Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune skin condition characterized by red, scaly patches that cause itching and discomfort. Understanding the triggers and treatment options can help manage symptoms effectively and improve your quality of life. Explore the rest of this article to learn how to better control psoriasis and reduce flare-ups.
Table of Comparison
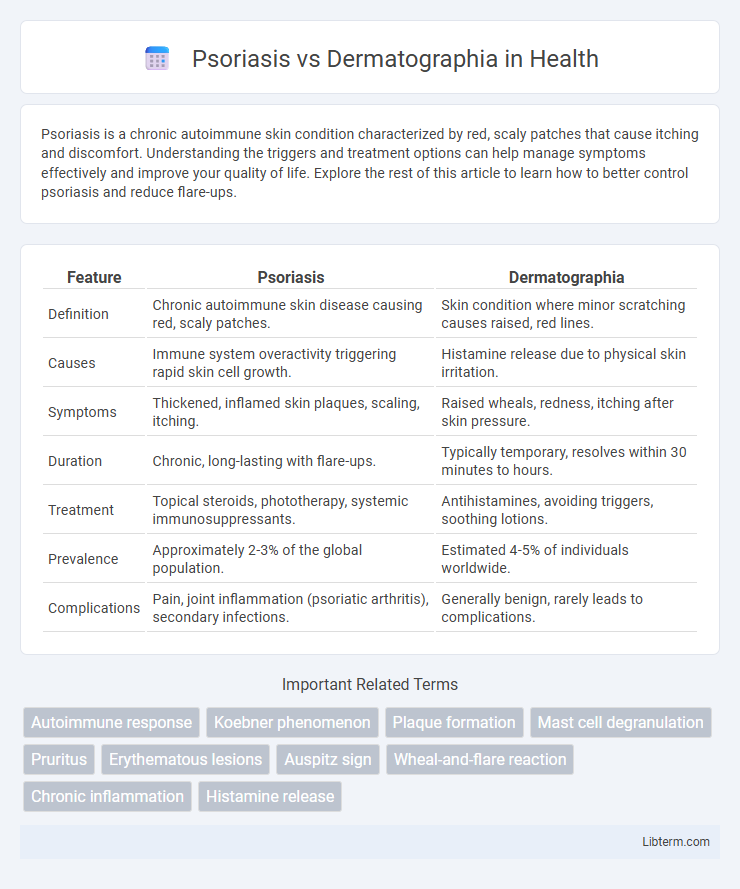
| Feature | Psoriasis | Dermatographia |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Chronic autoimmune skin disease causing red, scaly patches. | Skin condition where minor scratching causes raised, red lines. |
| Causes | Immune system overactivity triggering rapid skin cell growth. | Histamine release due to physical skin irritation. |
| Symptoms | Thickened, inflamed skin plaques, scaling, itching. | Raised wheals, redness, itching after skin pressure. |
| Duration | Chronic, long-lasting with flare-ups. | Typically temporary, resolves within 30 minutes to hours. |
| Treatment | Topical steroids, phototherapy, systemic immunosuppressants. | Antihistamines, avoiding triggers, soothing lotions. |
| Prevalence | Approximately 2-3% of the global population. | Estimated 4-5% of individuals worldwide. |
| Complications | Pain, joint inflammation (psoriatic arthritis), secondary infections. | Generally benign, rarely leads to complications. |
Understanding Psoriasis: Key Features and Causes
Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune condition characterized by rapid skin cell turnover, leading to thick, red, scaly patches often found on the elbows, knees, and scalp. The primary cause involves an overactive immune system triggering inflammation and accelerated skin production, influenced by genetic predisposition and environmental factors such as stress or infections. Unlike dermatographia, which is a physical urticaria causing raised welts after skin scratching, psoriasis involves systemic immune dysregulation and distinct histological features.
What is Dermatographia? Symptoms and Triggers
Dermatographia, also known as skin writing, is a common skin condition where light scratching causes raised, red lines or welts on the skin that resemble hives. Symptoms include itching, redness, and swelling triggered by scratching, pressure, or minor skin trauma, often lasting 30 minutes to an hour. Common triggers are heat, stress, tight clothing, and sweating, which can exacerbate skin sensitivity and flare-ups.
Differences in Skin Manifestations: Psoriasis vs Dermatographia
Psoriasis presents with thick, red, scaly plaques commonly found on the elbows, knees, and scalp, whereas dermatographia shows as raised, red lines or welts formed by minor skin scratching or pressure. Psoriatic plaques are characterized by silvery-white scales and chronic inflammation, contrasting with dermatographia's transient wheals that fade within 30 minutes to an hour. Unlike psoriasis, which involves immune-mediated skin cell proliferation, dermatographia results from histamine release causing localized skin swelling without scaling or persistent lesions.
Underlying Causes: Autoimmune vs Physical Response
Psoriasis is an autoimmune disorder characterized by the immune system attacking healthy skin cells, leading to rapid skin cell turnover and inflammation. In contrast, dermatographia is a physical skin response where minor scratching or pressure triggers raised, red welts without an autoimmune mechanism. Understanding the distinct underlying causes--immune dysregulation in psoriasis versus mechanical hypersensitivity in dermatographia--is crucial for accurate diagnosis and treatment.
Risk Factors for Developing Psoriasis and Dermatographia
Psoriasis risk factors include family history, immune system dysfunction, stress, smoking, and infections such as streptococcal throat infections. Dermatographia is often triggered by physical skin irritation, allergic reactions, or systemic conditions like urticaria or thyroid disorders. Both conditions may be influenced by genetic predisposition and environmental factors, but psoriasis primarily involves autoimmune mechanisms while dermatographia results from histamine release due to skin trauma.
Diagnostic Methods: How Doctors Differentiate the Two
Doctors differentiate psoriasis and dermatographia primarily through clinical examination and patient history, focusing on lesion appearance and triggers. Psoriasis presents with well-defined, scaly plaques commonly on elbows and knees, while dermatographia is characterized by raised, red wheals caused by skin pressure or scratching. Skin biopsy and dermatoscopy assist in confirming psoriasis by revealing epidermal hyperplasia, whereas dermatographia diagnosis relies on physical provocation tests showing transient wheal formation.
Treatment Options for Psoriasis
Psoriasis treatment options primarily include topical corticosteroids, vitamin D analogs, and phototherapy to reduce inflammation and slow skin cell turnover. Systemic treatments such as biologics targeting specific immune pathways (e.g., TNF-alpha inhibitors, IL-17 inhibitors) are effective for moderate to severe cases. Unlike dermatographia, which often responds to antihistamines to control skin sensitivity, psoriasis requires a tailored approach addressing its autoimmune nature and chronic inflammation.
Management Strategies for Dermatographia
Management strategies for dermatographia prioritize avoiding skin trauma and using antihistamines to reduce histamine release and alleviate itching. Topical corticosteroids and soothing emollients may help minimize inflammation and skin irritation. Patients are advised to maintain gentle skin care routines and avoid tight clothing to prevent flare-ups.
Lifestyle Tips for Living with Psoriasis or Dermatographia
Managing psoriasis involves maintaining a consistent skincare routine with moisturizers and avoiding known triggers like stress and certain foods to reduce flare-ups. For dermatographia, wearing loose clothing and using gentle skin cleansers can minimize irritation and prevent raised skin welts. Both conditions benefit from regular dermatological check-ups and avoiding harsh physical or chemical skin irritants to improve overall skin health.
When to See a Dermatologist: Warning Signs and Next Steps
Persistent itching, inflamed red patches, or silver-scaled plaques may indicate psoriasis, while raised red wheals triggered by skin scratching suggest dermatographia. Seek a dermatologist immediately if symptoms worsen, spreads rapidly, or interfere with daily activities, as early diagnosis and tailored treatment are crucial. A skin biopsy or allergy testing might be recommended to differentiate between psoriasis and dermatographia for effective management.
Psoriasis Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com