Diathesis predisposition refers to an individual's inherent vulnerability to developing certain mental or physical disorders due to genetic, biological, or psychological factors. This predisposition often interacts with environmental stressors, influencing the likelihood and severity of the condition. Explore the article to understand how diathesis predisposition impacts your health and what measures you can take.
Table of Comparison
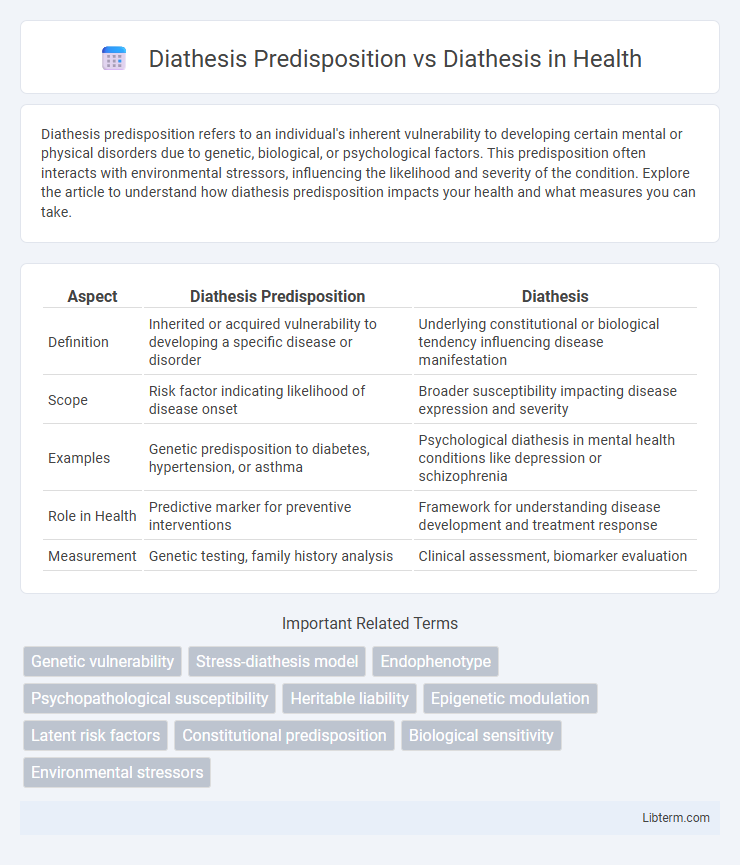
| Aspect | Diathesis Predisposition | Diathesis |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Inherited or acquired vulnerability to developing a specific disease or disorder | Underlying constitutional or biological tendency influencing disease manifestation |
| Scope | Risk factor indicating likelihood of disease onset | Broader susceptibility impacting disease expression and severity |
| Examples | Genetic predisposition to diabetes, hypertension, or asthma | Psychological diathesis in mental health conditions like depression or schizophrenia |
| Role in Health | Predictive marker for preventive interventions | Framework for understanding disease development and treatment response |
| Measurement | Genetic testing, family history analysis | Clinical assessment, biomarker evaluation |
Understanding Diathesis: A Foundational Overview
Diathesis refers to an individual's inherent vulnerability or predisposition to develop a particular disorder, often rooted in genetic, biological, or psychological factors. Diathesis predisposition specifically highlights the underlying susceptibility that interacts with environmental stressors to trigger the manifestation of mental or physical illness. Understanding diathesis provides a foundational framework for comprehending how inherent vulnerabilities combined with external influences contribute to disease onset and progression.
What is Diathesis Predisposition?
Diathesis Predisposition refers to an individual's inherent vulnerability or susceptibility to developing a disorder, often influenced by genetic, biological, or psychological factors. This predisposition interacts with environmental stressors to trigger the onset of conditions like mental illnesses or physical diseases. Understanding Diathesis Predisposition is crucial for identifying risk factors and implementing preventative strategies in healthcare.
Key Differences Between Diathesis and Diathesis Predisposition
Diathesis refers to an inherent vulnerability or tendency toward developing a particular disorder, often rooted in genetics or biology, while diathesis predisposition emphasizes the probabilistic nature of this vulnerability interacting with environmental stressors. The key difference lies in diathesis being a static constitutional factor, whereas diathesis predisposition highlights the dynamic risk influenced by both internal and external factors. Understanding this distinction aids in assessing the likelihood and potential triggers for mental health conditions.
Genetic Factors in Diathesis and Predisposition
Diathesis refers to an inherent vulnerability or susceptibility to a disorder, often influenced by genetic factors such as inherited gene mutations or polymorphisms that increase risk. Predisposition specifically denotes the genetic tendency to develop a condition, shaped by multiple genes interacting with environmental triggers to elevate disease likelihood. Understanding genetic factors in diathesis and predisposition aids in identifying individuals at higher risk for conditions like depression, schizophrenia, and autoimmune diseases.
Environmental Influences on Diathesis Expressions
Diathesis predisposition refers to an individual's inherent vulnerability to developing psychological disorders, while diathesis itself denotes the underlying genetic or biological susceptibility. Environmental influences such as stress, trauma, and socioeconomic factors significantly modulate the expression of diathesis, triggering or exacerbating symptoms. Research highlights the interaction between genetic predispositions and external conditions as crucial in determining the onset and severity of mental health disorders.
Diathesis-Stress Model: Bridging Predisposition and Outcome
The diathesis-stress model explains the interaction between diathesis, a predisposition or vulnerability to certain psychological disorders, and environmental stressors triggering the development of these conditions. Diathesis represents inherent genetic, biochemical, or psychological vulnerabilities, while predisposition specifically refers to the tendency or susceptibility encoded by these diatheses. This model bridges predisposition and outcome by highlighting how stress activates underlying diatheses, ultimately influencing the onset and severity of mental health disorders.
How Diathesis Predisposition Impacts Mental Health
Diathesis predisposition refers to an individual's inherent genetic or biological vulnerability to developing mental health disorders, which interacts with environmental stressors to trigger symptoms. This predisposition impacts mental health by increasing susceptibility to conditions such as depression, anxiety, and schizophrenia when exposed to adverse life events or trauma. Understanding diathesis predisposition enables early identification and targeted interventions to mitigate the onset or severity of mental illnesses.
Clinical Implications of Diathesis vs. Predisposition
Diathesis refers to an inherent vulnerability or susceptibility to developing a disorder, often influenced by genetic, biological, or psychological factors, while predisposition specifically denotes a tendency or risk factor that increases the likelihood of a particular condition. Clinically, understanding diathesis allows practitioners to identify individuals at high risk for mental health disorders, enabling early intervention and targeted prevention strategies. Differentiating diathesis from predisposition improves diagnostic accuracy and guides personalized treatment plans based on the patient's underlying vulnerabilities and risk profile.
Assessing Risk: Identifying Diathesis in Individuals
Assessing risk involves evaluating diathesis predisposition by identifying specific genetic, biological, and psychological vulnerabilities that increase an individual's likelihood of developing certain disorders under stress. Diathesis refers to the underlying inherent susceptibility, while diathesis predisposition emphasizes measurable risk factors that can predict potential outcomes. Accurate identification of diathesis through clinical assessments and genetic screening is crucial for early intervention and personalized treatment planning.
Future Directions in Diathesis Research and Prevention
Future directions in diathesis research emphasize integrating genetic, neurobiological, and environmental data to refine risk prediction models for mental disorders. Advanced neuroimaging and genomic sequencing techniques enable identification of specific diatheses and their interaction with stressors, enhancing personalized prevention strategies. Cross-disciplinary approaches focusing on early detection and resilience-building could revolutionize targeted interventions, reducing the incidence and severity of psychopathology related to diathesis predisposition.
Diathesis Predisposition Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com