Evaluation is the systematic process of assessing the value, quality, or performance of a product, service, or process to ensure it meets specified criteria and objectives. Effective evaluation helps identify strengths and areas for improvement, enabling informed decision-making and strategic planning. Discover how thorough evaluation techniques can enhance your outcomes by reading the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
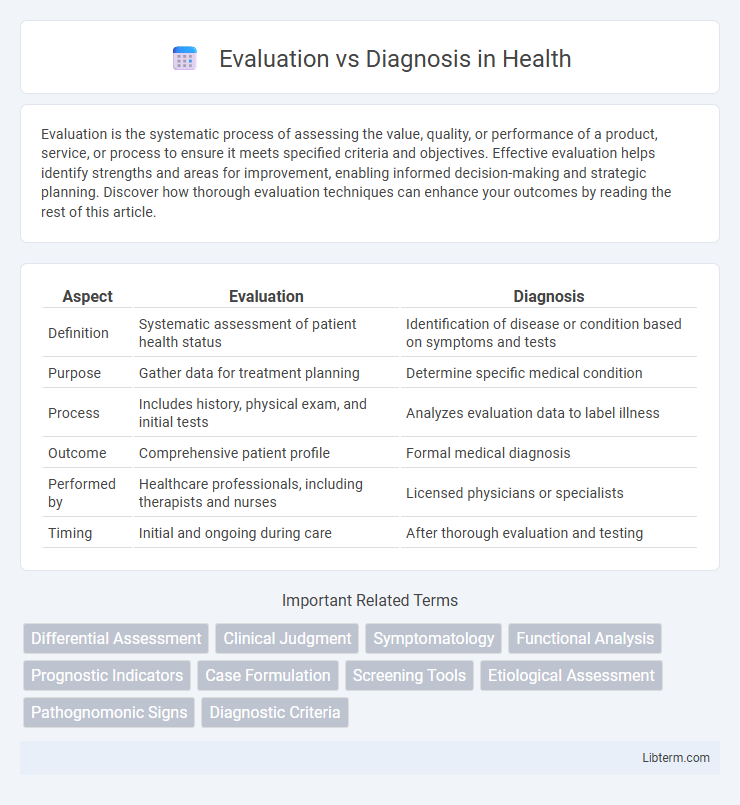
| Aspect | Evaluation | Diagnosis |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Systematic assessment of patient health status | Identification of disease or condition based on symptoms and tests |
| Purpose | Gather data for treatment planning | Determine specific medical condition |
| Process | Includes history, physical exam, and initial tests | Analyzes evaluation data to label illness |
| Outcome | Comprehensive patient profile | Formal medical diagnosis |
| Performed by | Healthcare professionals, including therapists and nurses | Licensed physicians or specialists |
| Timing | Initial and ongoing during care | After thorough evaluation and testing |
Introduction to Evaluation and Diagnosis
Evaluation involves a systematic process of gathering and interpreting information to understand an individual's needs, strengths, and challenges through various assessments and observations. Diagnosis refers to identifying and labeling specific medical or psychological conditions based on established criteria and clinical judgment. Both processes are essential in developing effective intervention plans, with evaluation providing comprehensive insights and diagnosis offering a clear understanding of underlying disorders.
Defining Evaluation in Healthcare
Evaluation in healthcare involves systematically gathering, analyzing, and interpreting patient data to assess health status, progress, and treatment effectiveness. It encompasses various methods such as physical examinations, diagnostic tests, and patient history reviews to inform clinical decisions. Unlike diagnosis, which identifies specific diseases or conditions, evaluation provides a broader assessment to guide ongoing care and interventions.
What Is a Diagnosis?
A diagnosis is the process of identifying a specific disease or medical condition based on a thorough analysis of symptoms, patient history, and diagnostic tests. It provides a precise medical label that guides targeted treatment plans and prognostic assessments. Accurate diagnosis is crucial for effective patient care, differentiating it from evaluation, which is a broader assessment to gather information.
Key Differences Between Evaluation and Diagnosis
Evaluation involves a comprehensive assessment process using various tools to gather data about a person's condition or needs, while diagnosis focuses on identifying a specific disease or disorder based on that data. Evaluation is broader and can include observations, tests, and interviews, whereas diagnosis aims to provide a definitive medical or psychological label. The key difference lies in evaluation's scope of understanding overall functioning versus diagnosis's goal of pinpointing an exact condition.
The Role of Evaluation in Patient Care
Evaluation plays a critical role in patient care by systematically gathering data to assess a patient's health status, guiding clinical decision-making, and identifying potential health issues before they become diagnosable conditions. Unlike diagnosis, which pinpoints specific diseases or disorders, evaluation encompasses a broader analysis of patient history, symptoms, and functional status to tailor individualized treatment plans. Effective evaluation enhances patient outcomes by enabling early intervention and continuous monitoring throughout the care process.
The Importance of Accurate Diagnosis
Accurate diagnosis is crucial in medical practice as it determines the appropriate treatment plan and patient outcomes. Evaluation involves gathering comprehensive data through tests and assessments, but diagnosis interprets this data to identify the specific disease or condition accurately. Misdiagnosis can lead to ineffective treatments, increased healthcare costs, and adverse patient health consequences.
Common Methods Used in Evaluation
Common methods used in evaluation include observational assessments, standardized tests, and interviews, which gather comprehensive data on an individual's skills and behaviors. These techniques provide critical information to tailor interventions and track progress over time. Evaluation methods emphasize ongoing monitoring and data collection to inform educational or clinical decision-making processes.
Diagnostic Tools and Techniques
Diagnostic tools and techniques play a crucial role in both evaluation and diagnosis processes but serve different purposes; evaluation utilizes broad assessment methods such as standardized tests, interviews, and observation to gather comprehensive data, whereas diagnosis relies on specific instruments like DSM-5 criteria, clinical scales, and differential diagnostic checklists to identify and categorize disorders precisely. Advanced diagnostic techniques include neuroimaging, genetic testing, and psychometric analysis, enhancing accuracy in identifying underlying conditions. The effectiveness of these tools depends on their validity, reliability, and applicability to the patient's unique presentation, ensuring accurate outcomes in clinical settings.
Challenges in Evaluation vs Diagnosis
Challenges in evaluation versus diagnosis often arise from the overlapping symptoms that complicate distinguishing between multiple potential conditions. The evaluation process requires comprehensive data collection and interpretation, which can be hindered by inconsistent patient reports or incomplete information. Diagnostic accuracy is further challenged by evolving medical knowledge and the subjective nature of certain assessment tools, leading to potential misclassification or delayed treatment.
Summary: Choosing the Right Approach
Evaluation involves gathering comprehensive data to understand a client's strengths and challenges, while diagnosis identifies specific disorders based on established criteria. Selecting the right approach depends on the purpose: evaluations guide intervention planning and progress monitoring, whereas diagnoses inform treatment decisions and eligibility for services. Clear communication of outcomes from either process ensures effective support tailored to individual needs.
Evaluation Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com