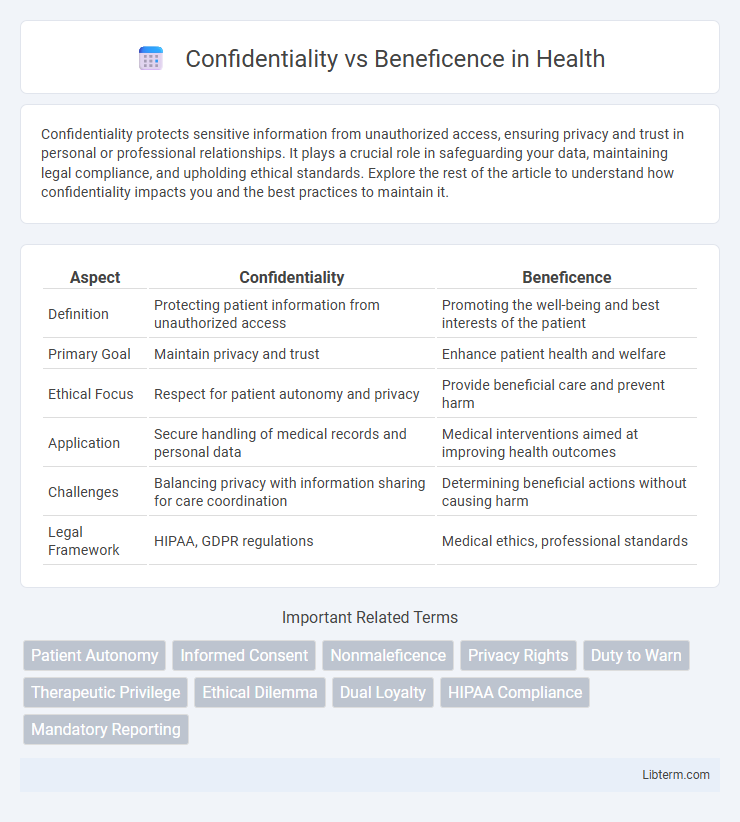
| Aspect | Confidentiality | Beneficence |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Protecting patient information from unauthorized access | Promoting the well-being and best interests of the patient |
| Primary Goal | Maintain privacy and trust | Enhance patient health and welfare |
| Ethical Focus | Respect for patient autonomy and privacy | Provide beneficial care and prevent harm |
| Application | Secure handling of medical records and personal data | Medical interventions aimed at improving health outcomes |
| Challenges | Balancing privacy with information sharing for care coordination | Determining beneficial actions without causing harm |
| Legal Framework | HIPAA, GDPR regulations | Medical ethics, professional standards |
Understanding Confidentiality in Healthcare
Confidentiality in healthcare ensures that patient information is protected from unauthorized access, maintaining trust between patients and providers. It is a fundamental ethical principle that supports patient autonomy and privacy, critical for effective diagnosis and treatment. Balancing confidentiality with beneficence requires healthcare professionals to safeguard sensitive data while promoting patient well-being and safety.
Defining Beneficence: A Core Ethical Principle
Beneficence, a core ethical principle in healthcare, emphasizes the obligation to act in the patient's best interest by promoting well-being and preventing harm. Unlike confidentiality, which safeguards private information, beneficence requires active interventions that maximize benefits and minimize risks for patients. It serves as a guiding framework for ethical decision-making, balancing patient care priorities with moral responsibilities.
Legal Frameworks Governing Confidentiality
Legal frameworks governing confidentiality, such as HIPAA in the United States and GDPR in the European Union, establish stringent standards for protecting patient information while balancing the principle of beneficence. These regulations mandate healthcare providers to safeguard sensitive data, ensuring privacy without compromising the delivery of beneficial medical care. Exceptions within these laws allow disclosure of confidential information when it serves a compelling public interest or prevents harm, highlighting the nuanced interplay between confidentiality and beneficence.
The Role of Beneficence in Patient Care
Beneficence in patient care emphasizes acting in the best interest of patients by promoting their well-being and preventing harm. It requires healthcare professionals to make decisions that prioritize patient health outcomes while balancing potential risks and benefits of treatments. Upholding beneficence often involves advocating for patients' needs, especially when confidentiality concerns may limit information disclosure.
Conflicts Between Confidentiality and Beneficence
Conflicts between confidentiality and beneficence arise when the duty to protect a patient's private information clashes with the obligation to act in their best interest or protect others from harm. Healthcare professionals often face ethical dilemmas when disclosing sensitive information could prevent harm but breaches patient trust. Balancing these principles requires careful consideration of legal standards, patient autonomy, and potential risks to both individuals and the public.
Case Studies: Real-World Ethical Dilemmas
Case studies reveal complex tensions between confidentiality and beneficence, such as when a therapist must decide whether to breach privacy to prevent harm, highlighting the ethical conflict between individual rights and public safety. In medical settings, scenarios involving infectious diseases demonstrate the dilemma of disclosing patient information to protect others, weighing moral responsibilities against professional confidentiality. These real-world dilemmas underscore the necessity for clear ethical guidelines that balance safeguarding patient trust with the imperative to act for the greater good.
Decision-Making Models for Ethical Conflicts
Decision-making models for ethical conflicts balance confidentiality and beneficence by incorporating frameworks such as the Four-Principles Approach, which weighs respect for patient privacy against the duty to promote well-being. The Balancing Test Model guides practitioners to evaluate potential harms and benefits when deciding whether to disclose private information for patient or public health protection. Ethical decision-making tools like the Professional-Patient Relationship Model emphasize transparent communication to navigate conflicts, prioritizing trust while ensuring actions serve the patient's best interests.
Impact on Patient Trust and Provider Accountability
Maintaining confidentiality strengthens patient trust by ensuring sensitive information remains private, which encourages open communication and adherence to treatment plans. Beneficence, while aiming to promote patient well-being, may sometimes necessitate overriding confidentiality to prevent harm, challenging the balance of trust in the patient-provider relationship. Healthcare providers must navigate these ethical tensions carefully, as accountability for protecting patient rights and delivering optimal care directly influences both trust and clinical outcomes.
Strategies for Balancing Confidentiality and Beneficence
Balancing confidentiality and beneficence requires implementing clear ethical guidelines that prioritize patient welfare while protecting sensitive information. Employing informed consent, data anonymization, and case-by-case risk assessment ensures that patient privacy is respected without compromising beneficial interventions. Healthcare professionals must continuously evaluate the potential harms and benefits to maintain trust and uphold ethical standards in clinical practice.
Future Trends in Medical Ethics: Navigating Dual Obligations
Emerging trends in medical ethics emphasize the integration of confidentiality and beneficence through advanced data encryption and patient-centered care models, ensuring both privacy and optimal health outcomes. Artificial intelligence and personalized medicine enable clinicians to tailor treatments while safeguarding sensitive information, highlighting the evolving balance between respecting patient autonomy and promoting well-being. Future frameworks are expected to incorporate multi-layered ethical algorithms that dynamically weigh confidentiality against beneficence to guide clinical decision-making in increasingly complex healthcare environments.
Confidentiality Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com